Seafood Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: seafood
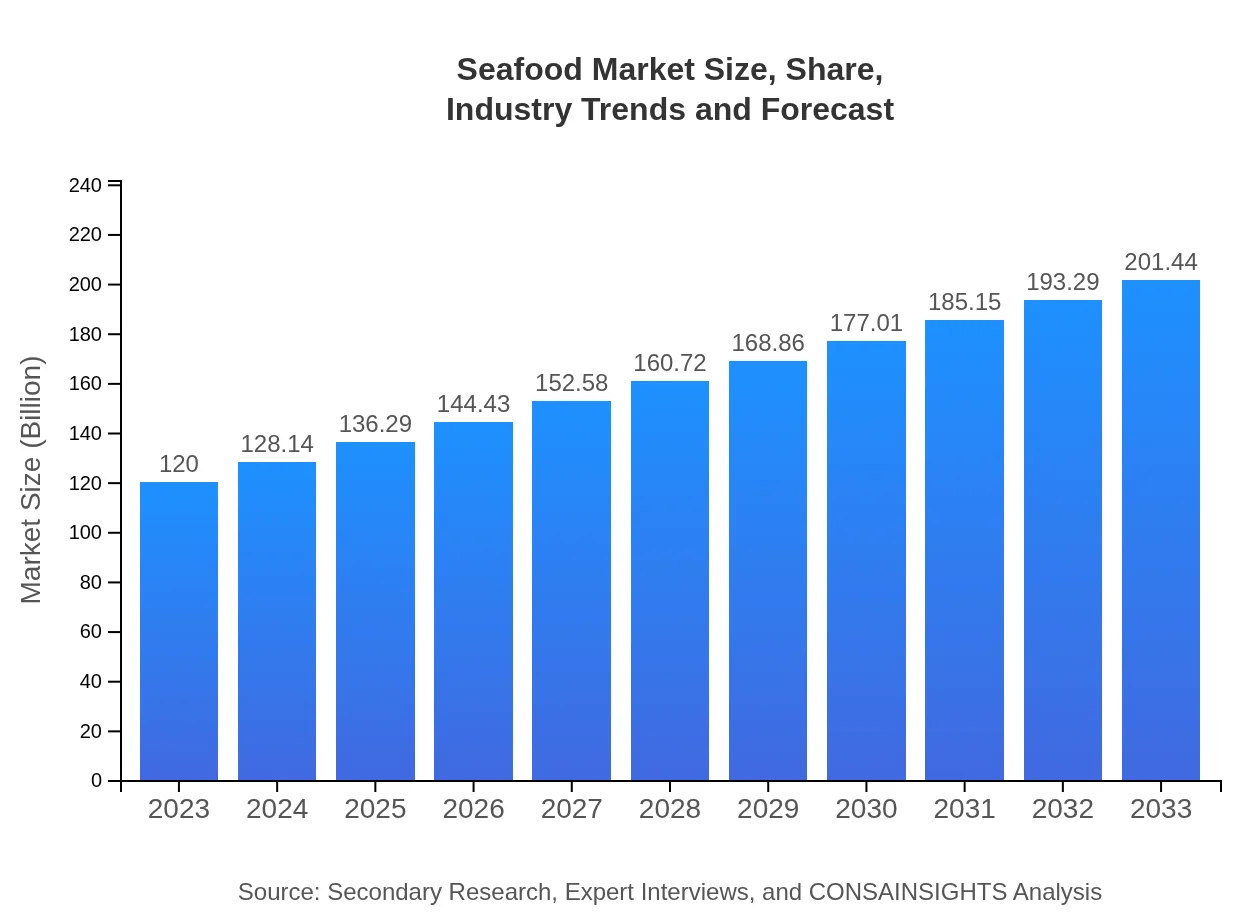
Seafood Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides a comprehensive analysis of the seafood industry, covering market size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include regional dynamics, product performance, segmentation, and the impact of technology on market growth.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $120.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $201.44 Billion |
| Top Companies | Maruha Nichiro Corporation, Thai Union Group, Domsea Fisheries |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Seafood Market Overview
Customize Seafood Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Seafood market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Seafood's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Seafood
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Seafood market in 2023?
Seafood Industry Analysis
Seafood Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Seafood Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Seafood Market Report:
Europe, currently valued at USD 39.20 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 65.81 billion by 2033. The demand for sustainably sourced seafood and environmental consciousness among European consumers drives market growth. Moreover, regulatory initiatives pushing for sustainable fishing practices will enhance market sustainability.Asia Pacific Seafood Market Report:
Asia Pacific represents one of the largest seafood markets, valued at USD 22.60 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 37.93 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing population, urbanization, and a strong cultural affinity for seafood, particularly in countries like China and Japan. Additionally, the region's advancements in aquaculture technologies are expected to sustain this expansion.North America Seafood Market Report:
North America’s seafood market is projected to grow from USD 40.24 billion in 2023 to USD 67.54 billion by 2033. The increase stems from rising health consciousness, a shift toward plant-based diets that still incorporate seafood, and the continued growth of the food service industry, particularly restaurants emphasizing seafood dishes.South America Seafood Market Report:
In South America, the seafood market is evolving with a value of USD 1.67 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to USD 2.80 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to a burgeoning demand for seafood among local populations and an increase in exports driven by international markets, particularly for sustainable fish products from countries like Chile.Middle East & Africa Seafood Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa seafood market is projected to grow from USD 16.30 billion in 2023 to USD 27.36 billion by 2033. A rising population and increasing tourist inflow are boosting demand for seafood in the food service sector. Aquaculture’s significance is increasing to meet dietary needs and drive market growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
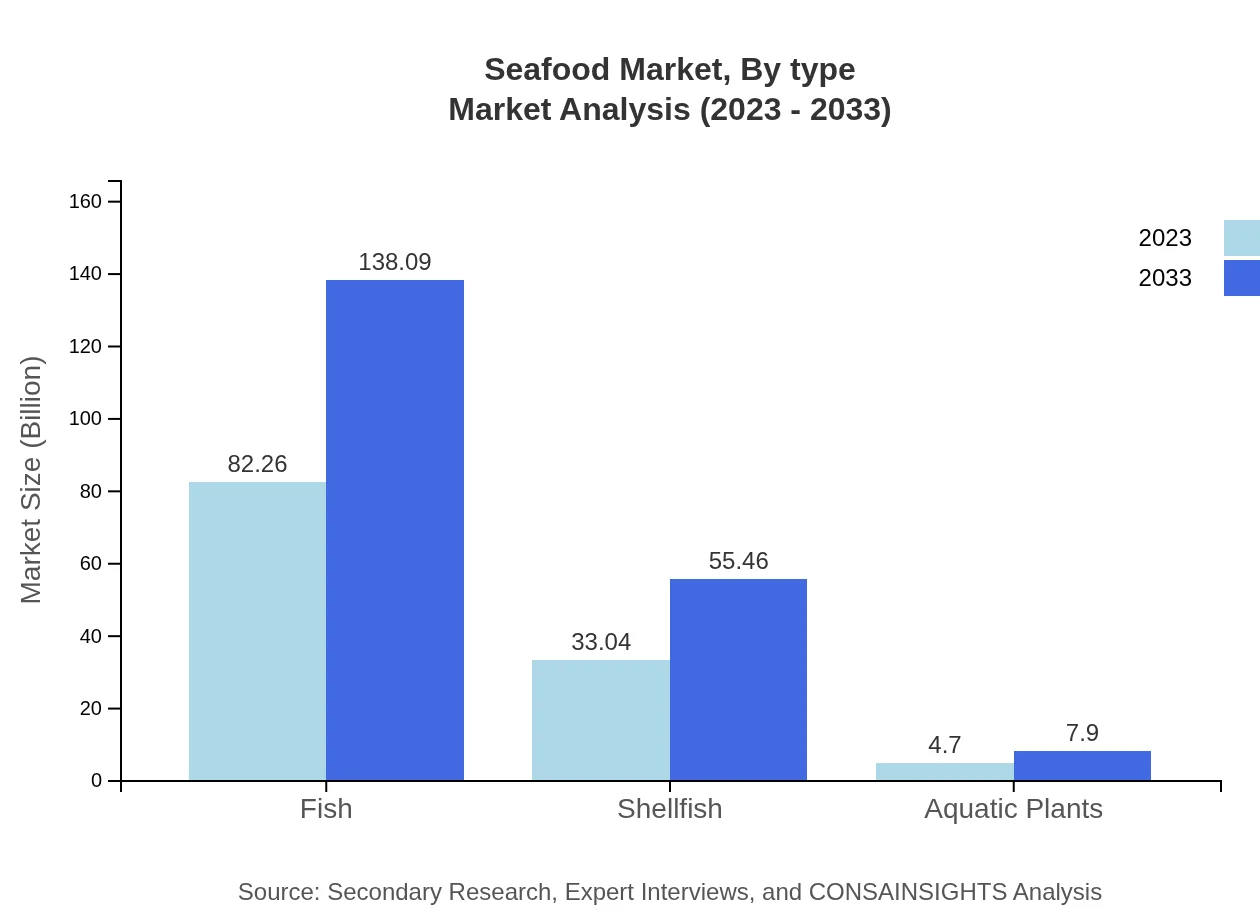
Seafood Market Analysis By Type
The seafood market is primarily segmented into fresh, frozen, canned, and smoked products. In 2023, the fresh seafood category dominated with a size of USD 67.87 billion, projected to rise to USD 113.93 billion by 2033, comprising a significant 56.56% share. The frozen segment, valued at USD 25.18 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to USD 42.26 billion. Canned seafood, currently at USD 13.99 billion, will reach USD 23.49 billion, indicating the growing convenience-driven demand. Smoked seafood products, worth USD 12.96 billion in 2023, are expected to evolve similarly, signaling ongoing consumer interest.
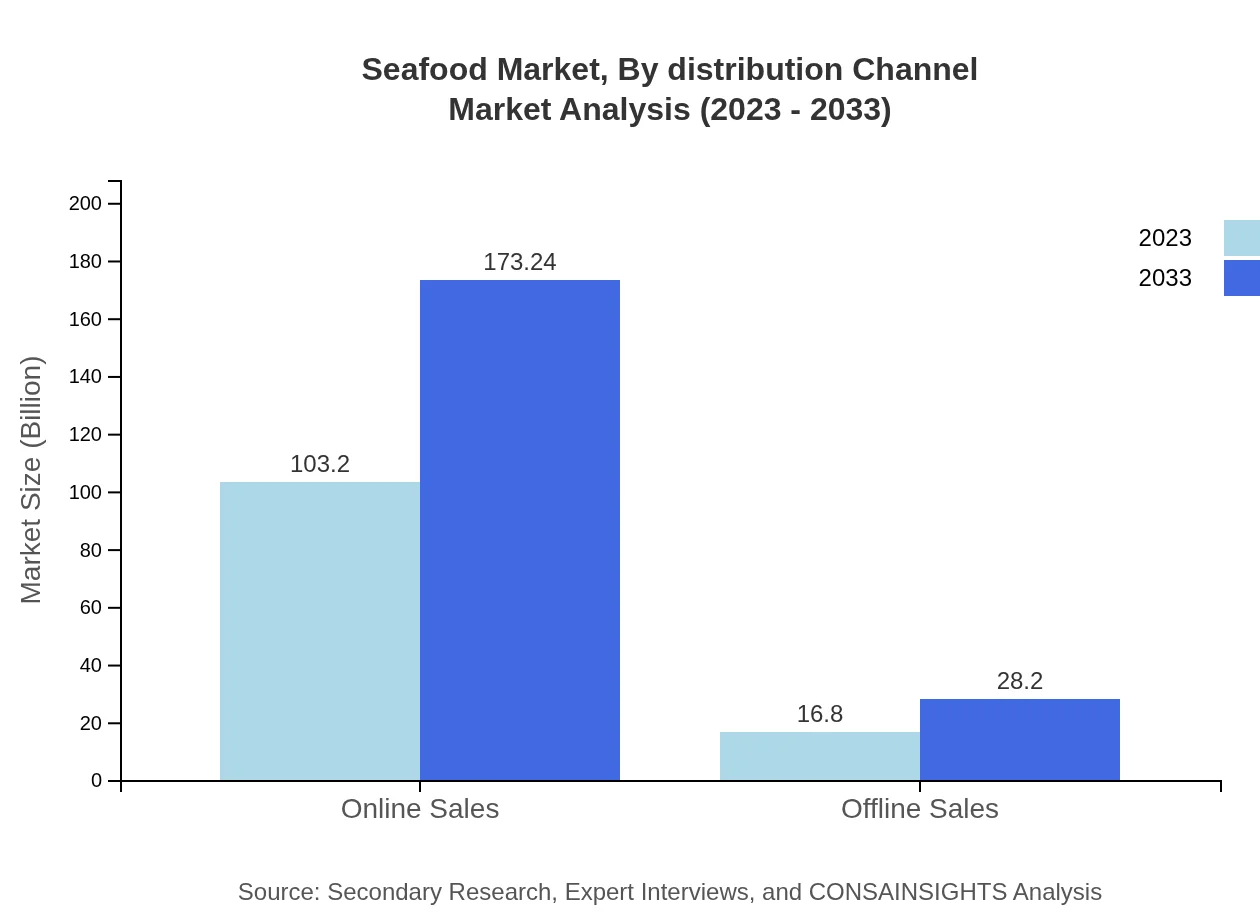
Seafood Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Seafood distribution is categorized into online and offline channels. Online sales are projected to account for a substantial share, valued at USD 103.20 billion in 2023 and anticipated to grow to USD 173.24 billion by 2033 (86% share). Meanwhile, offline retailing will also see growth, expanding from USD 16.80 billion to USD 28.20 billion as traditional retail channels adapt to meet consumer preferences.
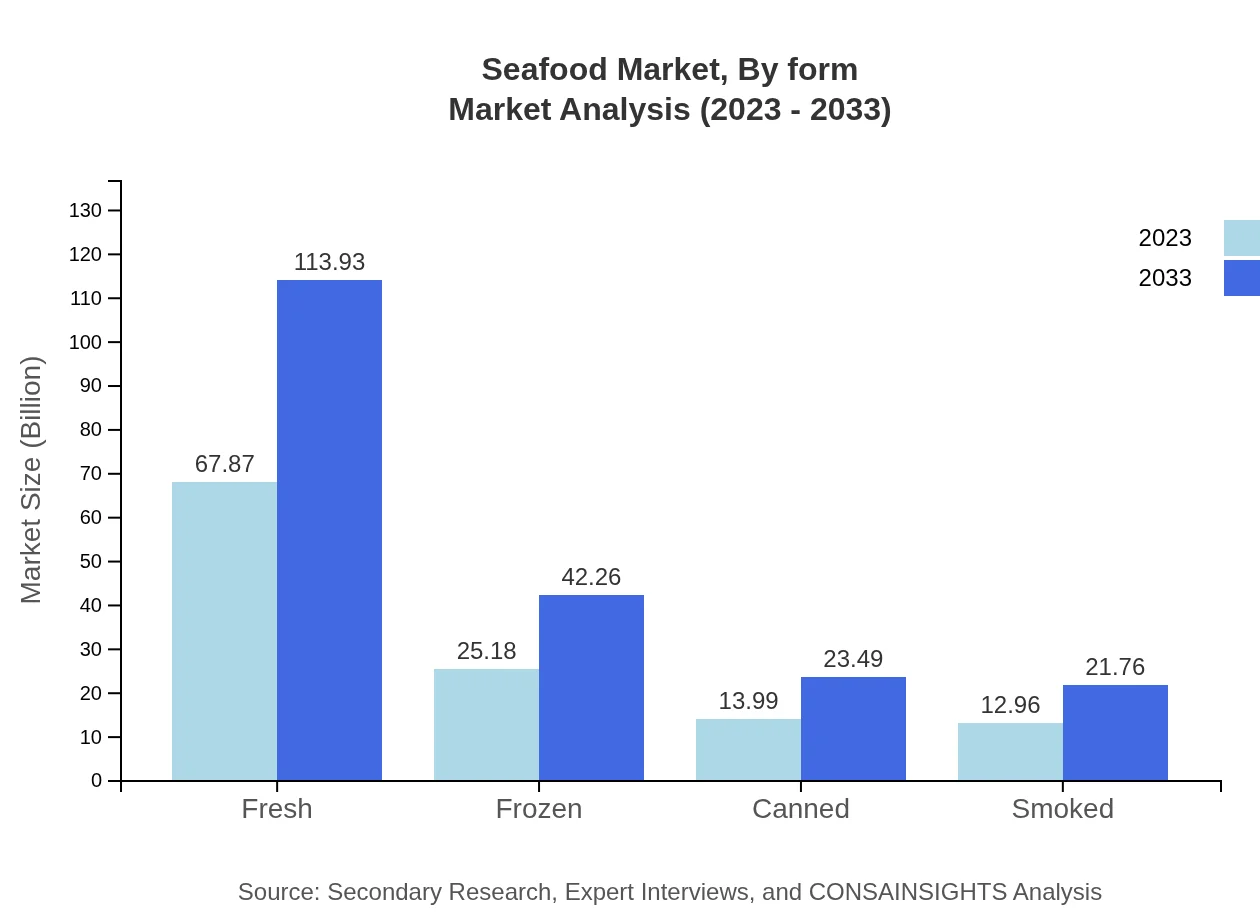
Seafood Market Analysis By Form
The market is significantly influenced by various forms such as whole seafood, fillets, and prepared seafood products. Whole seafood is expected to retain its popularity among consumers seeking freshness, while fillets and prepared options will benefit from convenience-oriented shopping trends.
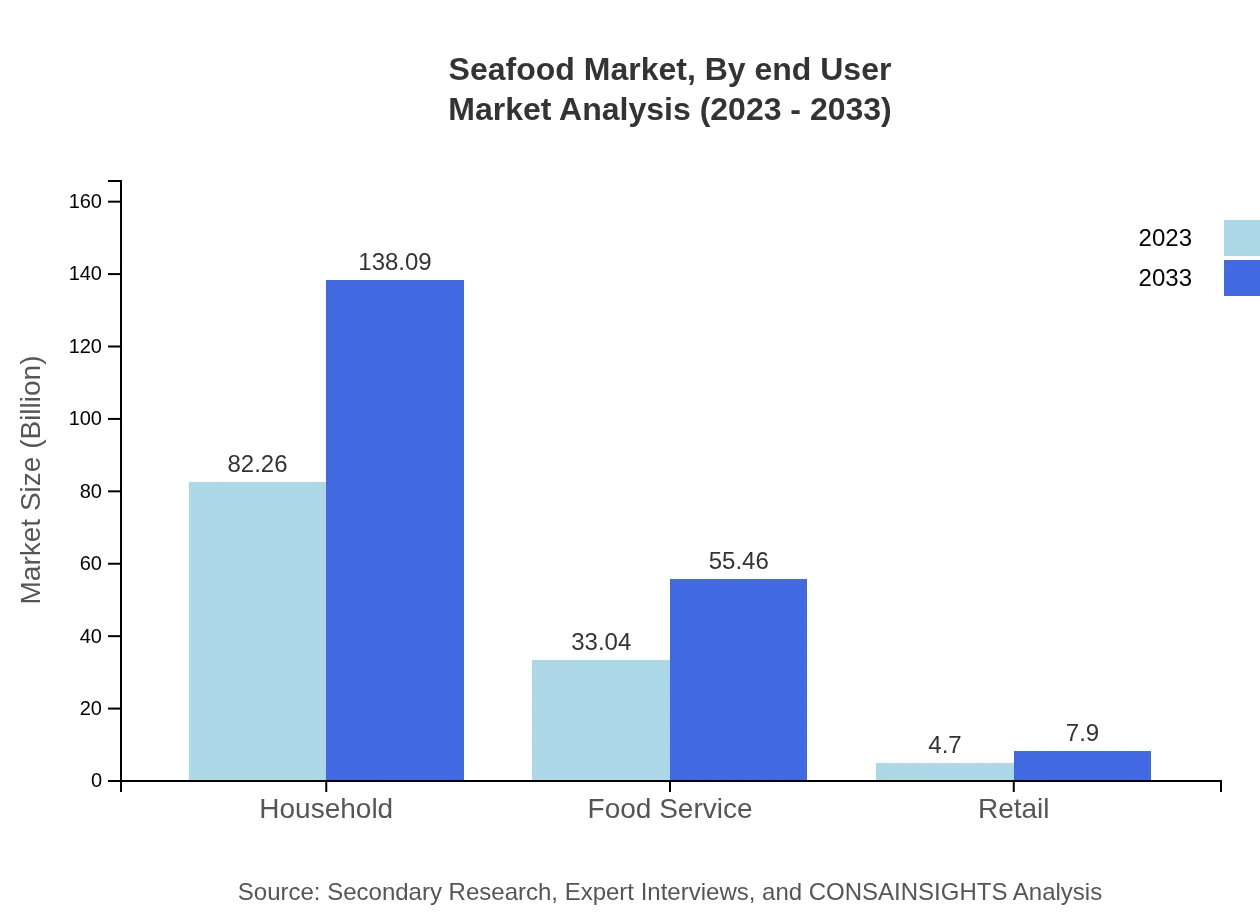
Seafood Market Analysis By End User
The seafood market is segmented by end-users into household, food service, and retail. The household segment, valued at USD 82.26 billion in 2023, shows consistent demand as consumers gravitate towards preparing fresh seafood at home. The food service segment, currently at USD 33.04 billion, is projected to grow with the rise of seafood-focused restaurants and culinary innovation.
Seafood Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Seafood Industry
Maruha Nichiro Corporation:
A leading global seafood supplier, Maruha Nichiro is renowned for its innovations in aquaculture and sustainable fishing practices. The company excels in delivering a diverse range of seafood products.Thai Union Group:
Renowned for its extensive portfolio in canned seafood, Thai Union Group focuses on sustainable sourcing and innovation, marking its significant impact on the global seafood industry.Domsea Fisheries:
An emerging player specialized in sustainable aquaculture, Domsea Fisheries is recognized for its high-quality fish products and commitment to environmental stewardship.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of seafood?
The seafood market is projected to reach approximately $120 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2%. This growth is driven by increasing consumer demand for protein-rich diets and sustainable sourcing practices.
What are the key market players or companies in this seafood industry?
Key players in the seafood industry include major companies like Thai Union Group PLC, Marine Harvest, and Nippon Suisan Kaisha. These companies lead the market through innovative product offerings, sustainability initiatives, and extensive distribution networks.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the seafood industry?
Growth in the seafood industry is primarily driven by rising health consciousness among consumers, increasing global population, and enhanced availability of seafood products. Additionally, sustainability trends and innovations in aquaculture are pivotal.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the seafood market?
The fastest-growing region in the seafood market is projected to be North America, with market growth from $40.24 billion in 2023 to $67.54 billion by 2033. Asia Pacific also shows significant growth, driven by rising middle-class consumption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the seafood industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market reports for the seafood industry, providing clients with deeply researched data customized to specific geographical regions, market segments, and consumer trends to support strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this seafood market research project?
From the seafood market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports covering market dynamics, trend analysis, competitive landscape, consumer insights, forecasts, and segment-specific data including fresh, frozen, canned, and smoked seafood.
What are the market trends of seafood?
Market trends in seafood include a shift towards sustainable sourcing, increasing preference for fresh and frozen products, and growing e-commerce sales. Innovations in packaging and readiness to eat meals are also on the rise within consumer preferences.