Robotic Welding Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: robotic-welding
Robotic Welding Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Robotic Welding market for the forecast period of 2023 to 2033, covering key insights, market trends, regional performance, and competitive landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
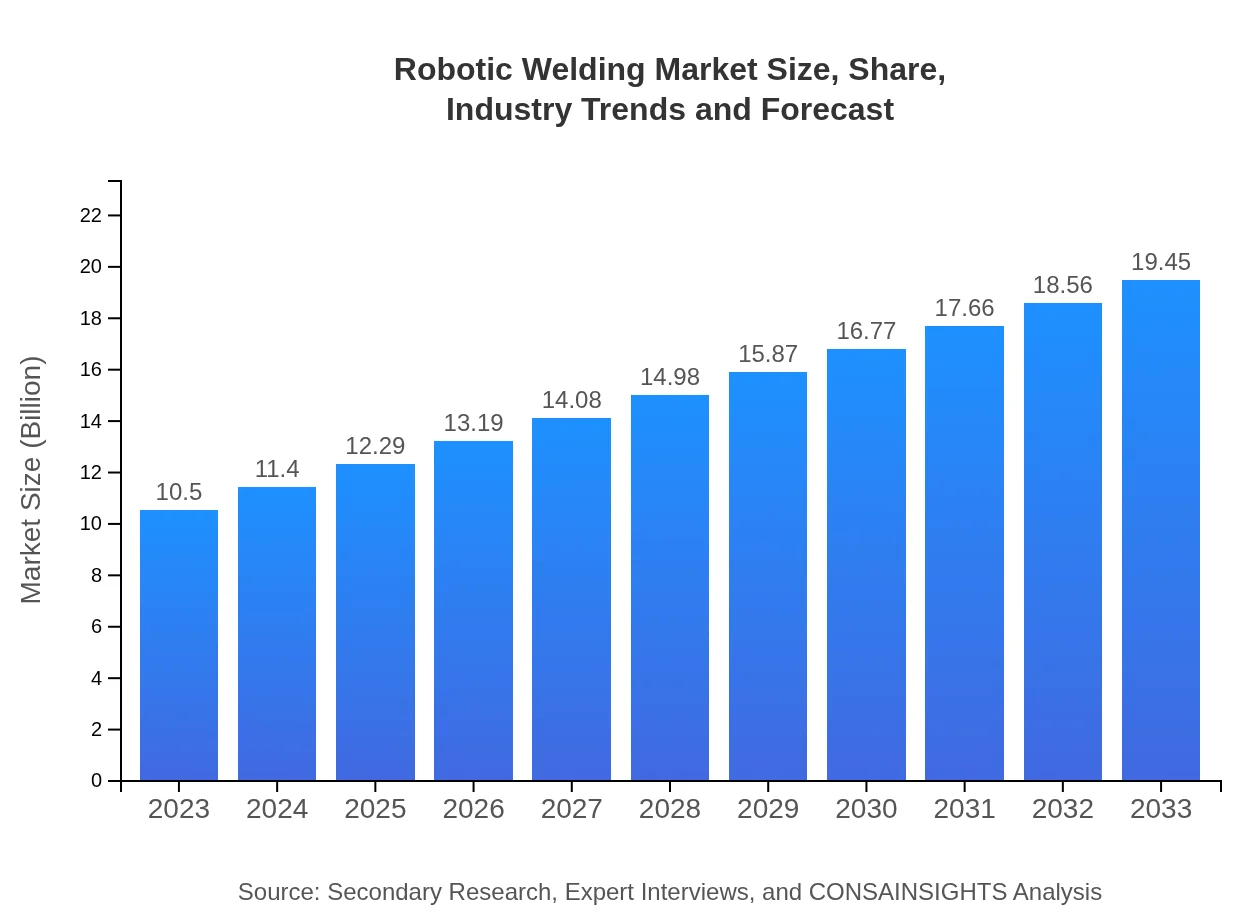
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $19.45 Billion |
| Top Companies | ABB Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, KUKA AG, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Comau S.r.l. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Robotic Welding Market Overview
Customize Robotic Welding Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Robotic Welding market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Robotic Welding's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Robotic Welding
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Robotic Welding market in 2023?
Robotic Welding Industry Analysis
Robotic Welding Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Robotic Welding Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Robotic Welding Market Report:
The European market for Robotic Welding is predicted to grow from $2.91 billion in 2023 to $5.39 billion by 2033. Europe is at the forefront of adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, with countries like Germany, France, and Italy leading in automotive and industrial sectors.Asia Pacific Robotic Welding Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to be a significant contributor to the Robotic Welding market, projected to grow from $2.03 billion in 2023 to $3.76 billion by 2033. The increasing industrialization, particularly in countries like China and India, coupled with a rise in automotive production, is driving the demand for robotic welding solutions.North America Robotic Welding Market Report:
North America stands as a major market for Robotic Welding, with its size increasing from $3.85 billion in 2023 to $7.14 billion in 2033. The region benefits from advanced manufacturing capabilities, technological advancements, and substantial investments in automation, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors.South America Robotic Welding Market Report:
In South America, the Robotic Welding market is expected to expand from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.61 billion by 2033. Growth in infrastructure projects and the burgeoning automotive sector, primarily in Brazil and Argentina, are driving this demand.Middle East & Africa Robotic Welding Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are projected to experience growth in the Robotic Welding market, rising from $0.84 billion in 2023 to $1.55 billion by 2033. Increasing investments in the oil and gas industry, as well as construction activities, are contributing to the adoption of robotic welding technologies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
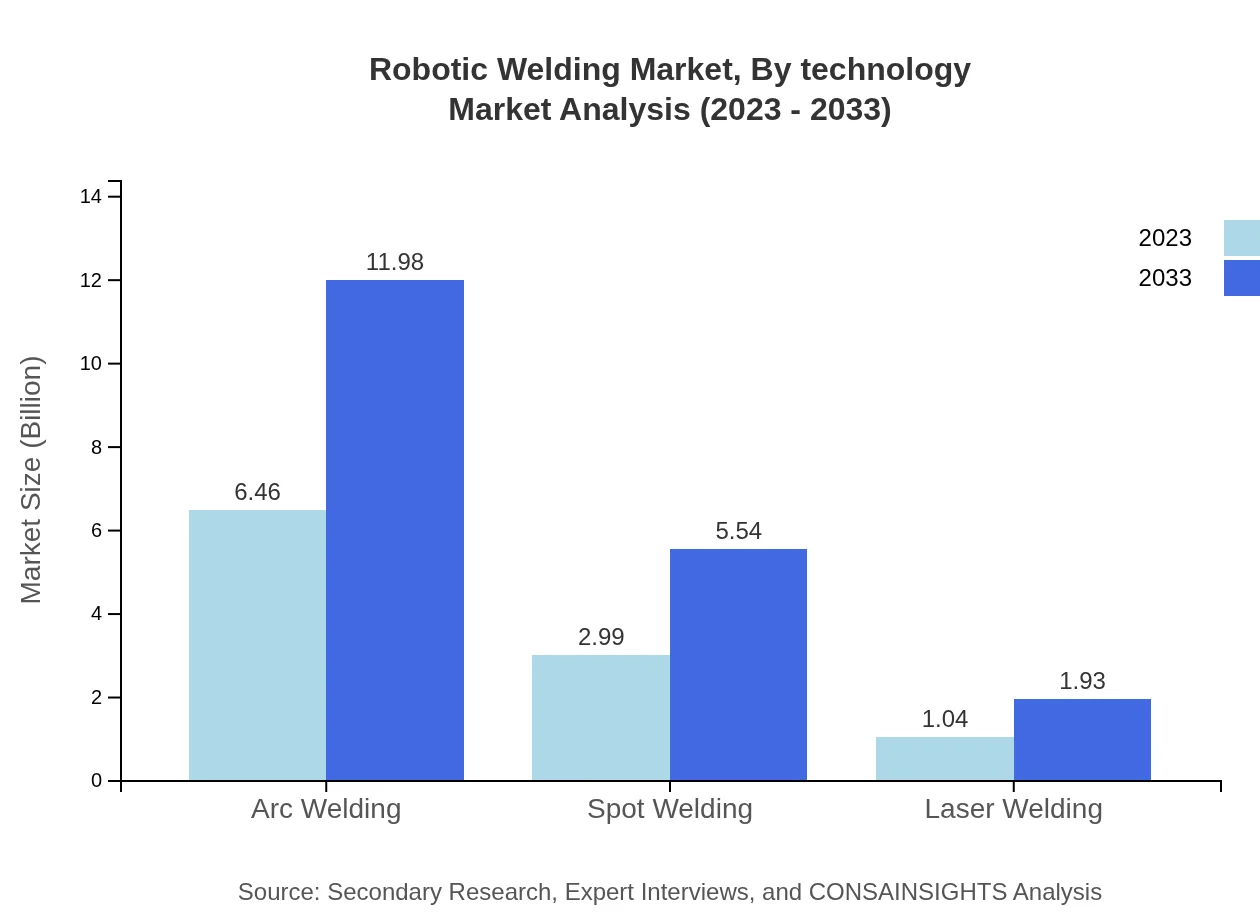
Robotic Welding Market Analysis By Technology
The Robotic Welding market by technology is dominated by Arc Welding, with a size of $6.46 billion in 2023, expected to reach $11.98 billion by 2033. This technology holds a market share of 61.57% in 2023. Spot Welding follows with $2.99 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $5.54 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of 28.49%. Laser Welding represents a growing segment as well, with a market size of $1.04 billion in 2023, anticipated to rise to $1.93 billion by 2033, contributing 9.94% market share.
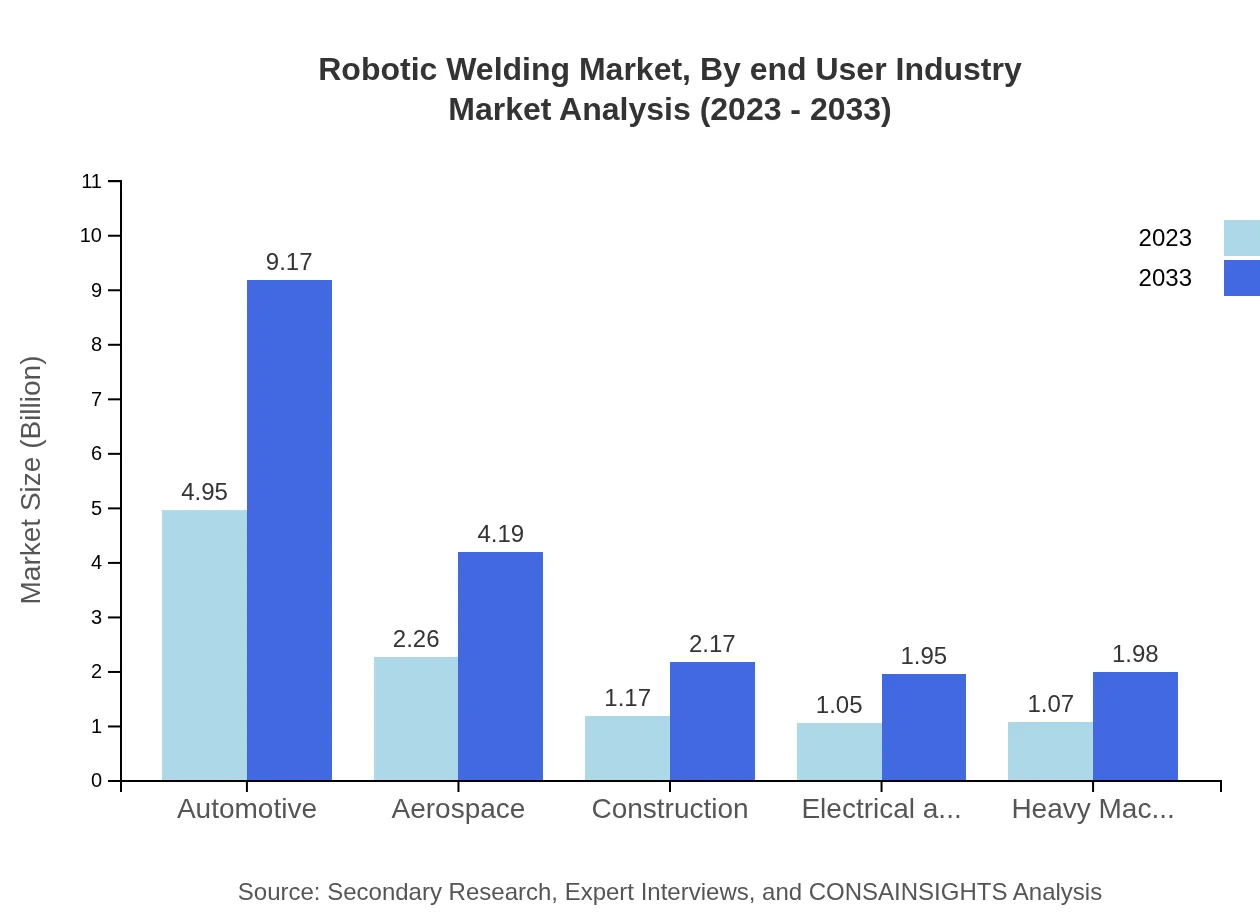
Robotic Welding Market Analysis By End User Industry
The automotive sector is the largest end-user of robotic welding, with a market size of $4.95 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $9.17 billion by 2033. This segment is responsible for a 47.12% market share in 2023. Other key industries include aerospace with a size of $2.26 billion in 2023, growing to $4.19 billion by 2033, and construction, expected to rise from $1.17 billion to $2.17 billion during the same period.
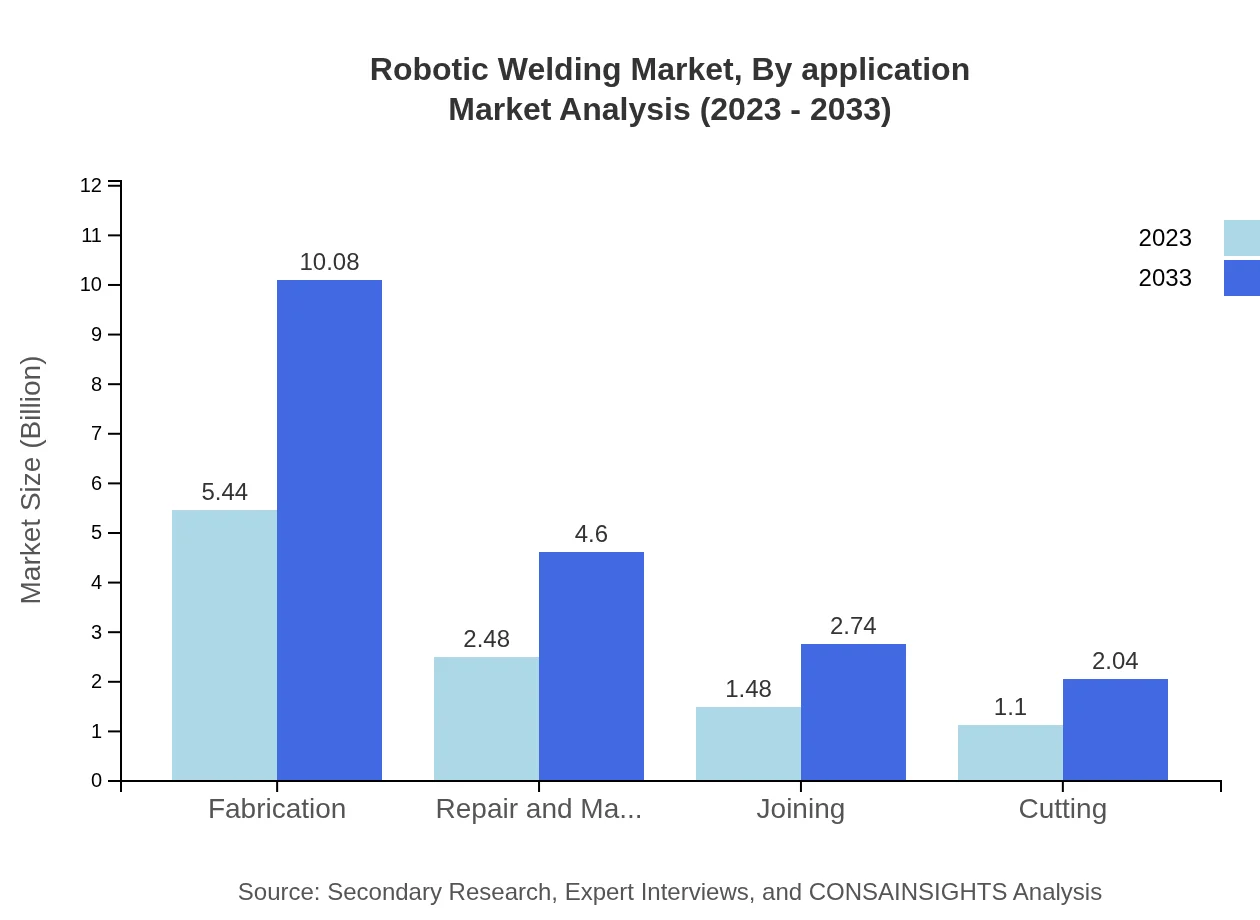
Robotic Welding Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the major segments include Fabrication, with revenue increasing from $5.44 billion in 2023 to $10.08 billion by 2033, representing 51.83% market share. Repair and Maintenance takes up 23.62% of the share, sized at $2.48 billion in 2023 and anticipated to reach $4.60 billion. Joining and Cutting applications also contribute to the market significantly with steady growth expected.
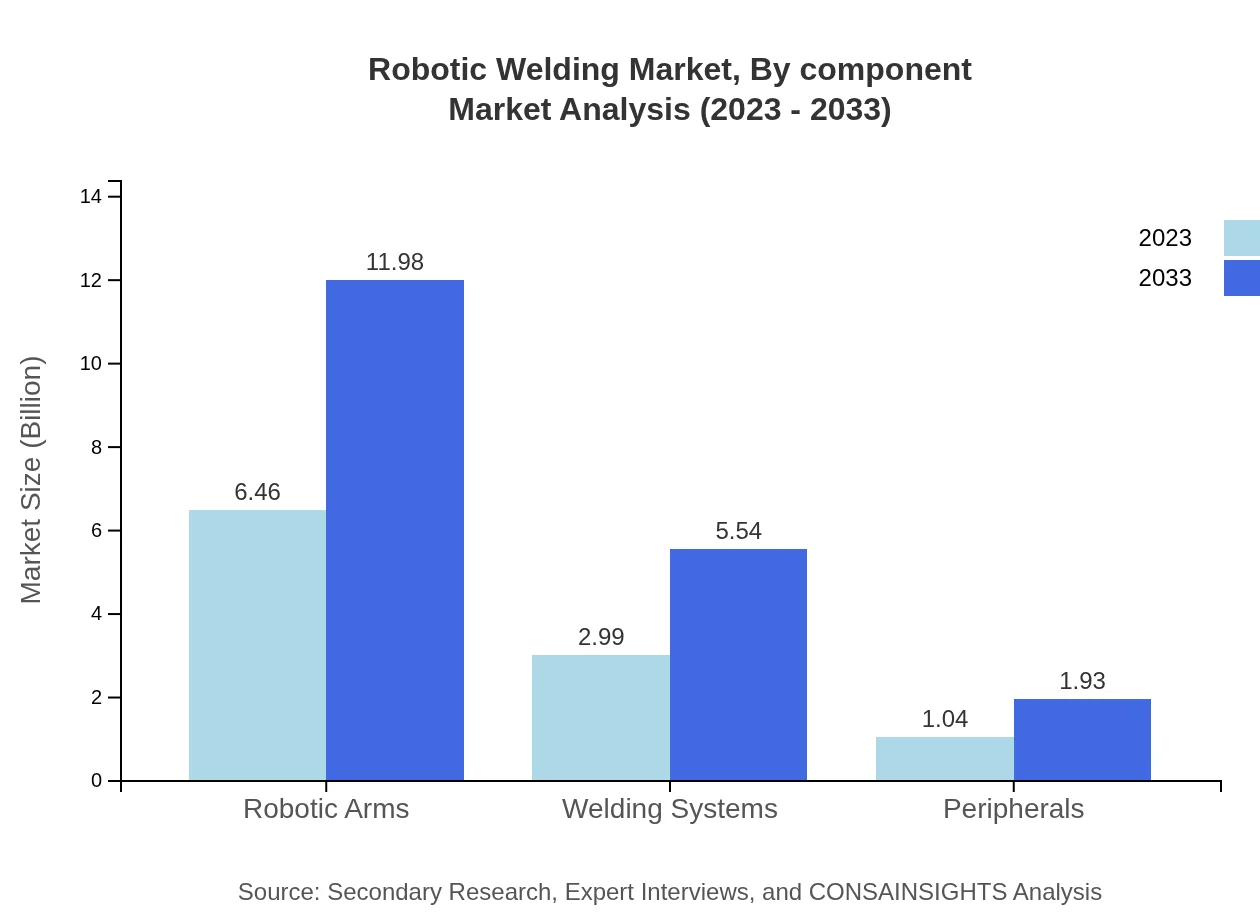
Robotic Welding Market Analysis By Component
The market components include robotic arms, welding systems, and peripherals. The robotic arms segment leads with a market size of $6.46 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $11.98 billion by 2033. The welding systems segment size is projected to increase from $2.99 billion to $5.54 billion, while peripherals are growing from $1.04 billion to $1.93 billion, supporting the overall infrastructure of robotic welding.
Robotic Welding Market Analysis By Region Application
The market's regional applications show varied growth rates. North America and Europe showcase high adoption rates due to advanced technology infrastructure, with Asia-Pacific emerging rapidly from increased industrial activity. South America and Africa are catching up, fueled by investments in local industries, indicating a global shift towards sophisticated manufacturing processes.
Robotic Welding Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Robotic Welding Industry
ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a leader in industrial technology, offering innovative solutions in robotic welding with a focus on high-speed performance and precision in automation.Fanuc Corporation:
Fanuc specializes in robotics and factory automation, providing high-quality robotic welding solutions serving numerous sectors worldwide.KUKA AG:
KUKA is renowned for its robotics manufacturing solutions, including advanced welding technology that enhances productivity and safety.Yaskawa Electric Corporation:
As a pioneer in industrial robotics, Yaskawa delivers innovative robotic welding systems, emphasizing energy efficiency and productivity.Comau S.r.l.:
Comau is recognized for its automation solutions in manufacturing and offers extensive experience in robotic welding for various industries.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of robotic Welding?
The global robotic-welding market is currently valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with a projected annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2%. This growth reflects increasing automation in manufacturing processes worldwide.
What are the key market players or companies in this robotic Welding industry?
Key players in the robotic-welding industry include Yaskawa Electric Corporation, ABB Ltd., KUKA AG, FANUC Corporation, and Lincoln Electric Holdings, Inc. These companies dominate through advanced technology and expansive global presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the robotic Welding industry?
Growth drivers include rising demand for automation in manufacturing, improved welding precision, lower operational costs, and the need for enhanced production efficiency in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the robotic Welding market?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the robotic-welding market, with a projected market size growth from $3.85 billion in 2023 to $7.14 billion in 2033, influenced by technological advancements and increased manufacturing activities.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the robotic Welding industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the robotic-welding industry, providing insights that are aligned with unique business requirements and market conditions.
What deliverables can I expect from this robotic Welding market research project?
Deliverables typically include a detailed report with market analysis, forecasts, competitive landscape insights, segment analysis, and strategic recommendations to inform decision-making in the robotic-welding space.
What are the market trends of robotic Welding?
Current trends include increased adoption of robotic arms which contributed $6.46 billion in 2023, expansion into emerging markets, and advancements in AI and machine learning enhancing robotic welding capabilities.