Nfc Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: nfc
Nfc Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the NFC market, with a comprehensive overview of current trends, growth trajectories, and forecasts spanning the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
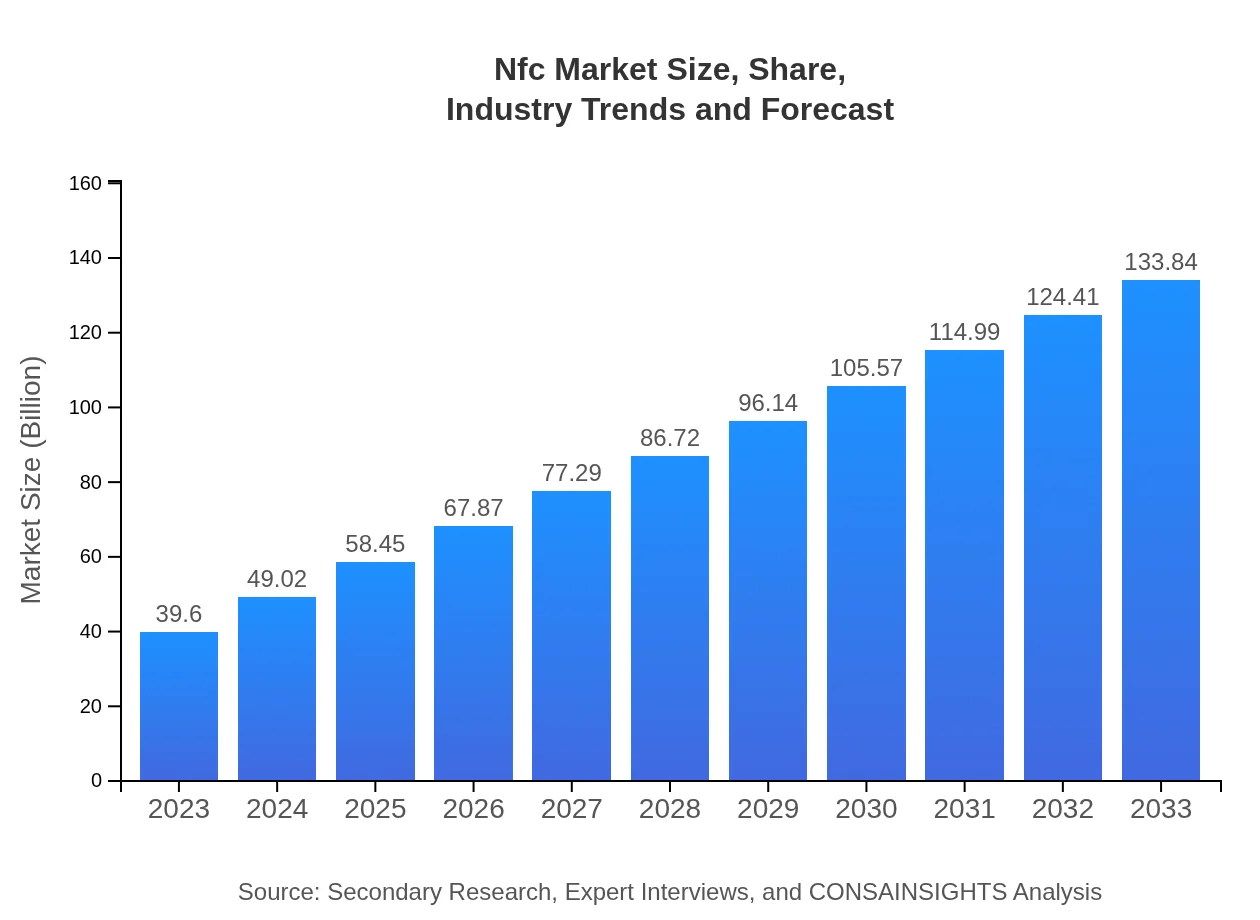
| 2023 Market Size | $39.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $133.84 Billion |
| Top Companies | Sony Corporation, NXP Semiconductors, Infineon Technologies, Samsung Electronics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Nfc Market Overview
Customize Nfc Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Nfc market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Nfc's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Nfc
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Nfc market in 2023?
Nfc Industry Analysis
Nfc Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Nfc Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Nfc Market Report:
Europe's NFC market is anticipated to expand from $11.56 billion in 2023 to $39.07 billion by 2033. Countries in this region are early adopters of NFC technology, primarily in the retail and banking sectors. The European Union's regulations promoting digital payments also contribute to market growth, as consumers increasingly prefer contactless payment solutions.Asia Pacific Nfc Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is an emerging market for NFC technology, with initial market size figures of $7.26 billion in 2023, projected to reach $24.55 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, increasing smartphone penetration, and burgeoning e-commerce contribute heavily to this growth. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea play significant roles in the market due to their advanced technological infrastructure and high consumer adoption of smart devices.North America Nfc Market Report:
North America represents a substantial portion of the NFC market, with a market size of $15.23 billion in 2023 expected to grow to $51.49 billion by 2033. The region's strong focus on innovation and technology adoption, along with the presence of major players and extensive use of mobile payment systems, boosts market growth. The United States predominantly drives this expansion.South America Nfc Market Report:
In South America, the NFC market is projected to grow from $2.91 billion in 2023 to $9.85 billion by 2033. Growth is driven by the rising adoption of mobile payment solutions and the expansion of retail outlets utilizing digital payment methods. Brazil and Argentina are leading markets in the adoption of NFC technology across various applications.Middle East & Africa Nfc Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are expected to show considerable growth in the NFC market, with sizes estimated at $2.63 billion in 2023, growing to $8.89 billion by 2033. The region's growing smartphone adoption and increasing investment in digital payment infrastructures are pivotal in driving this growth. Countries like the UAE and South Africa are at the forefront of NFC technology adoption.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Nfc Market Analysis By Technology
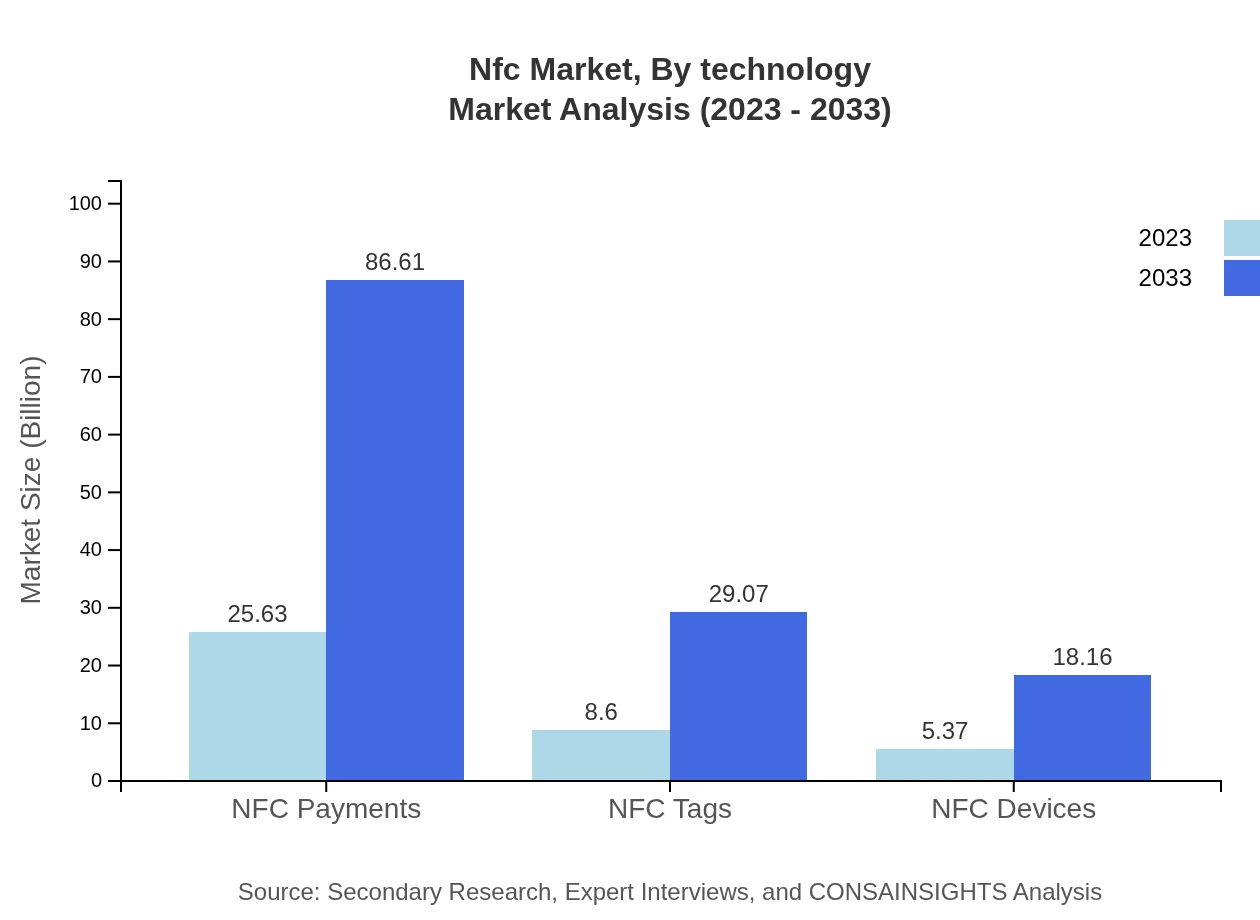
The NFC market, segmented by technology, primarily features NFC chips, NFC-enabled devices, and NFC software as major components. NFC chips are projected to dominate the market, growing from $25.63 billion in 2023 to $86.61 billion by 2033. Similarly, NFC-enabled devices are expected to rise from $8.60 billion to $29.07 billion in the same period. NFC software will also see considerable growth, from $5.37 billion to $18.16 billion, showcasing a robust technological adoption across sectors.
Nfc Market Analysis By Application
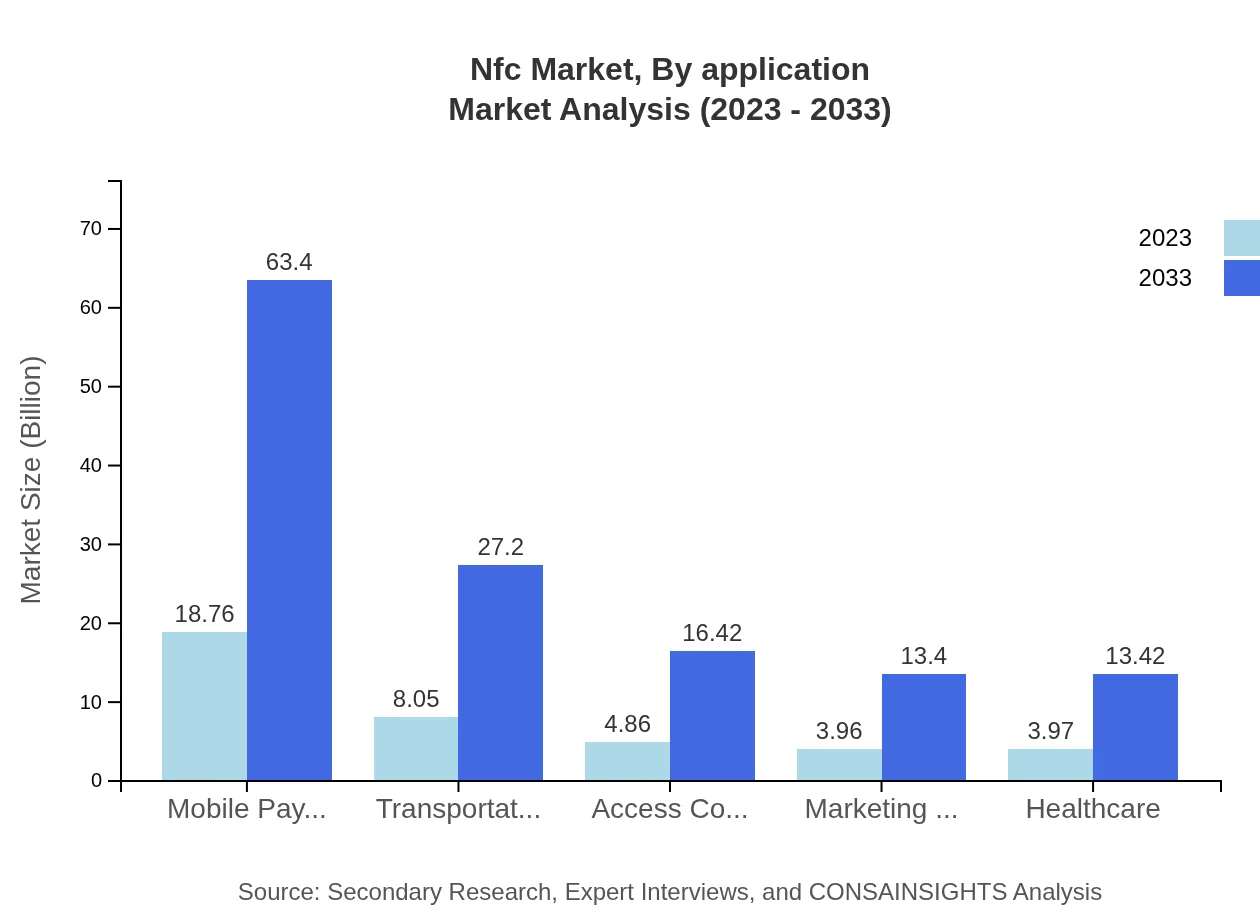
The NFC market, when segmented by applications, reflects significant growth in mobile payments and retail solutions. Mobile payments, which include NFC payments, will grow from $25.63 billion in 2023 to $86.61 billion by 2033. The retail sector also shows tremendous potential, expanding from $18.76 billion to $63.40 billion, underscoring the need for businesses to innovate and streamline transaction processes.
Nfc Market Analysis By End User
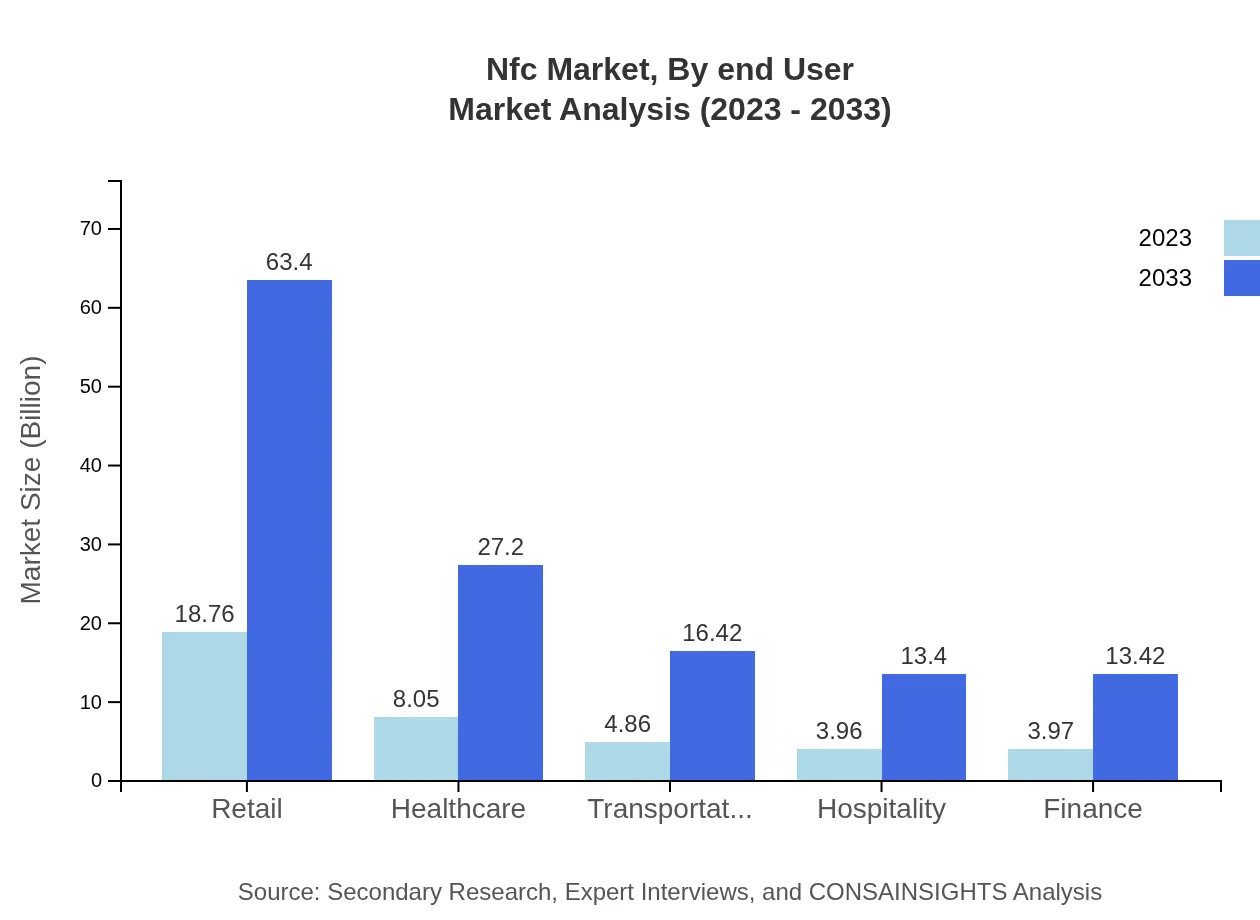
Various end-user industries leverage NFC technology significantly. Retail occupies a substantial share, demonstrating growth from $18.76 billion in 2023 to $63.40 billion in 2033. Healthcare is another prominent sector, with a market size growing from $8.05 billion to $27.20 billion, emphasizing the importance of technology in improving patient care and management.
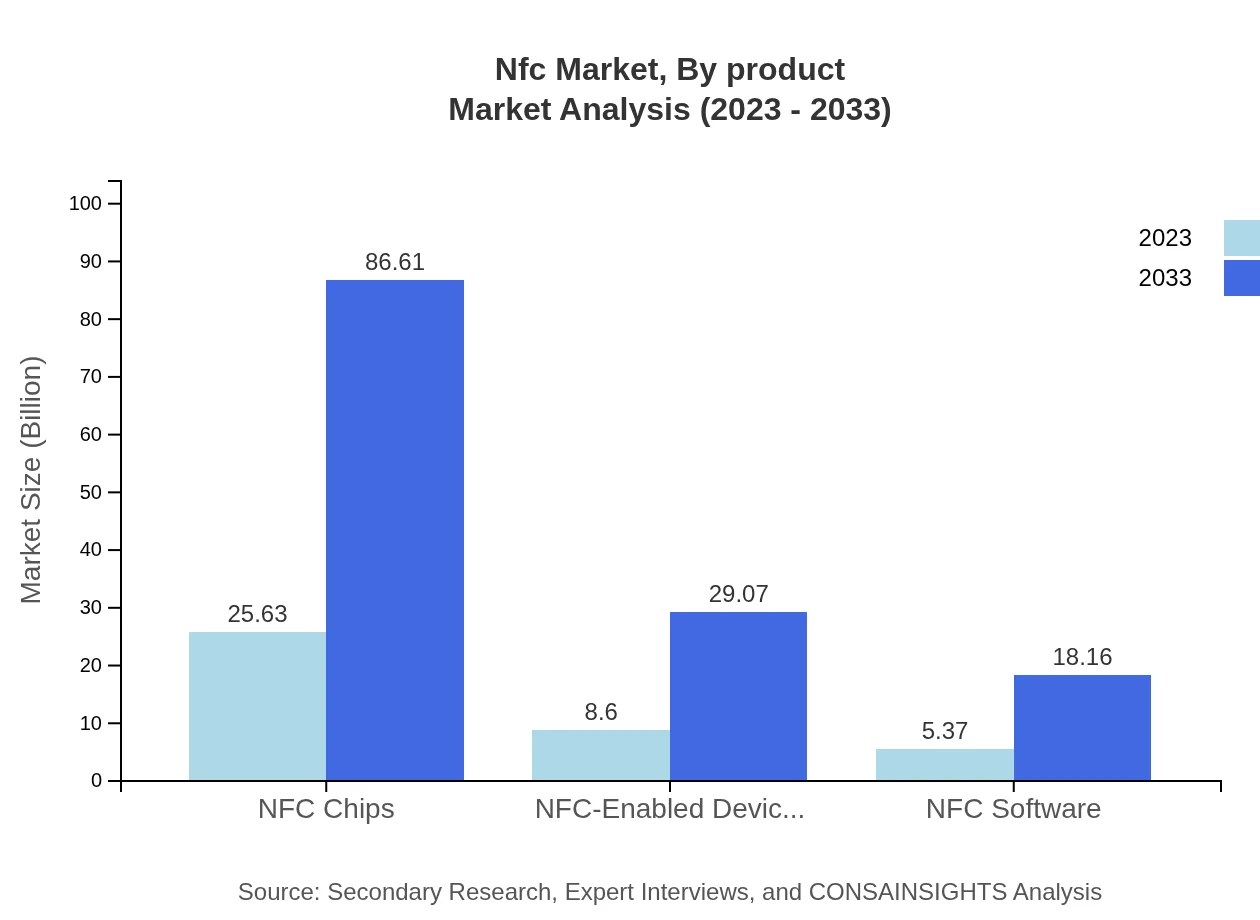
Nfc Market Analysis By Product
The product analysis of the NFC market underscores NFC-enabled devices' growing significance. The NFC devices market is expected to grow from $5.37 billion in 2023 to $18.16 billion by 2033. Additionally, NFC tags will also grow, from $8.60 billion to $29.07 billion, reflecting increased application in various industries, including logistics and retail.
Nfc Market Analysis By Challenges Opportunities
The NFC market faces challenges related to security issues and technology adoption inertia. However, it also presents substantial opportunities, particularly in expanding applications across the retail and healthcare sectors. As digital transformation accelerates, companies that leverage NFC effectively can gain a significant competitive advantage, positioning themselves for long-term growth.
Nfc Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Nfc Industry
Sony Corporation:
A leading innovator in NFC technology, Sony has developed various NFC-enabled devices and solutions that enhance consumer experiences in sectors like mobile payments and smart devices.NXP Semiconductors:
NXP is a pioneer in NFC chip manufacturing. Their chips facilitate the widespread use of NFC technology in smartphones, wearables, and other connected devices, playing a crucial role in the market's growth.Infineon Technologies:
Infineon is known for its advanced NFC solutions that drive security and performance in mobile payment systems, emphasizing innovation in securing transactions.Samsung Electronics:
A major player in the electronics market, Samsung incorporates NFC technology into its mobile devices, contributing to the widespread adoption of contactless payments and services.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of NFC?
The NFC market is projected to reach approximately $39.6 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 12.4% from 2023 to 2033, indicating significant growth driven by increasing adoption across various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the NFC industry?
Key players include major technology firms and manufacturers specializing in NFC chips, devices, and software solutions, contributing to a competitive landscape fostering innovation and growth in the NFC sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the NFC industry?
Drivers include the surge in contactless payment systems, increasing smartphone penetration, and the growing demand for secure and efficient transactions across retail, healthcare, and hospitality sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the NFC market?
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for NFC technologies, with projections to grow from $7.26 billion in 2023 to $24.55 billion by 2033, indicating robust regional development.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the NFC industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers tailored market report data specifically designed to meet the unique needs and preferences of clients in the NFC industry, ensuring relevant insights for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this NFC market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analyses, detailed segment breakdown, competitive landscape evaluations, and forecast data, ensuring actionable insights for stakeholders in the NFC market.
What are the market trends of NFC?
Trends include the rising adoption of NFC-enabled devices, growth in mobile payments, and advancements in NFC technology, which are reshaping consumer engagement and operational efficiencies across various industries.