Ewaste Management Market Report
Published Date: 01 February 2026 | Report Code: ewaste-management
Ewaste Management Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the Ewaste Management market, covering current conditions, key trends, and detailed forecasts from 2023 to 2033, providing valuable insights into market size, segmentation, and regional performance.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
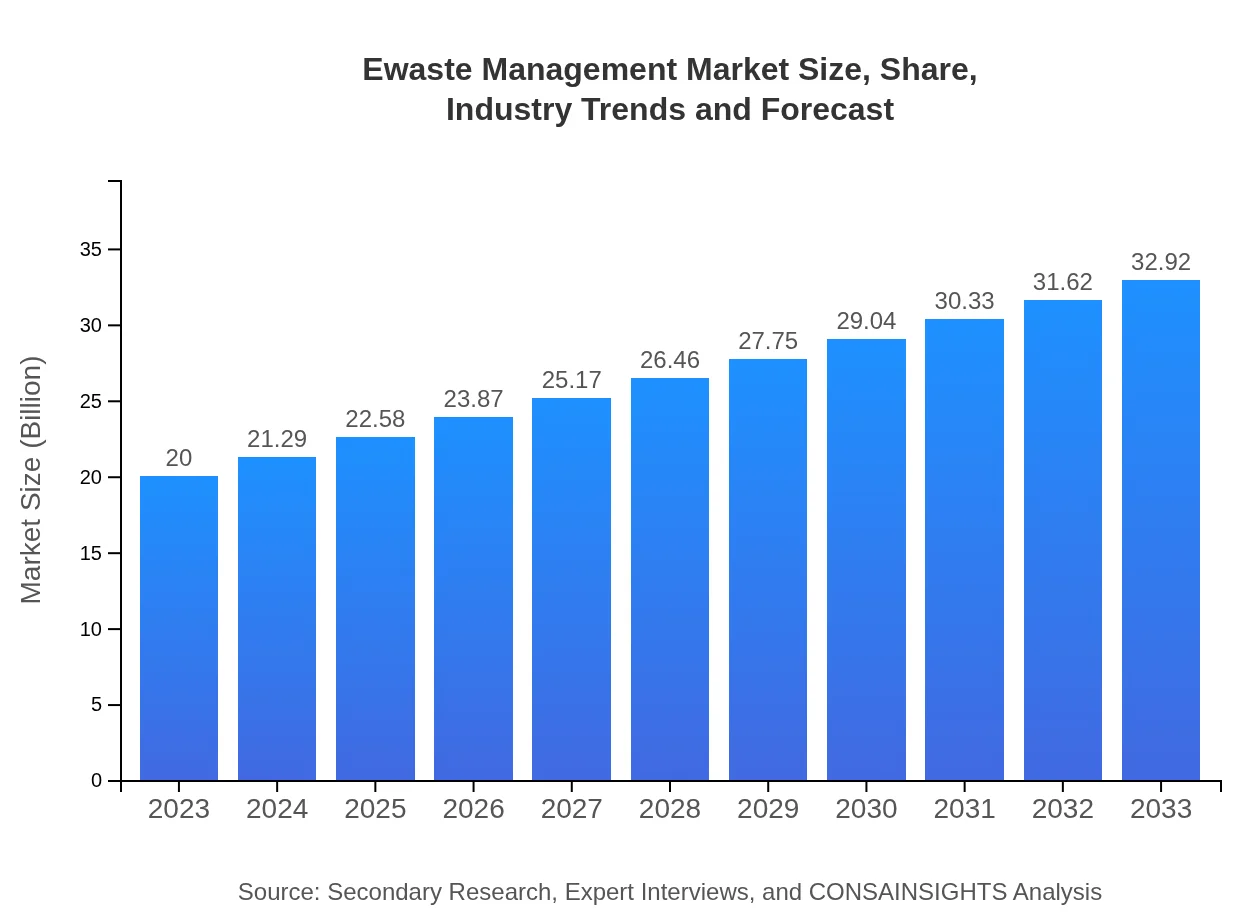
| 2023 Market Size | $20.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | Sims Recycling Solutions, ERD Environmental Resource Management, Veolia, Electronic Waste Management (EWM) |
| Last Modified Date | 01 February 2026 |
Ewaste Management Market Overview
Customize Ewaste Management Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Ewaste Management market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Ewaste Management's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Ewaste Management
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Ewaste Management market in 2023?
Ewaste Management Industry Analysis
Ewaste Management Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Ewaste Management Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Ewaste Management Market Report:
Europe shows a robust market, valued at 6.99 billion USD in 2023 and expected to rise to 11.51 billion USD by 2033. The region's emphasis on circular economies and stringent regulatory frameworks positions it as a leader in Ewaste Management.Asia Pacific Ewaste Management Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region held a market size of approximately 3.64 billion USD in 2023, projected to grow to 6.00 billion USD by 2033. Rapid urbanization and technological adoption raise Ewaste levels, while growing environmental regulations are pushing better waste management practices.North America Ewaste Management Market Report:
North America’s market size in 2023 stands at 6.71 billion USD, with projections indicating it will grow to 11.05 billion USD by 2033. The area benefits from stringent regulations aiming for sustainability and a high awareness regarding electronic waste.South America Ewaste Management Market Report:
In South America, the Ewaste Management market was valued at 1.84 billion USD in 2023 and is expected to reach 3.03 billion USD by 2033. Increasing consumer electronics penetration and regulatory measures are vital contributors to this market growth.Middle East & Africa Ewaste Management Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market for Ewaste Management is valued at 0.81 billion USD in 2023 and projected to increase to 1.33 billion USD by 2033. Growing consumer awareness and emerging regulations are expected to drive the market forward.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Ewaste Management Market Analysis By Product Category
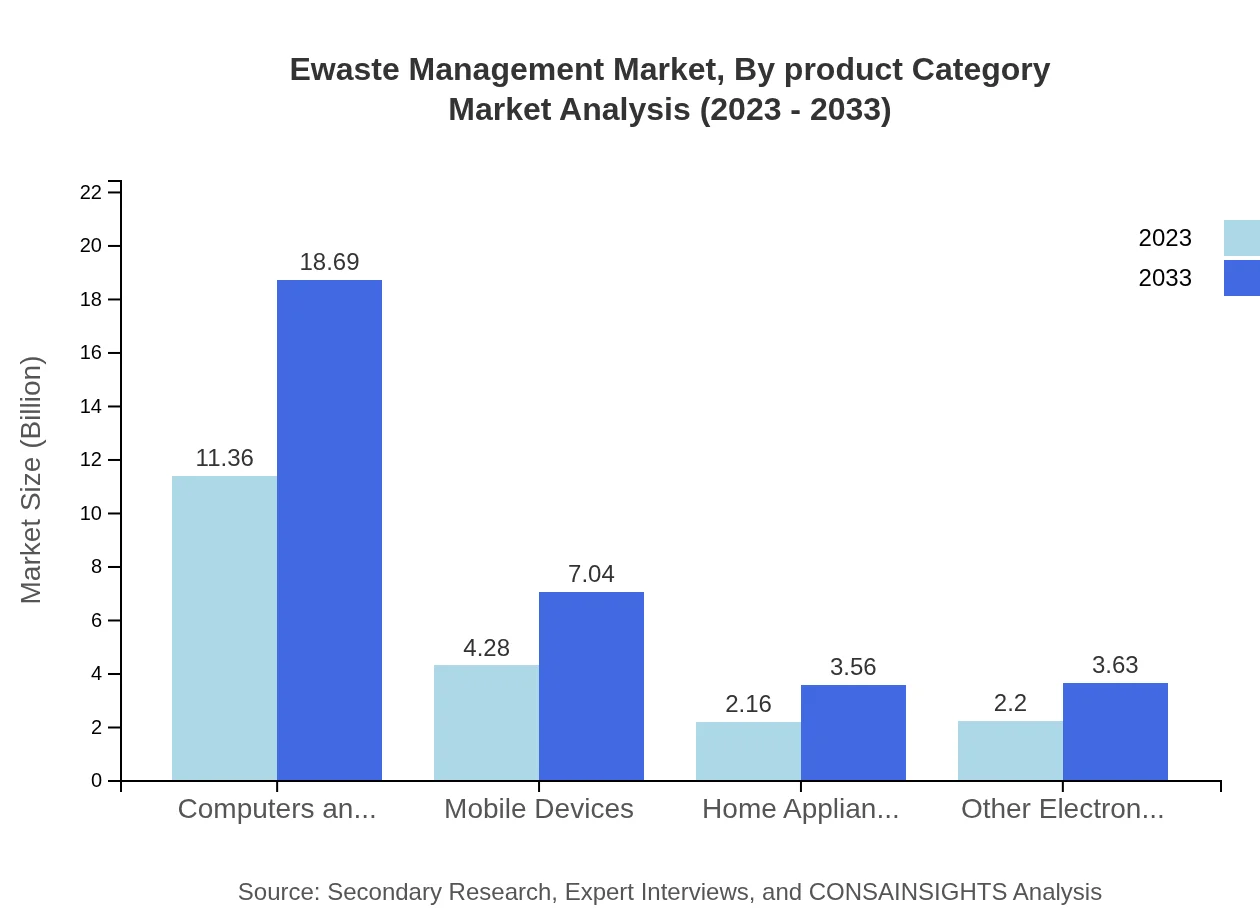
The product category segment represents the largest share of the Ewaste Management market, with growth driven primarily by increasing end-of-life electronics. In 2023, the Computers and Laptops segment is valued at 11.36 billion USD, accounting for 56.78% of the market share. The Mobile Devices segment follows closely at 4.28 billion USD (21.39%). Home Appliances and Other Electronics are also significant contributors to the market.
Ewaste Management Market Analysis By Recycling Method
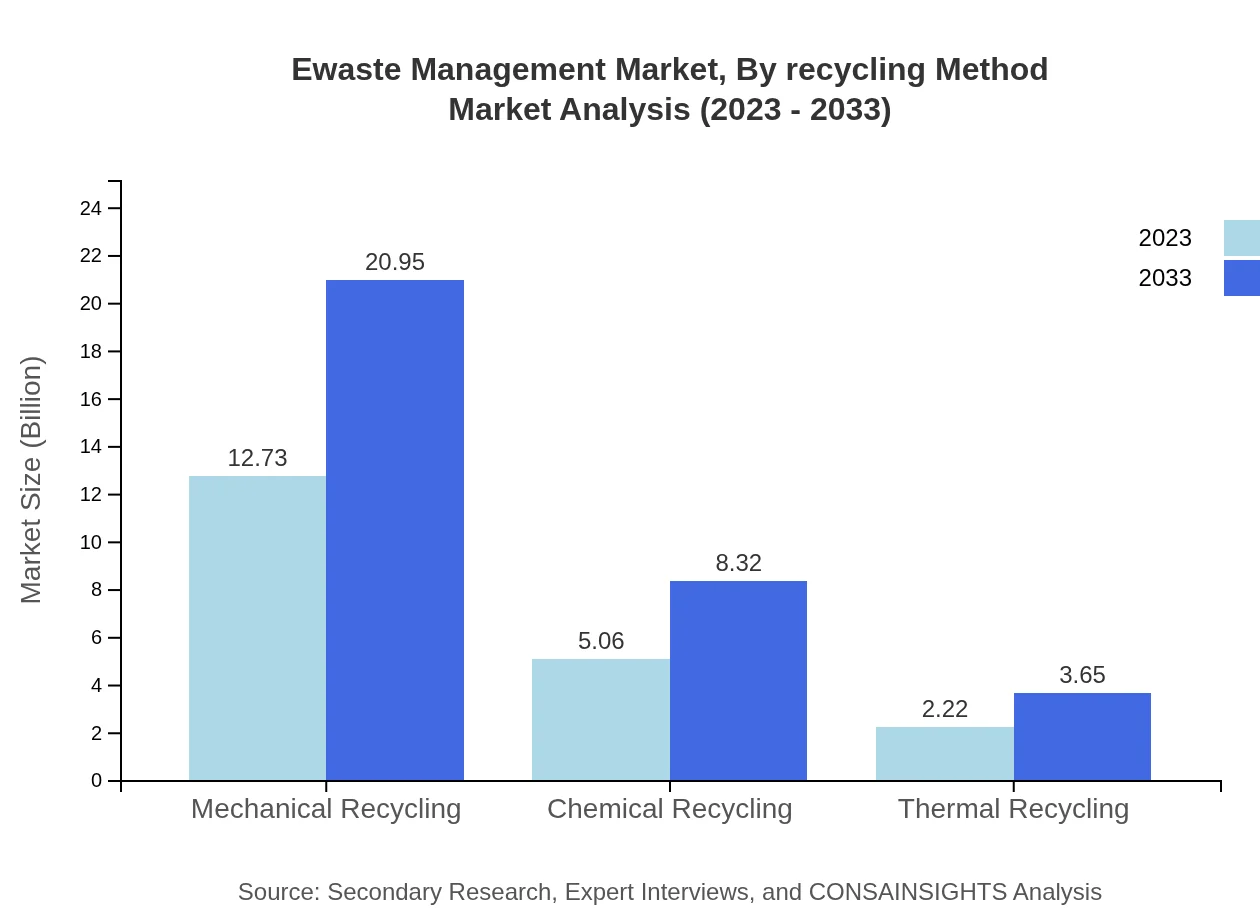
The Ewaste Management market can also be segmented by recycling methods, notably Mechanical, Chemical, and Thermal Recycling. In 2023, Mechanical Recycling is the leading method, valued at 12.73 billion USD (63.64% share). Chemical and Thermal methods hold significant market share as well, addressing specific types of electronic waste with unique processing needs.
Ewaste Management Market Analysis By Application
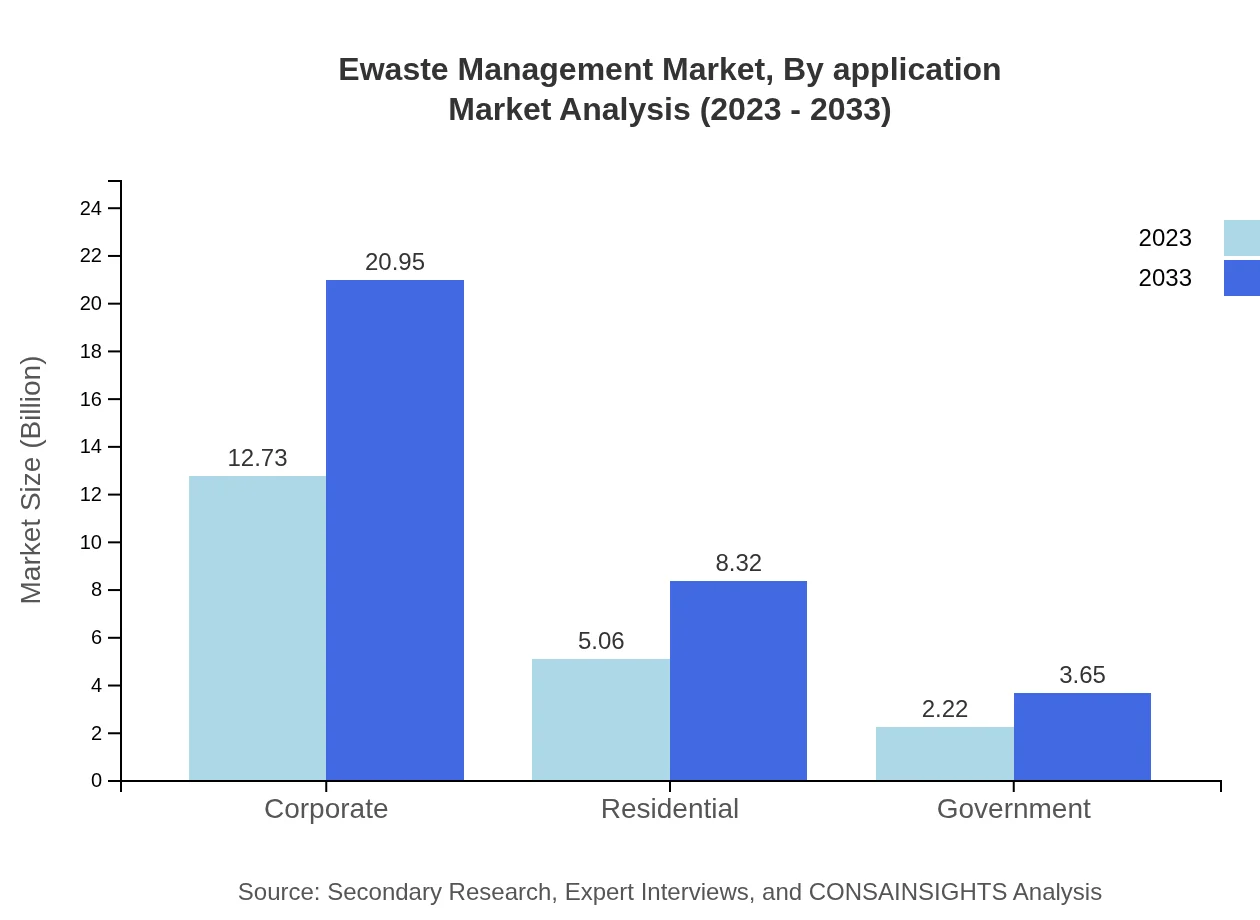
In terms of application, the Ewaste Management market covers various sectors including IT, Education, Government, and Corporate. IT holds the largest share with a size of 12.73 billion USD (63.64%). Retail accounts for 5.06 billion USD (25.28%), reflecting the growing trend of electronic consumption in retail environments.
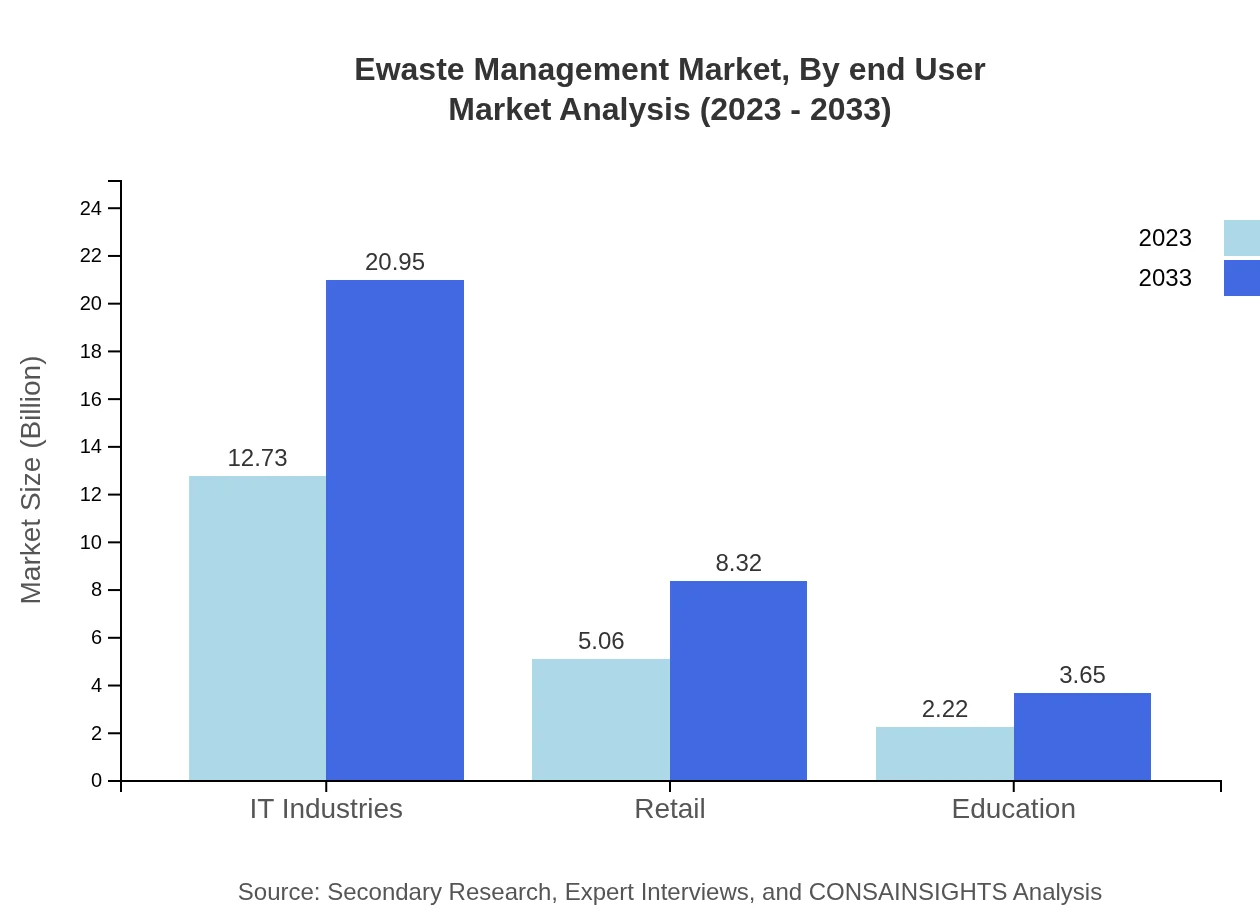
Ewaste Management Market Analysis By End User
Segmentation by end-user reflects diverse requirements, with Corporate and IT sectors leading allocations. Both Corporate and IT segments are valued at 12.73 billion USD, while other segments like Government and Residential also contribute substantially to the market, indicating the widespread implications of Ewaste management across various profiles.
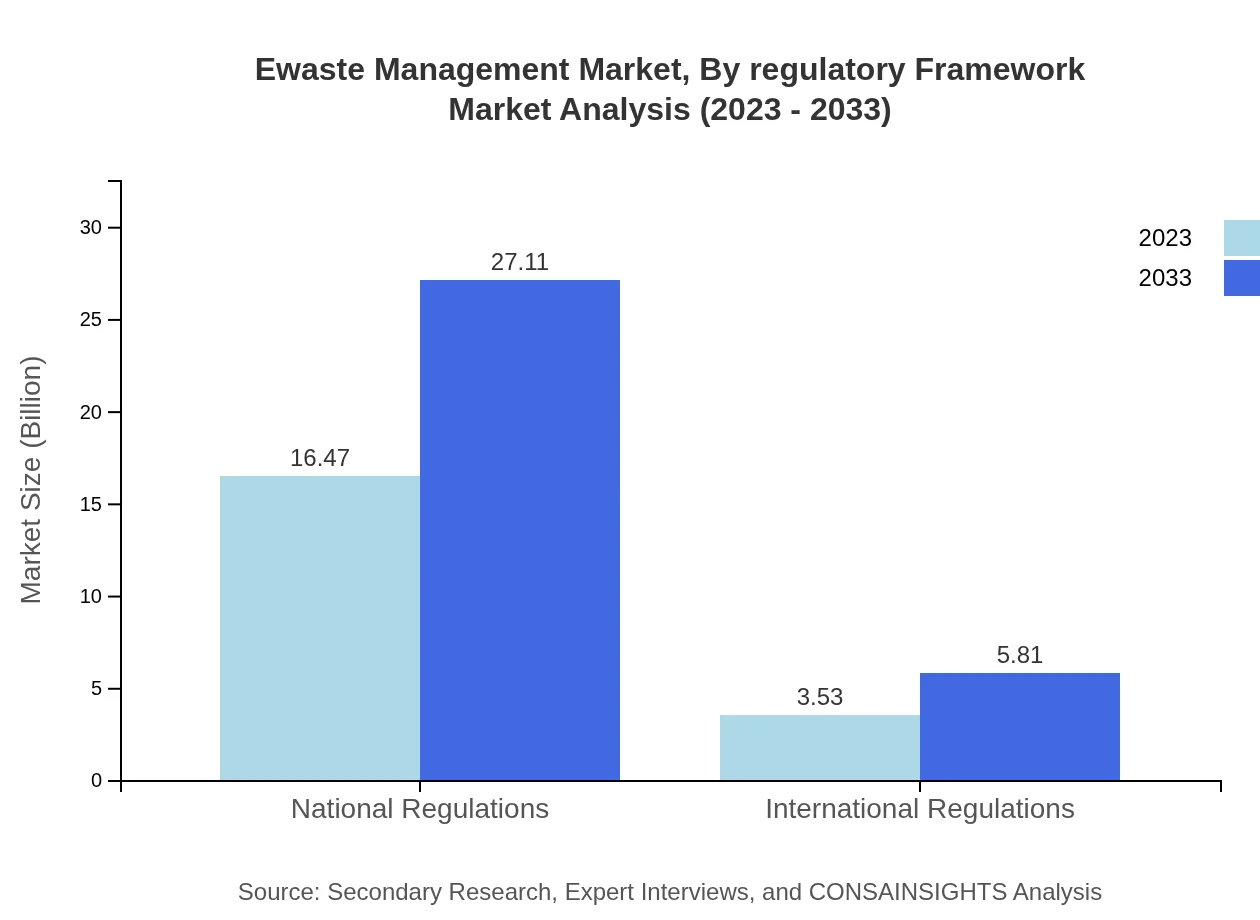
Ewaste Management Market Analysis By Regulatory Framework
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence market dynamics. In 2023, National Regulations dominate the market at 16.47 billion USD (82.35% share), reflecting governments' strong inclinations to legislate electronic waste management. International Regulations also show notable participation with 3.53 billion USD (17.65%).
Ewaste Management Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Ewaste Management Industry
Sims Recycling Solutions:
A leading player in the recycling and trade of electronic waste, Sims Recycling Solutions emphasizes sustainable practices and innovation in Ewaste processing.ERD Environmental Resource Management:
ERD focuses on comprehensive waste management and recycling services, ensuring compliance with environmental standards while offering tailored solutions for Ewaste management.Veolia:
Veolia is a global environmental services company with a strong portfolio in electronic waste management, focusing on developing specialized recycling technologies.Electronic Waste Management (EWM):
EWM specializes in thorough processing of electronic waste, operating advanced recycling facilities, and championing eco-friendly methods for managing Ewaste.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Ewaste Management?
The global Ewaste Management market is valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 5% through 2033. This reflects the rising demand for sustainable waste disposal and recycling solutions for electronic waste.
What are the key market players or companies in the Ewaste Management industry?
Key players in the Ewaste Management industry include major recycling firms, technology conglomerates, and waste management companies. These include prominent organizations known for their innovative recycling technologies and commitment to sustainable practices.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Ewaste Management industry?
The growth in the Ewaste Management industry is driven by increasing electronic consumption, stringent regulations, growing awareness of environmental issues, and technological advancements in recycling methods, fostering more effective waste management solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Ewaste Management?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the Ewaste Management market, expected to grow from $3.64 billion in 2023 to $6.00 billion by 2033. Other regions like North America and Europe also show significant growth trajectories.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Ewaste Management industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the Ewaste Management industry, providing specific insights, market analyses, and tailored solutions to suit individual client needs and preferences.
What deliverables can I expect from this Ewaste Management market research project?
Deliverables from the Ewaste Management market research project include comprehensive market analysis reports, presentations, segmentation data, forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and strategic recommendations based on the latest trends.
What are the market trends of Ewaste Management?
Current market trends in Ewaste Management include increasing adoption of recycling technologies, a shift towards circular economy models, enhanced regulatory measures, and growing consumer awareness about sustainable electronic disposal practices.