5g Infrastructure Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: 5g-infrastructure
5g Infrastructure Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 5G Infrastructure market, covering insights on market size, trends, regional performance, and industry leaders from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
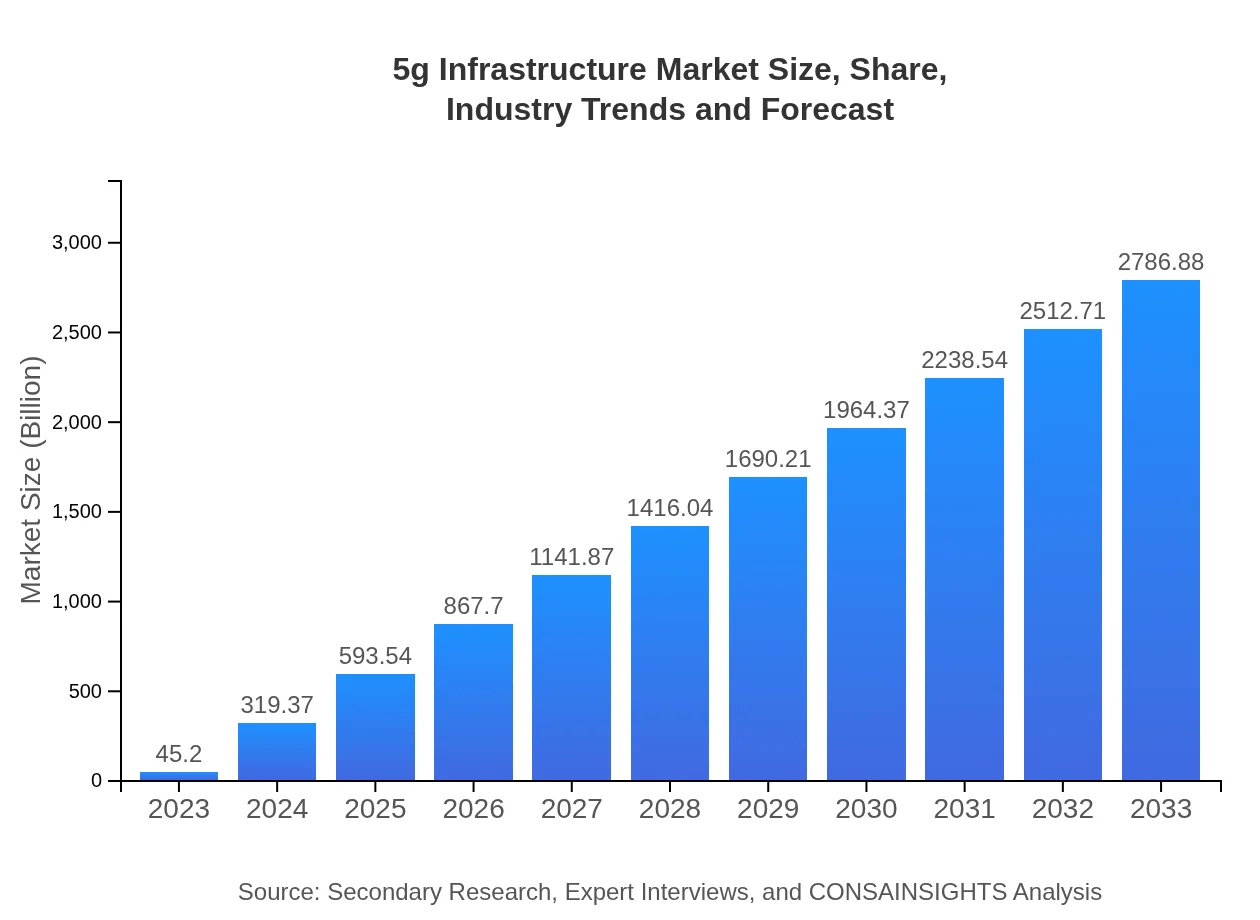
| 2023 Market Size | $45.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 46.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2786.88 Billion |
| Top Companies | Huawei , Ericsson , Nokia , Qualcomm , Samsung |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
5g Infrastructure Market Overview
Customize 5g Infrastructure Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 5g Infrastructure market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 5g Infrastructure's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 5g Infrastructure
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 5g Infrastructure market in 2023?
5g Infrastructure Industry Analysis
5g Infrastructure Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 5g Infrastructure Market Report:
In Europe, the 5G Infrastructure market is poised to expand from USD 16.23 billion in 2023 to an estimated USD 1,000.77 billion by 2033, fueled by strategic initiatives and funding from the European Union aimed at enhancing digital infrastructure and connectivity across member states.Asia Pacific 5g Infrastructure Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to generate approximately USD 8.48 billion in the 5G Infrastructure market, with expectations to grow to USD 522.54 billion by 2033, achieving a significant CAGR. This growth is driven by countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan, which are leading in 5G network rollouts and deployments, as well as large-scale investments in technology and infrastructure.North America 5g Infrastructure Market Report:
North America is a key player in the 5G Infrastructure market, expected to reach USD 14.93 billion in 2023 and grow substantially to USD 920.78 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads in 5G technology adoption and deployment, with significant investments from major telecom players like Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile.South America 5g Infrastructure Market Report:
The South American region, currently valued at USD 1.10 billion in 2023, is forecasted to expand to USD 67.72 billion by 2033. The adoption of 5G technology is still in its early stages, but with increasing demand for mobile broadband and the IoT, countries like Brazil and Argentina are expected to play a significant role in market growth.Middle East & Africa 5g Infrastructure Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region has a 5G Infrastructure market size of USD 4.46 billion projected for 2023, with forecasts indicating a rise to USD 275.06 billion by 2033. Countries like the UAE and South Africa are leading the way in 5G rollouts, supported by growing mobile connectivity demands.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
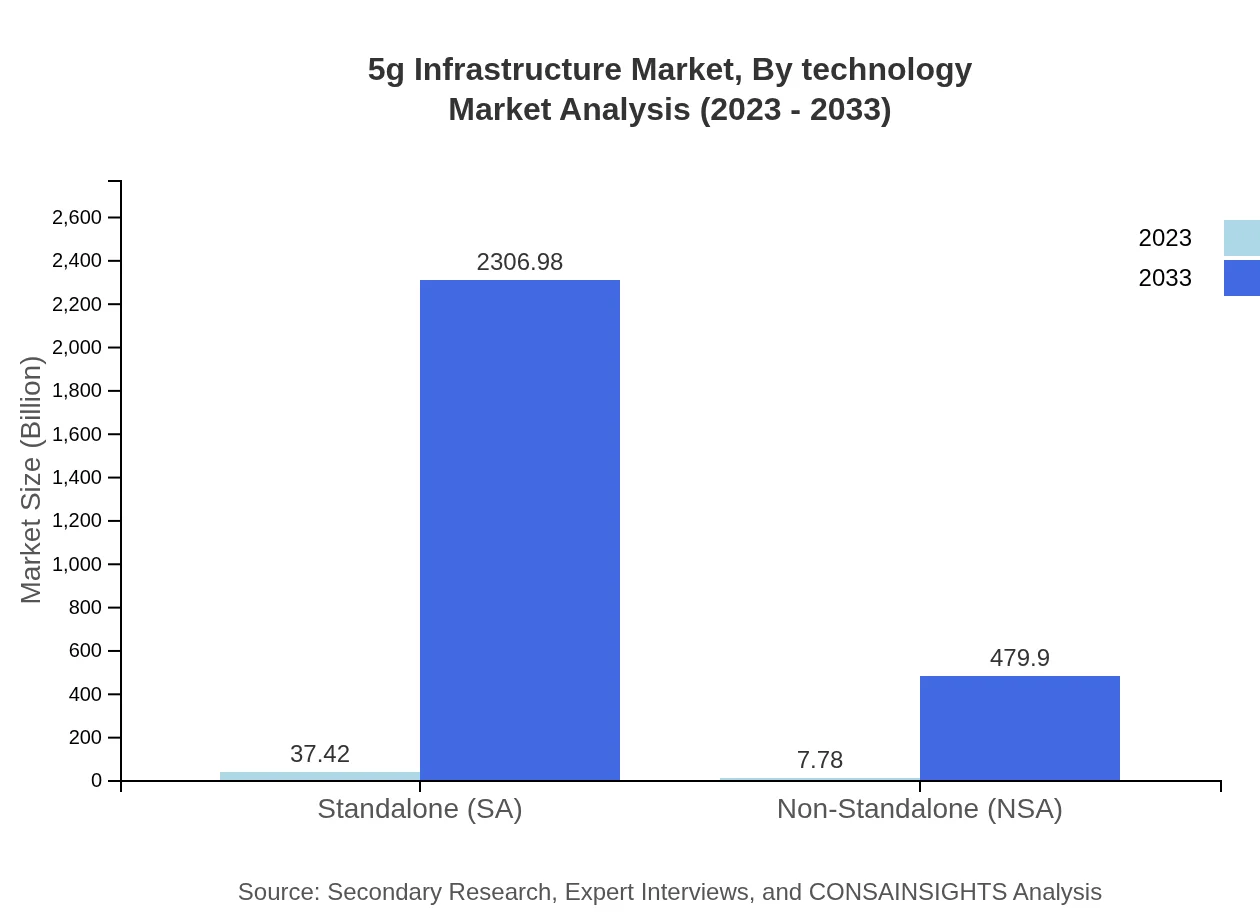
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Technology
The 5G Infrastructure market is segmented into standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) technologies. By 2033, SA technology is expected to command a market size of USD 2,306.98 billion, while NSA technology is anticipated to reach USD 479.90 billion. The preference for SA technology is driven by its emphasis on low latency and network efficiency, critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
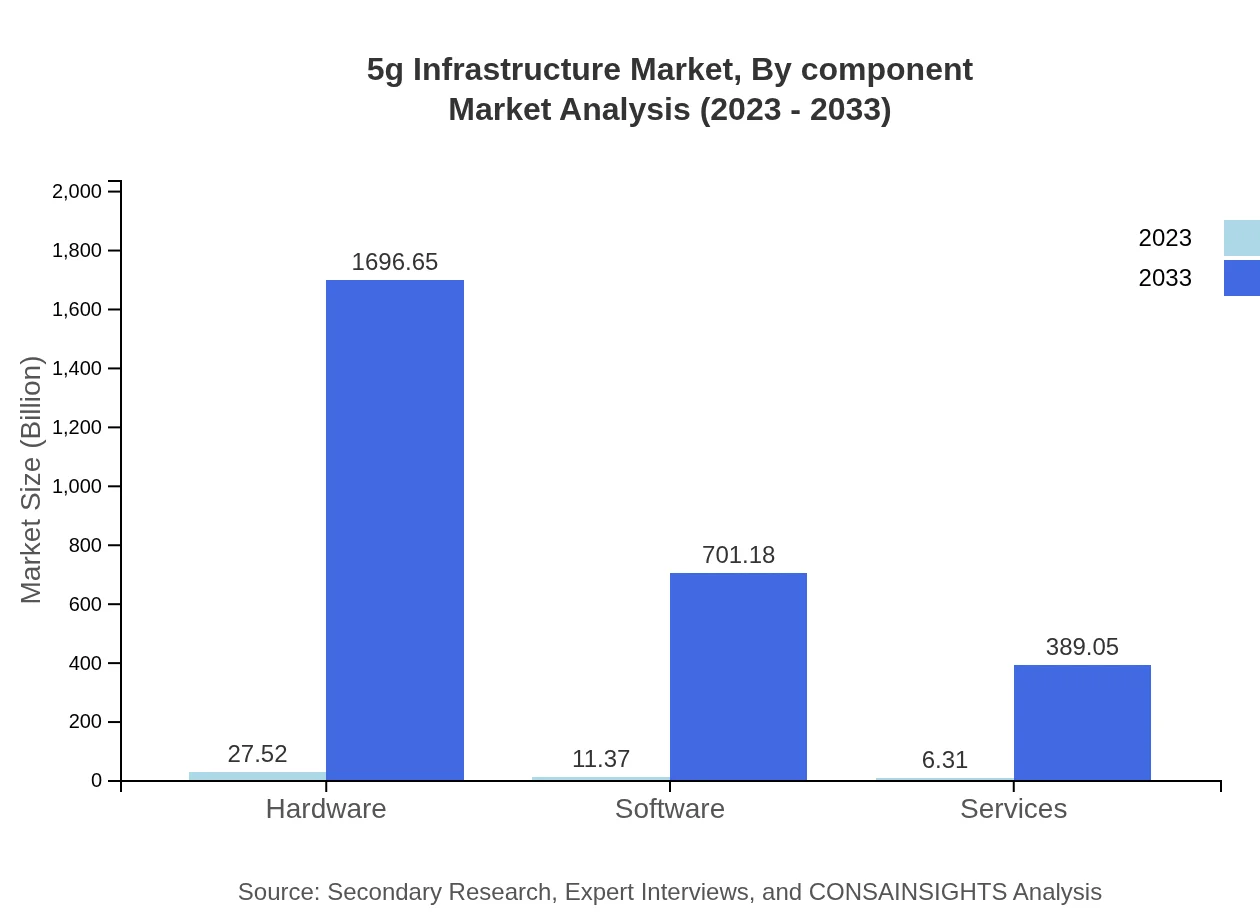
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Component
Examining the components, the hardware segment is projected to dominate the 5G Infrastructure market with a size of USD 1,696.65 billion by 2033. Software and services are expected to reach USD 701.18 billion and USD 389.05 billion, respectively, demonstrating their importance in maintaining and managing 5G networks, particularly for telecom operators.
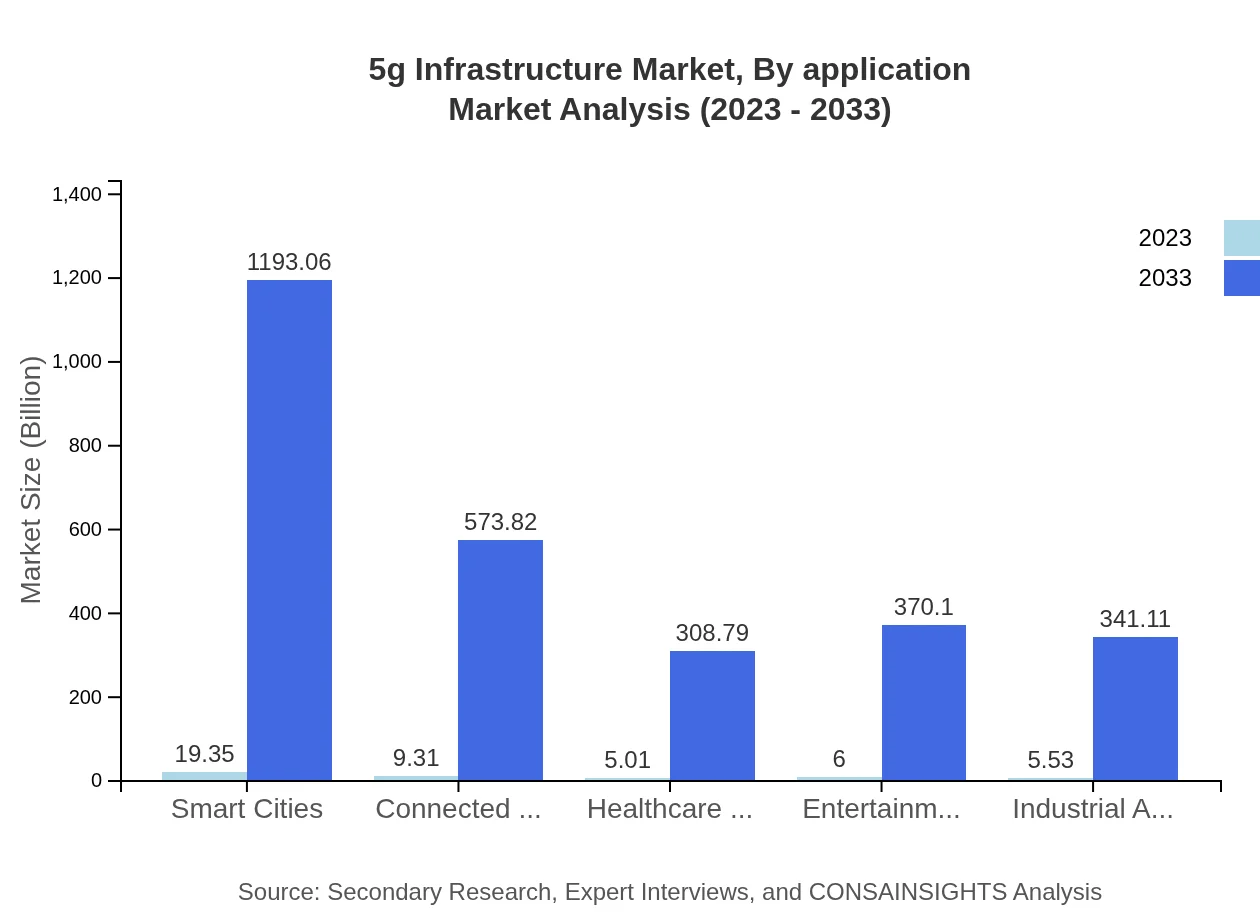
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Application
Applications within the market include smart cities, connected automotive, healthcare, and entertainment. The smart cities segment is forecasted to grow from USD 19.35 billion in 2023 to USD 1,193.06 billion by 2033, showcasing the transformative potential of 5G technology across urban environments.
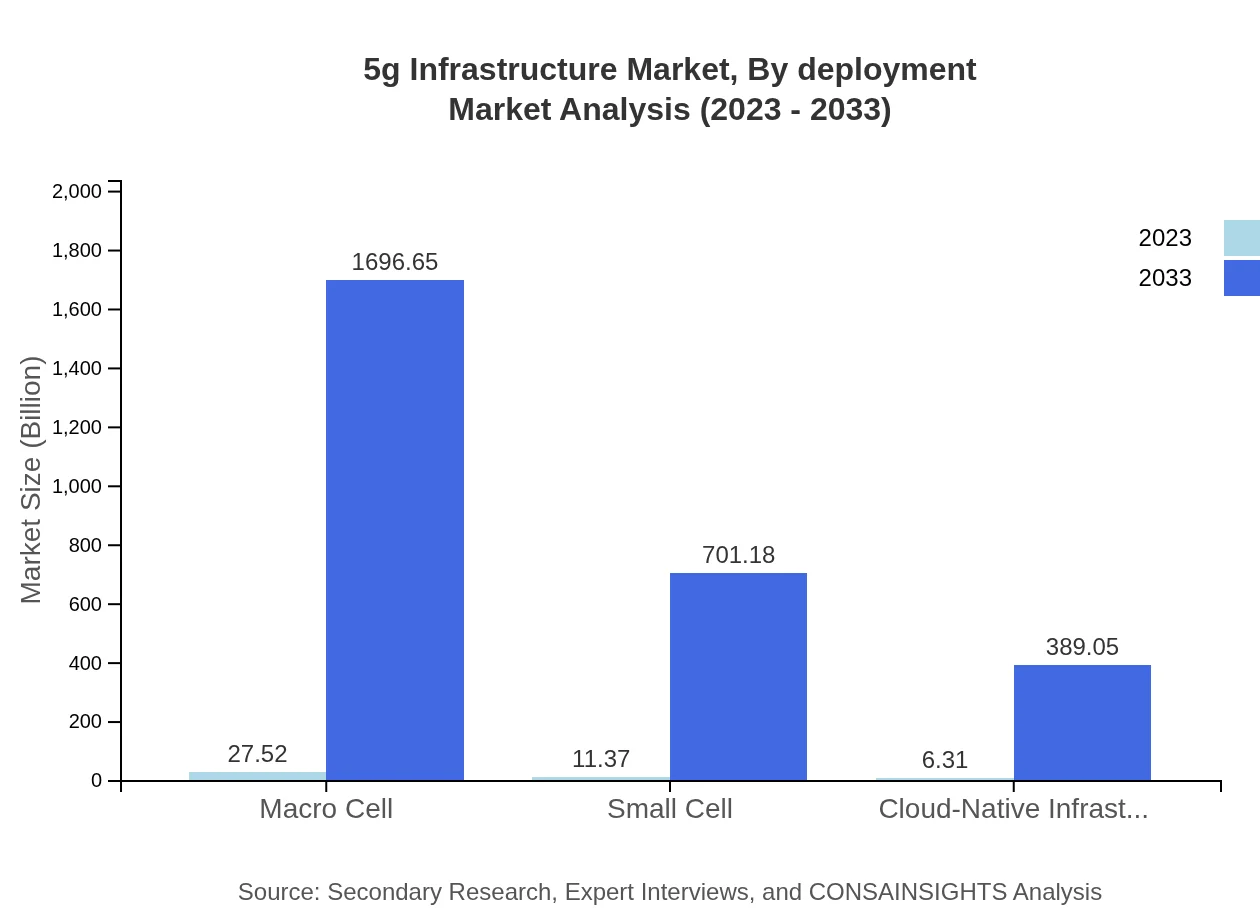
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Deployment
Deployment types encompass fixed wireless access (FWA) and network deployment. FWA is expected to see substantial growth due to its capability to offer high-speed internet to underserved areas, reflecting the overall expansion of 5G connectivity.
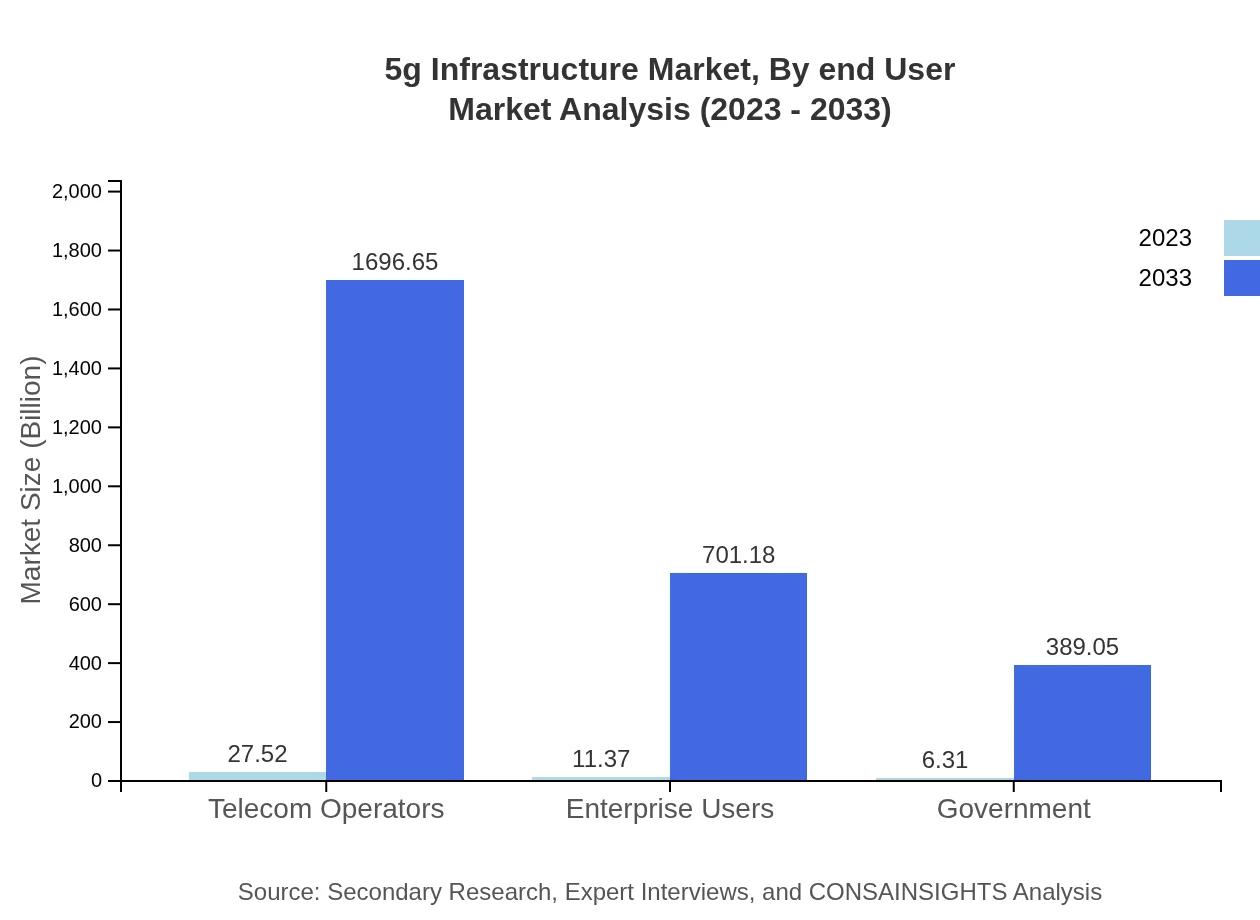
5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By End User
End-user segments consist of telecom operators, government entities, and enterprise users. The telecom operators' share is approximately 60.88% in 2023 and is expected to remain steady as they drive the majority of investments, shaping the market landscape significantly.
5g Infrastructure Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 5g Infrastructure Industry
Huawei :
A leading global provider of information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure and smart devices, Huawei plays a crucial role in the 5G equipment market, offering advanced solutions that enable seamless connectivity.Ericsson :
Ericsson is a major player in the telecommunications landscape, recognized for its extensive portfolio in 5G infrastructure solutions, providing service providers with technologies to enhance network performance and enable new services.Nokia :
Nokia provides 5G network equipment and solutions focused on improving network capacity and digital transformation, contributing significantly to the rollout of 5G networks worldwide.Qualcomm :
Known for its innovations in semiconductor technology and telecommunications equipment, Qualcomm plays a pivotal role in developing technologies that facilitate the deployment of 5G infrastructure.Samsung :
Samsung is involved in manufacturing essential 5G equipment and devices while investing heavily in research to advance 5G technology solutions across various markets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 5g Infrastructure?
The global 5G infrastructure market is projected to grow from $45.2 billion in 2023 to significantly larger figures by 2033, with a remarkable CAGR of 46.7%. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity.
What are the key market players or companies in this 5g Infrastructure industry?
Key market players in the 5G infrastructure industry include major telecommunications companies and technology firms innovating in hardware, software, and services tailored for next-gen networks, contributing to competitive advancements in the sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 5g Infrastructure industry?
Growth in the 5G infrastructure sector is driven by increasing demand for high-speed internet, the proliferation of IoT devices, advancements in mobile technology, government initiatives for digital transformation, and the need for enhanced connectivity solutions across sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 5g Infrastructure?
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region for 5G infrastructure, with a market increase from $8.48 billion in 2023 to $522.54 billion in 2033. Europe and North America also show significant growth trajectories in 5G investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 5g Infrastructure industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the 5G infrastructure industry, enabling businesses to gather insights relevant to their strategic planning and investment decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this 5g Infrastructure market research project?
Deliverables from a 5G infrastructure market research project include comprehensive reports, market forecasts, competitive analysis, regional insights, and tailored recommendations that inform strategic business decisions in the telecom sector.
What are the market trends of 5g Infrastructure?
Key market trends in 5G infrastructure include the rise of standalone networks, accelerated deployment of small cells, emphasis on smart cities, and innovative applications in connected automotive and telemedicine, driving the overall market growth.