Cloud Engineering Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cloud-engineering
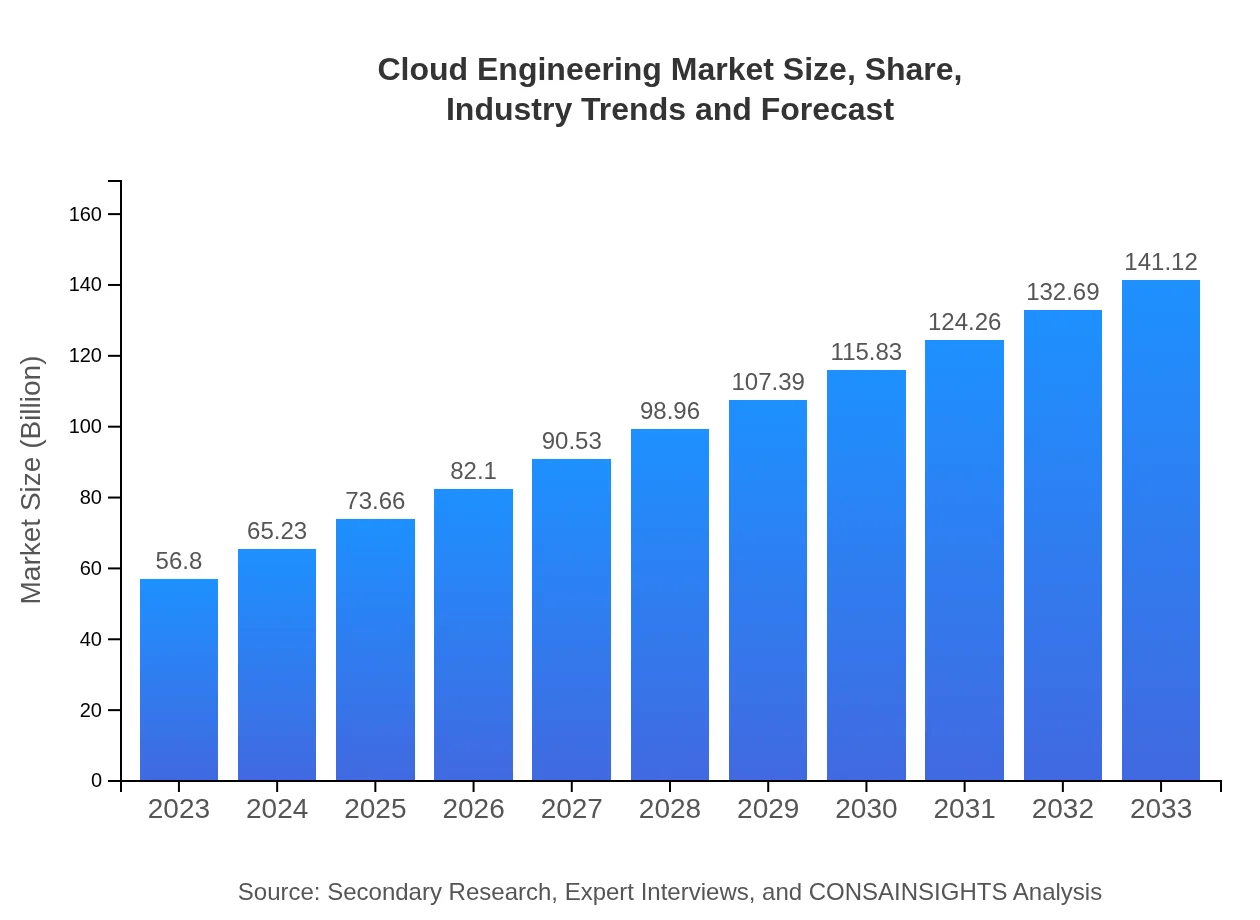
Cloud Engineering Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Cloud Engineering market, highlighting key trends, industry analysis, market segmentation, and regional performance from 2023 to 2033 to aid stakeholders in strategic planning.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $56.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $141.12 Billion |
| Top Companies | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Salesforce |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cloud Engineering Market Overview
Customize Cloud Engineering Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cloud Engineering market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cloud Engineering's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cloud Engineering
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cloud Engineering market in 2023?
Cloud Engineering Industry Analysis
Cloud Engineering Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cloud Engineering Market Report:
Europe's market stands at $15.84 billion in 2023, with expectations of growth to $39.36 billion by 2033, influenced by stringent data protection regulations and a robust technology adoption rate.Asia Pacific Cloud Engineering Market Report:
In 2023, the Cloud Engineering market in Asia Pacific is valued at approximately $11.94 billion, with a doubling projected to $29.66 billion by 2033. Growing demand for cloud solutions from SMEs and rising investments in IT infrastructure underpin this growth.North America Cloud Engineering Market Report:
North America is the largest market, with a size of $20.49 billion in 2023, projected to reach $50.90 billion by 2033. The presence of major tech companies and significant investments in cloud infrastructure contribute to its dominance.South America Cloud Engineering Market Report:
The South American market, valued at $4.83 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $12.00 billion by 2033. Adoption is driven by increasing digitalization and cloud migration efforts among local enterprises.Middle East & Africa Cloud Engineering Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the current market size is $3.70 billion, projected to grow to $9.20 billion by 2033 as cloud technology adoption rises amid digital transformation agendas.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
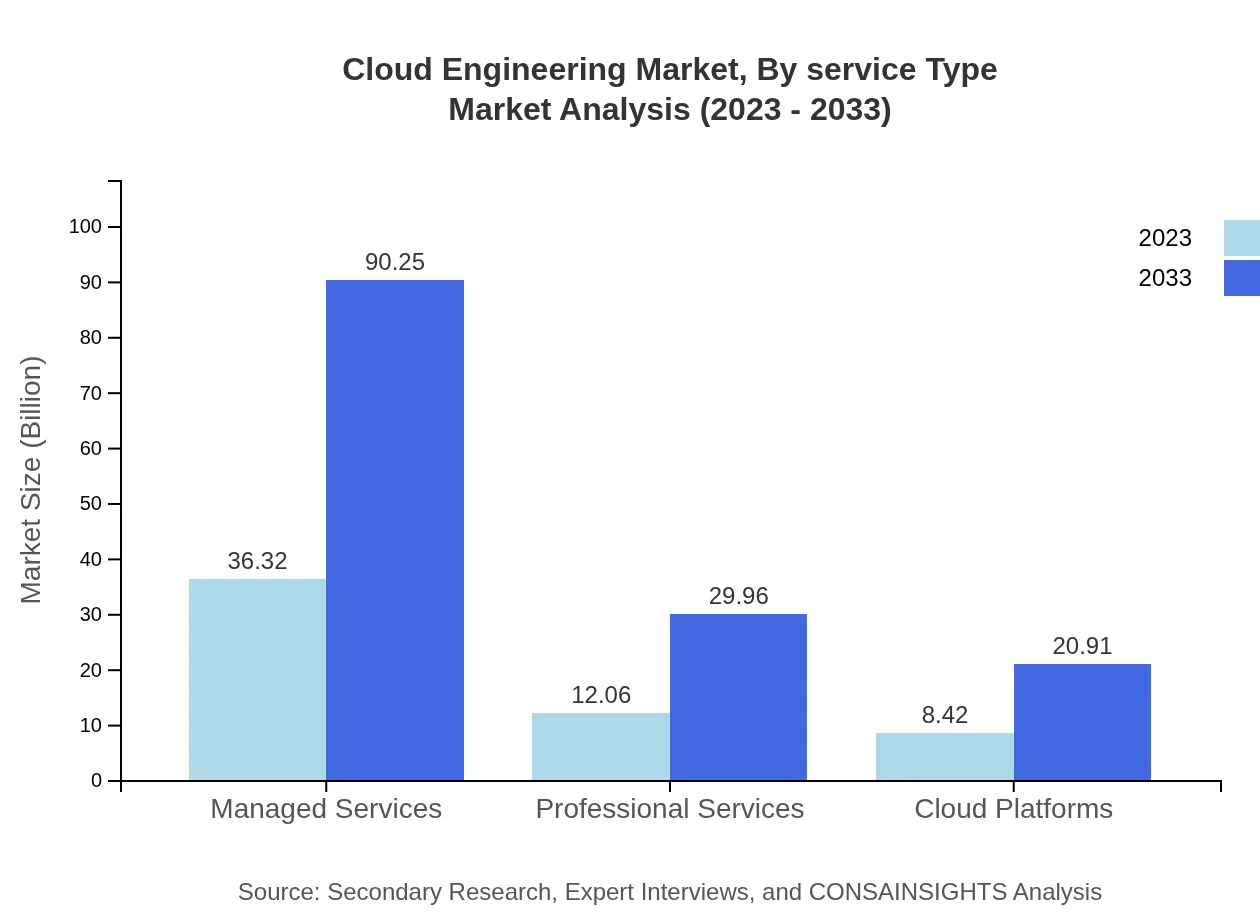
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis By Service Type
The Cloud Engineering market segment by service type demonstrates strong demand for cloud infrastructure, which accounts for significant revenue. Managed services and cloud security also show steady growth due to escalating security concerns and the need for expert management of cloud resources.
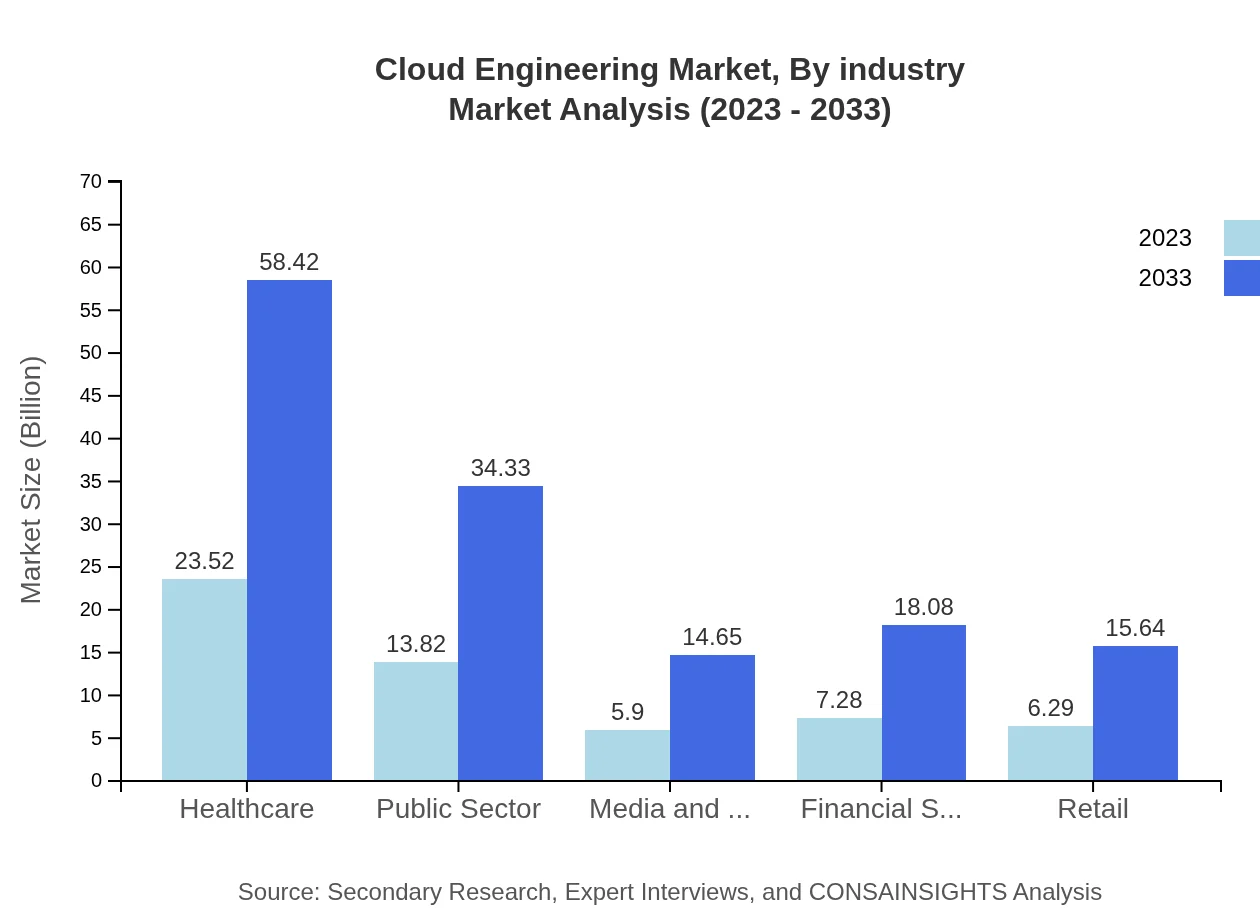
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis By Industry
The healthcare sector leads with a market size of $23.52 billion in 2023, anticipated to escalate to $58.42 billion by 2033, driven by the need for data management and compliance. The public sector follows with substantial growth, emphasizing digital services and record management solutions.
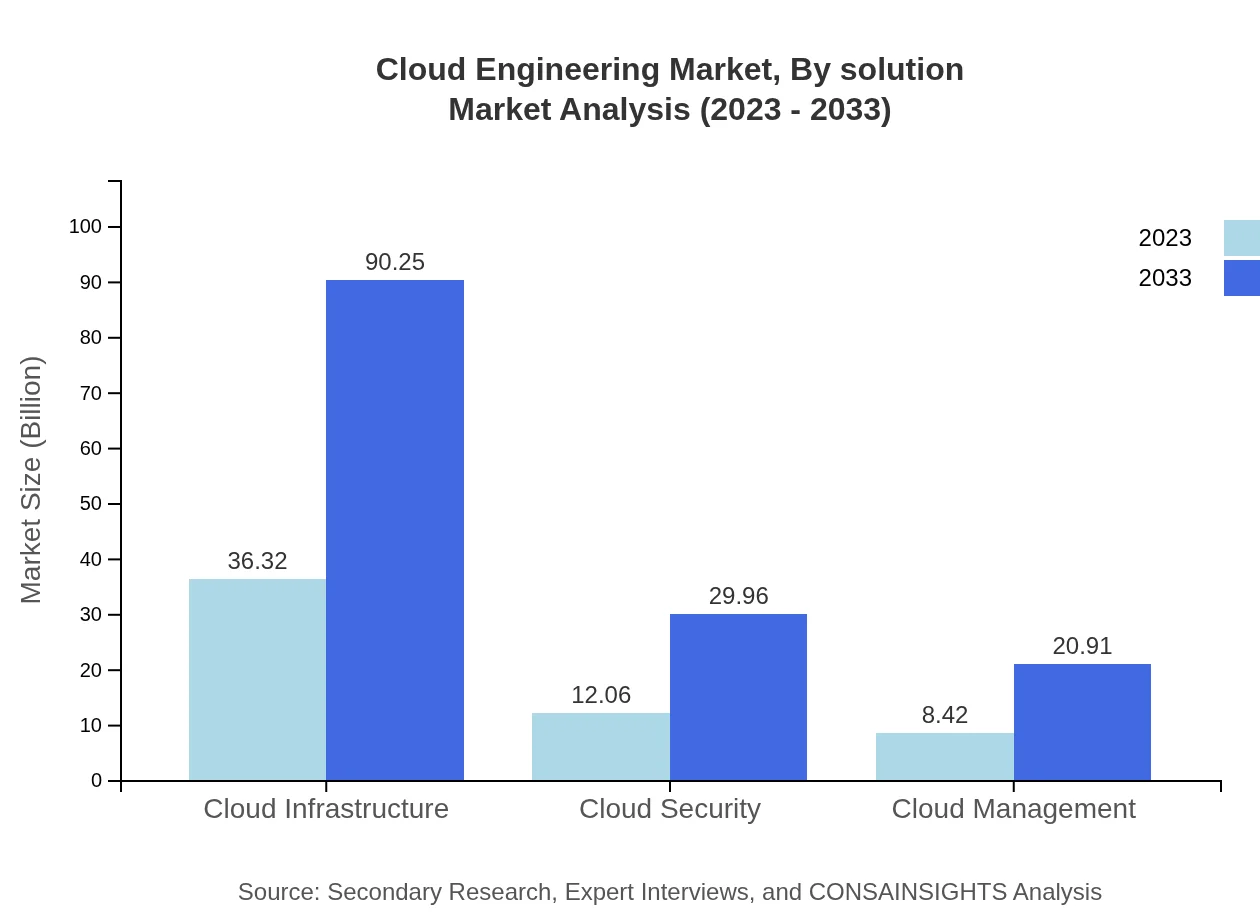
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis By Solution
Solutions such as cloud infrastructure and cloud management feature prominently in the market. Cloud infrastructure is expected to grow from $36.32 billion in 2023 to $90.25 billion by 2033, reflecting a significant shift towards operational efficiency and flexibility.
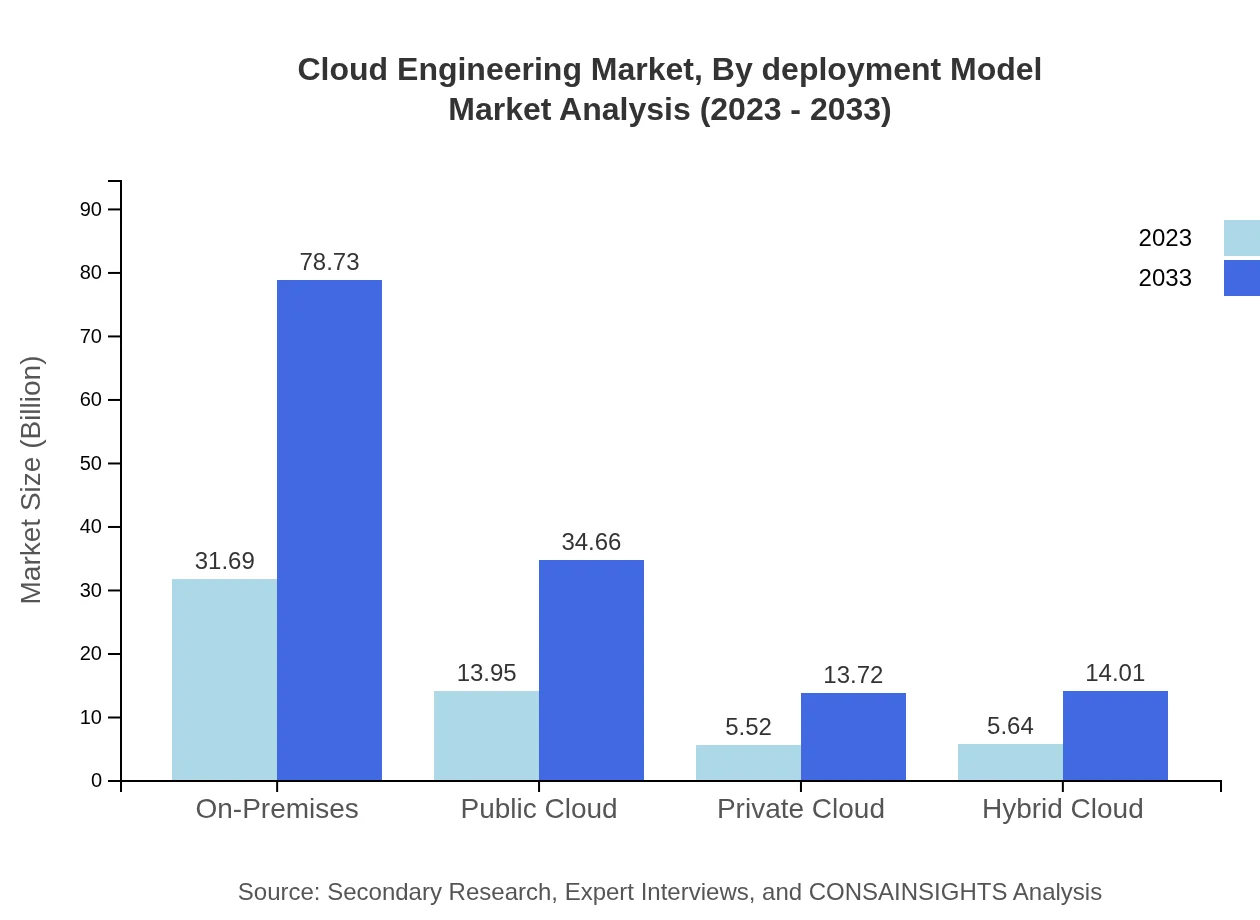
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis By Deployment Model
Deployment models show a notable inclination towards hybrid and public clouds. The public cloud is set to grow from $13.95 billion in 2023 to $34.66 billion by 2033, highlighting increased adoption among various industries seeking cost savings and scalability.
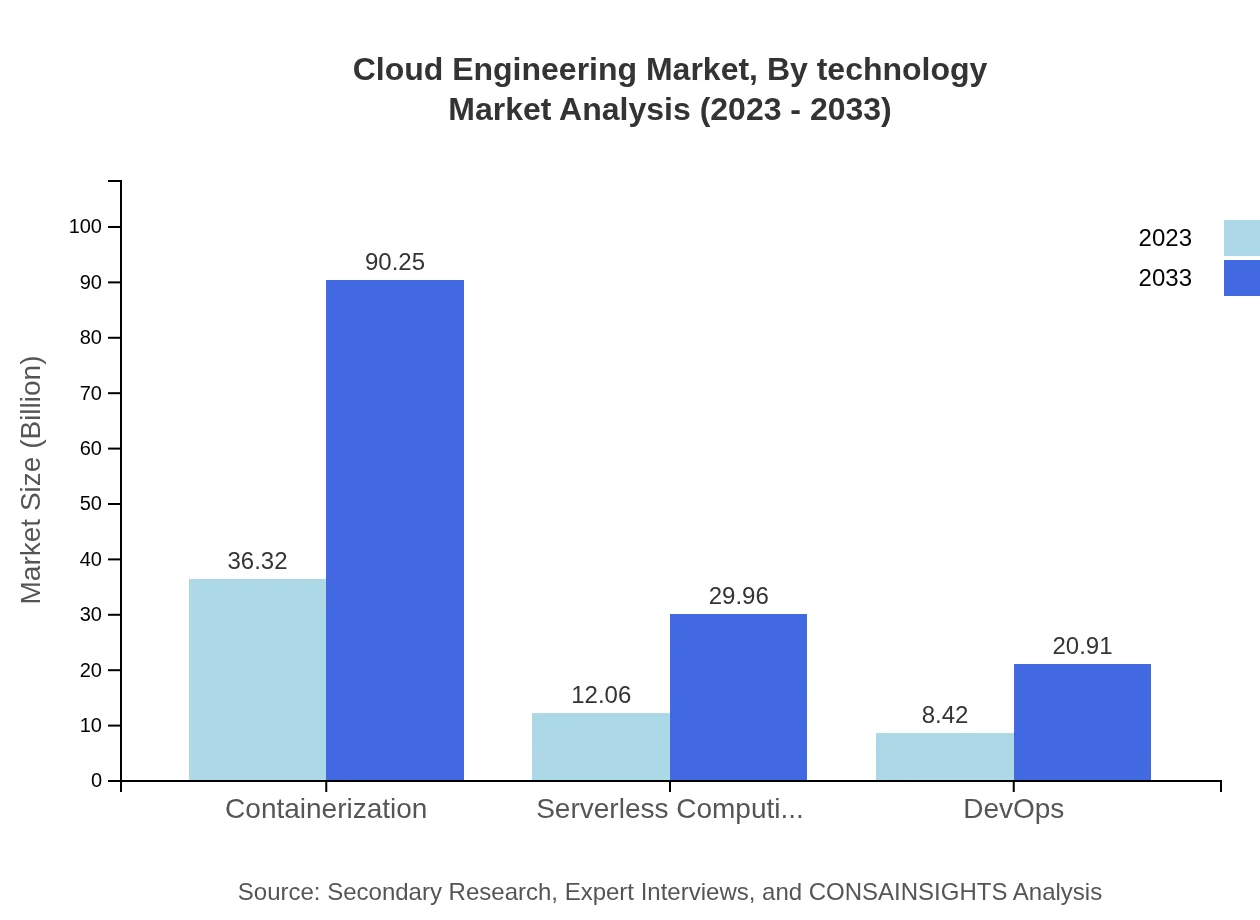
Cloud Engineering Market Analysis By Technology
Technologies such as containerization and serverless computing are gaining traction, transforming how enterprises deploy applications and manage workloads in a cloud environment. The containerization segment alone shows significant growth potential, indicating a shift towards microservices architectures.
Cloud Engineering Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cloud Engineering Industry
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS is a leader in the cloud infrastructure market, providing a comprehensive suite of services and solutions tailored for businesses globally.Microsoft Azure:
Microsoft Azure offers a range of cloud services that enhance enterprise mobility, covering everything from infrastructure to applications.Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP is recognized for its advanced data analytics and machine learning offerings and continues to attract organizations globally for cloud solutions.IBM Cloud:
IBM Cloud specializes in integrated cloud solutions with robust security features aimed at enterprises within regulated industries.Salesforce:
Salesforce dominates the cloud CRM space, consistently adding capabilities that bridge business functionalities with cloud computing.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cloud Engineering?
The global cloud engineering market is projected to reach a size of $56.8 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% from its current size in 2023.
What are the key market players or companies in this cloud Engineering industry?
Key players in the cloud engineering industry include leading technology firms noted for their innovative cloud solutions and infrastructure capabilities, although specific company names were not provided.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cloud Engineering industry?
The growth is driven by rising demand for cloud solutions, digital transformation initiatives, and the need for increased scalability and flexibility within organizations.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cloud Engineering market?
The North America region is the fastest growing in cloud engineering, projected to expand from $20.49 billion in 2023 to $50.90 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cloud Engineering industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients in the cloud-engineering sector.
What deliverables can I expect from this cloud Engineering market research project?
Deliverables typically include comprehensive market analysis reports, trends identification, competitive landscape insights, and strategic recommendations tailored to the client's objectives.
What are the market trends of cloud Engineering?
Current trends include increased adoption of cloud-based services, a focus on cybersecurity in cloud settings, and the growing popularity of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud strategies.