Commercial Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: commercial-seed
Commercial Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Commercial Seed market from 2023 to 2033. It includes insights on market size, growth trends, regional dynamics, and key players, offering valuable data for stakeholders in agriculture and seed production.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
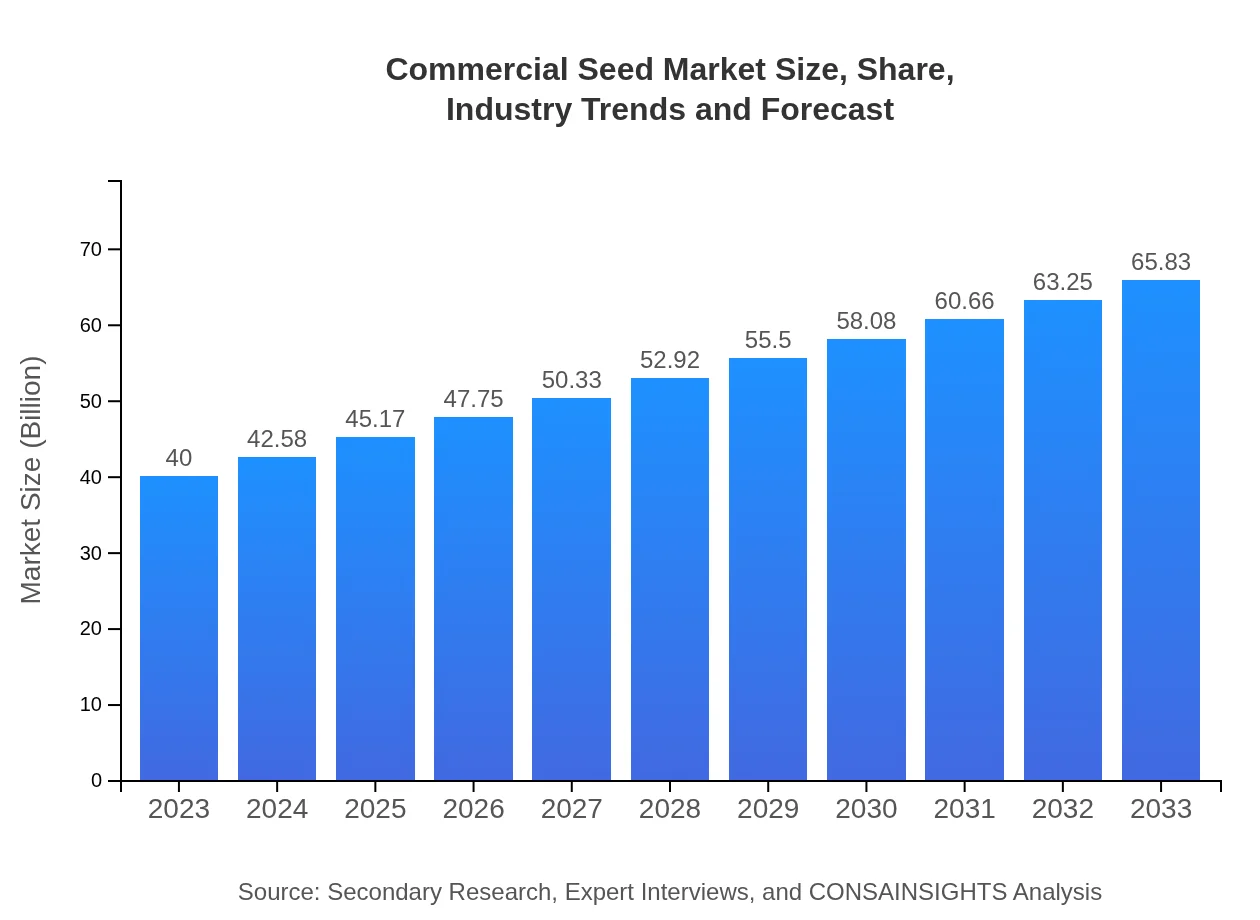
| 2023 Market Size | $40.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $65.83 Billion |
| Top Companies | Bayer Crop Science, Syngenta, Corteva Agriscience, Monsanto Company, Limagrain |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Commercial Seed Market Overview
Customize Commercial Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Commercial Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Commercial Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Commercial Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Commercial Seed market in 2023?
Commercial Seed Industry Analysis
Commercial Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Commercial Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Commercial Seed Market Report:
Europe's Commercial Seed market is anticipated to grow from USD 12.46 billion in 2023 to USD 20.51 billion by 2033. The increasing popularity of organic products and sustainable farming techniques drive this growth, along with stringent regulations that demand improved seed quality.Asia Pacific Commercial Seed Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region holds a significant share of the Commercial Seed market, with a market size of USD 7.88 billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 12.96 billion by 2033. Factors such as increased food demand and emphasis on agricultural productivity drive growth in countries like India and China, where technological adoption in agriculture is ramping up.North America Commercial Seed Market Report:
North America remains a key player in the Commercial Seed market, with a valuation of USD 13.57 billion in 2023, forecasted to reach USD 22.33 billion by 2033. The region's advanced agricultural technology and significant investments in biological seed innovations contribute to its leading position.South America Commercial Seed Market Report:
In South America, the Commercial Seed market is expected to grow from USD 1.81 billion in 2023 to USD 2.98 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by the rising production of cash crops and the adoption of modern agricultural practices, particularly in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Commercial Seed Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa segment is predicted to expand from USD 4.29 billion in 2023 to USD 7.06 billion by 2033. Efforts to enhance food security in the region, alongside investments in agriculture, are key growth factors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
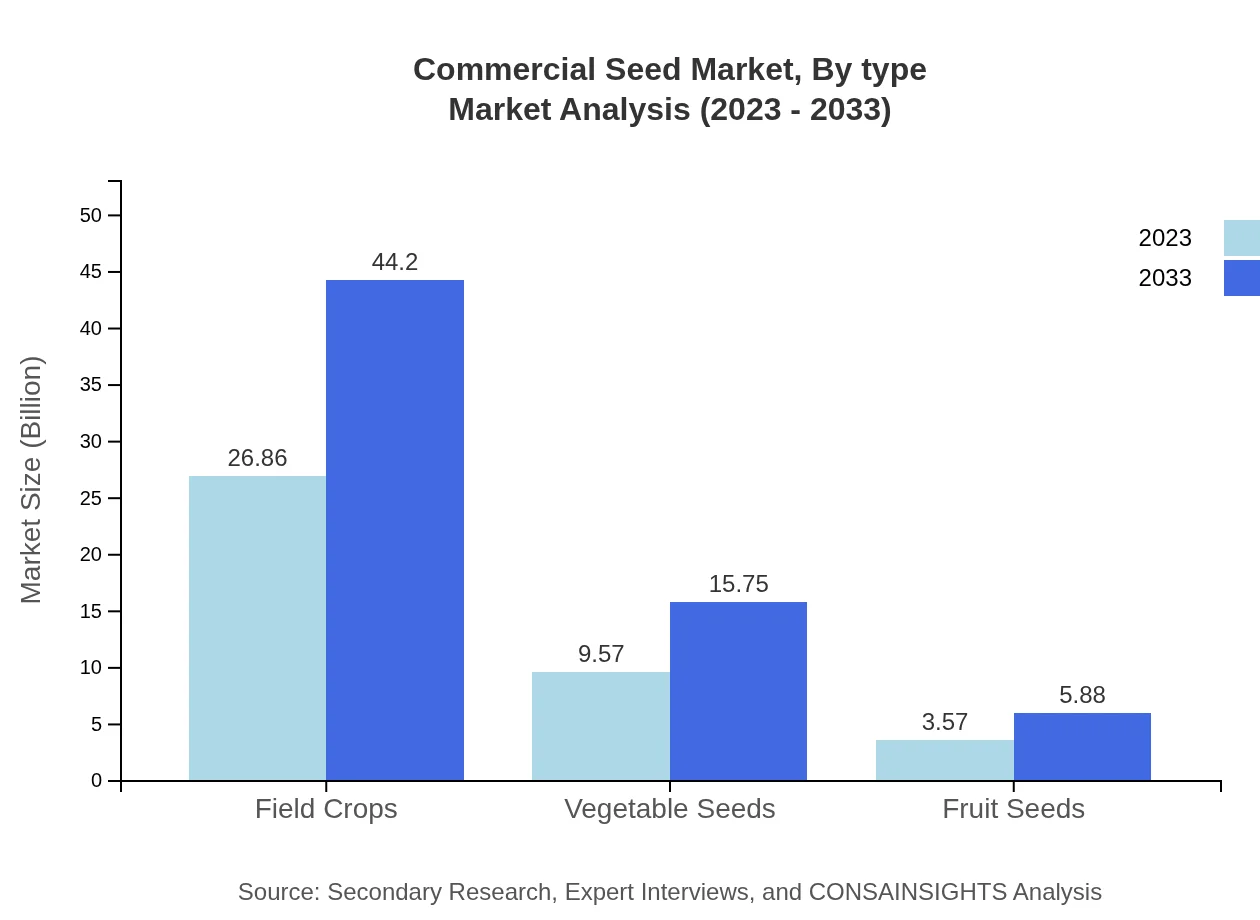
Commercial Seed Market Analysis By Type
The Commercial Seed market is primarily segmented into Field Crops, Vegetable Seeds, and Fruit Seeds. Field Crops dominate the market, with a size of USD 26.86 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 44.20 billion by 2033. Vegetable Seeds and Fruit Seeds contribute significantly as well, providing essential varieties to meet consumer demand.
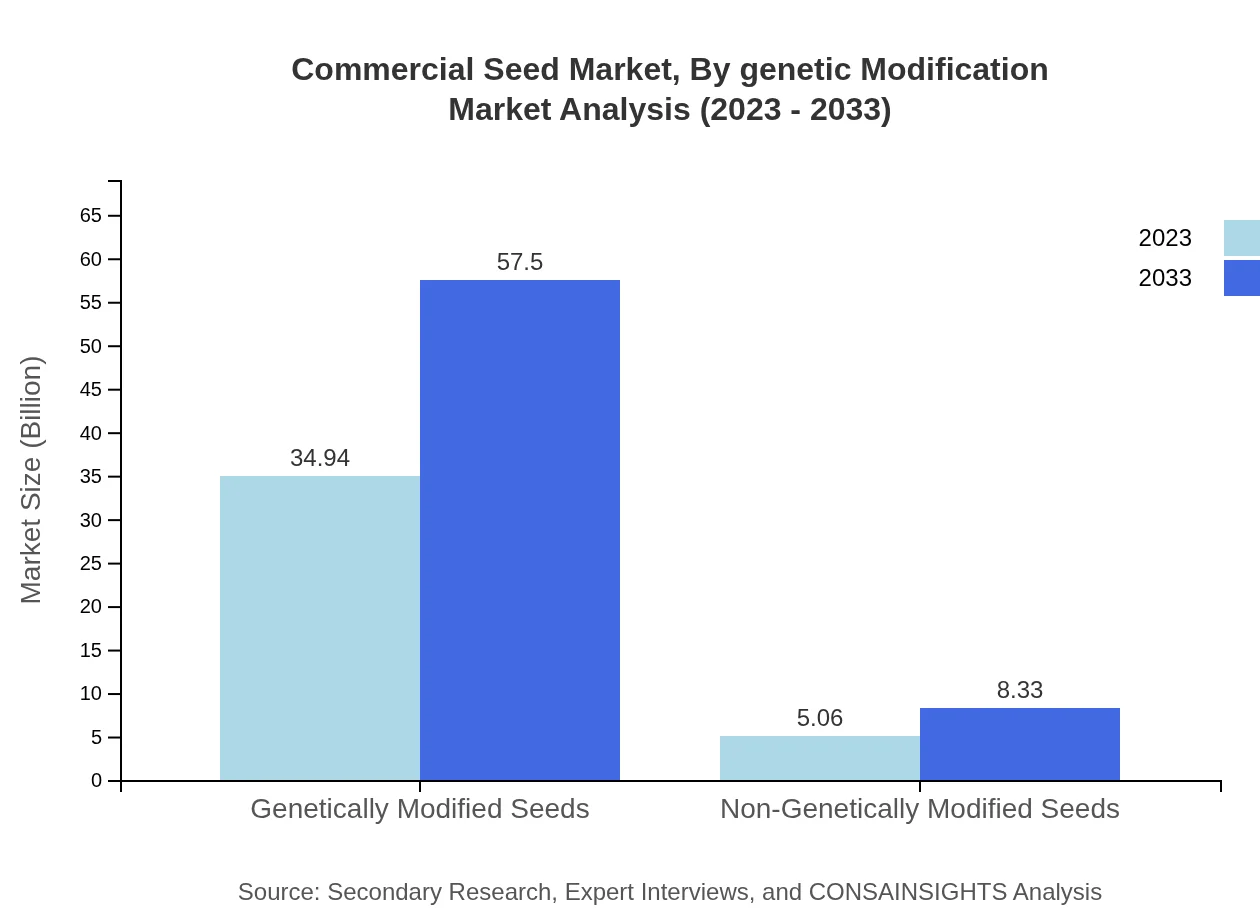
Commercial Seed Market Analysis By Genetic Modification
Genetically Modified Seeds account for a major portion of the Commercial Seed market, with a market size of USD 34.94 billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 57.50 billion by 2033. These seeds offer enhanced traits such as pest resistance and better yield, aligning with modern agricultural needs.
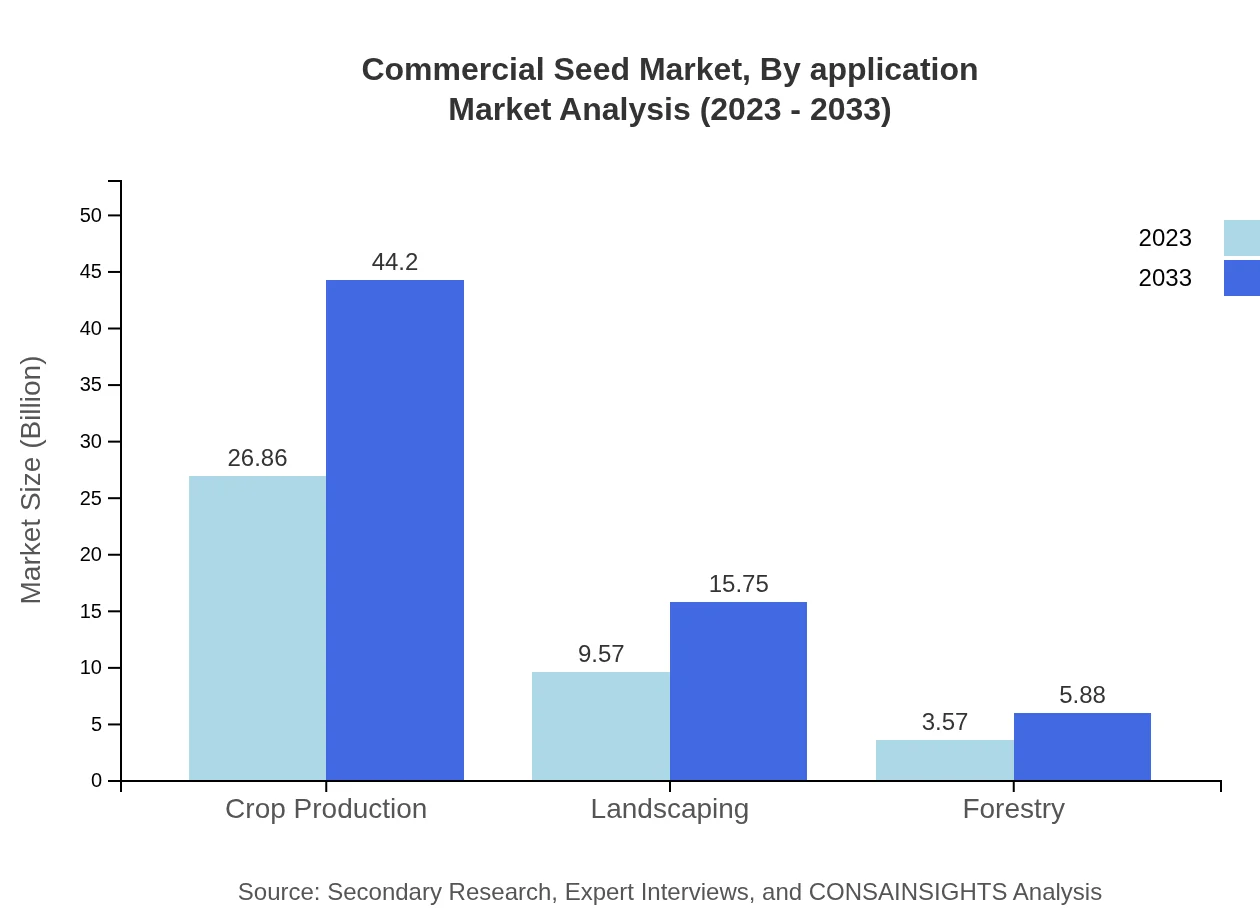
Commercial Seed Market Analysis By Application
The applications of Commercial Seeds include Crop Production, Landscaping, and Forestry. Crop Production leads with USD 26.86 billion in 2023, and the significance of landscaping products is rising, anticipating a growth from USD 9.57 billion to USD 15.75 billion by 2033.
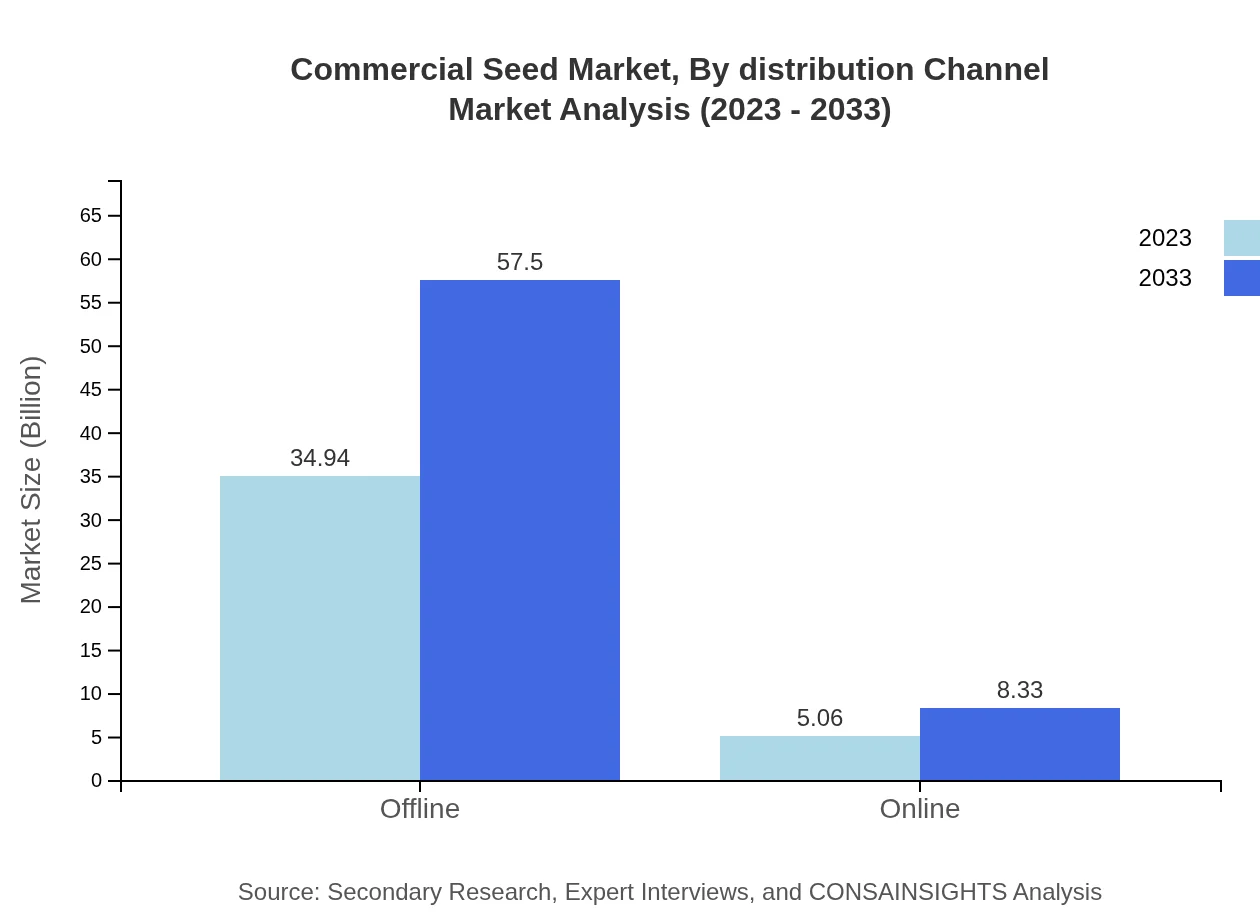
Commercial Seed Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution of Commercial Seeds occurs through Offline and Online channels. Offline sales dominate with a value of USD 34.94 billion in 2023, while Online sales are steadily increasing, expected to rise from USD 5.06 billion to USD 8.33 billion by 2033.
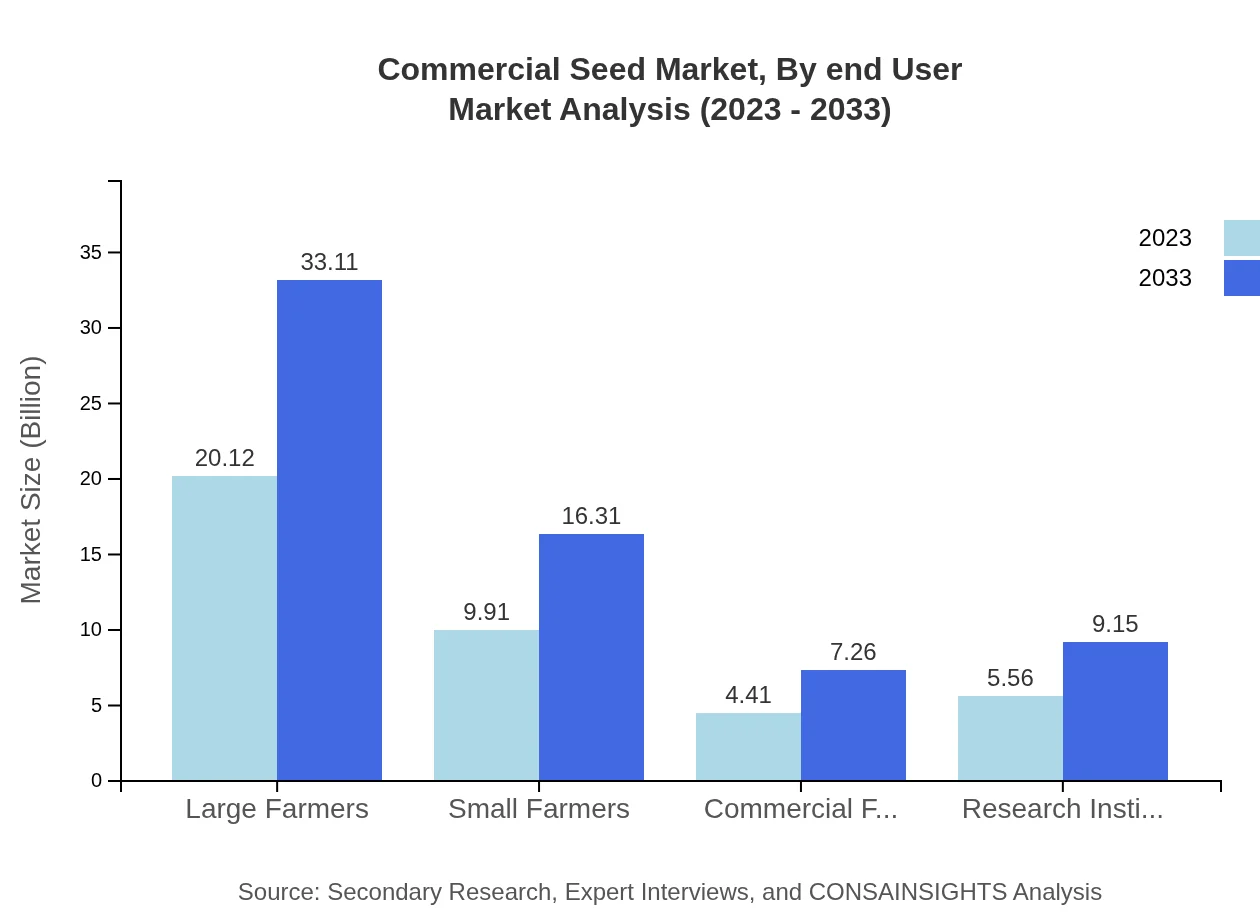
Commercial Seed Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segmentation includes Large Farmers, Small Farmers, Commercial Farms, and Research Institutions. Large Farmers lead the market with USD 20.12 billion in 2023, while Research Institutions play a crucial role in innovation and development within the sector.
Commercial Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Commercial Seed Industry
Bayer Crop Science:
A leading global player in agriculture, Bayer Crop Science specializes in high-quality seeds and crop protection solutions, helping farmers optimize their yields.Syngenta:
Syngenta is a prominent global agribusiness focused on developing seeds and crop protection products to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability.Corteva Agriscience:
Corteva Agriscience specializes in seed and crop protection products, emphasizing innovation and sustainability in farming practices.Monsanto Company:
Now a part of Bayer, Monsanto has been a pioneer in seed technology, including genetically modified seeds that have revolutionized modern agriculture.Limagrain:
Limagrain is a French cooperative focused on developing high-performance seeds for various crops, emphasizing innovation and quality in seed production.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of commercial seed?
The commercial seed market is valued at approximately $40 billion as of 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% from 2023 to 2033, indicating a robust growth trajectory in the upcoming years.
What are the key market players or companies in this commercial seed industry?
Key players in the commercial seed market include companies such as Bayer Cropscience, Syngenta, DuPont, and BASF, which dominate through innovation and extensive distribution networks across global markets.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the commercial seed industry?
Factors such as increasing global population, rising demand for food security, advancements in seed technology, and growing adoption of genetically modified crops are key drivers for the robust growth in the commercial seed industry.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the commercial seed?
Regions such as North America are experiencing significant growth, with the market projected to expand from $13.57 billion in 2023 to $22.33 billion by 2033, reflecting an increasing focus on modern agricultural practices.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the commercial seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the commercial seed industry, ensuring clients receive tailored insights based on their target market and strategic requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this commercial seed market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables such as detailed market analysis, segment performance, competitive landscape overview, and insightful forecasts that aid strategic decision-making in the commercial seed market.
What are the market trends of commercial seed?
Notable trends in the commercial seed market include the rising popularity of organic seeds, increasing investment in biotechnology, and a shift towards sustainable farming practices aimed at reducing environmental impact.