3d Food Printing Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-food-printing
3d Food Printing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 3D food printing market, covering key trends, technological advancements, and forecasts for 2023 to 2033. It aims to deliver insights into market size, growth factors, industry leaders, and regional performances.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
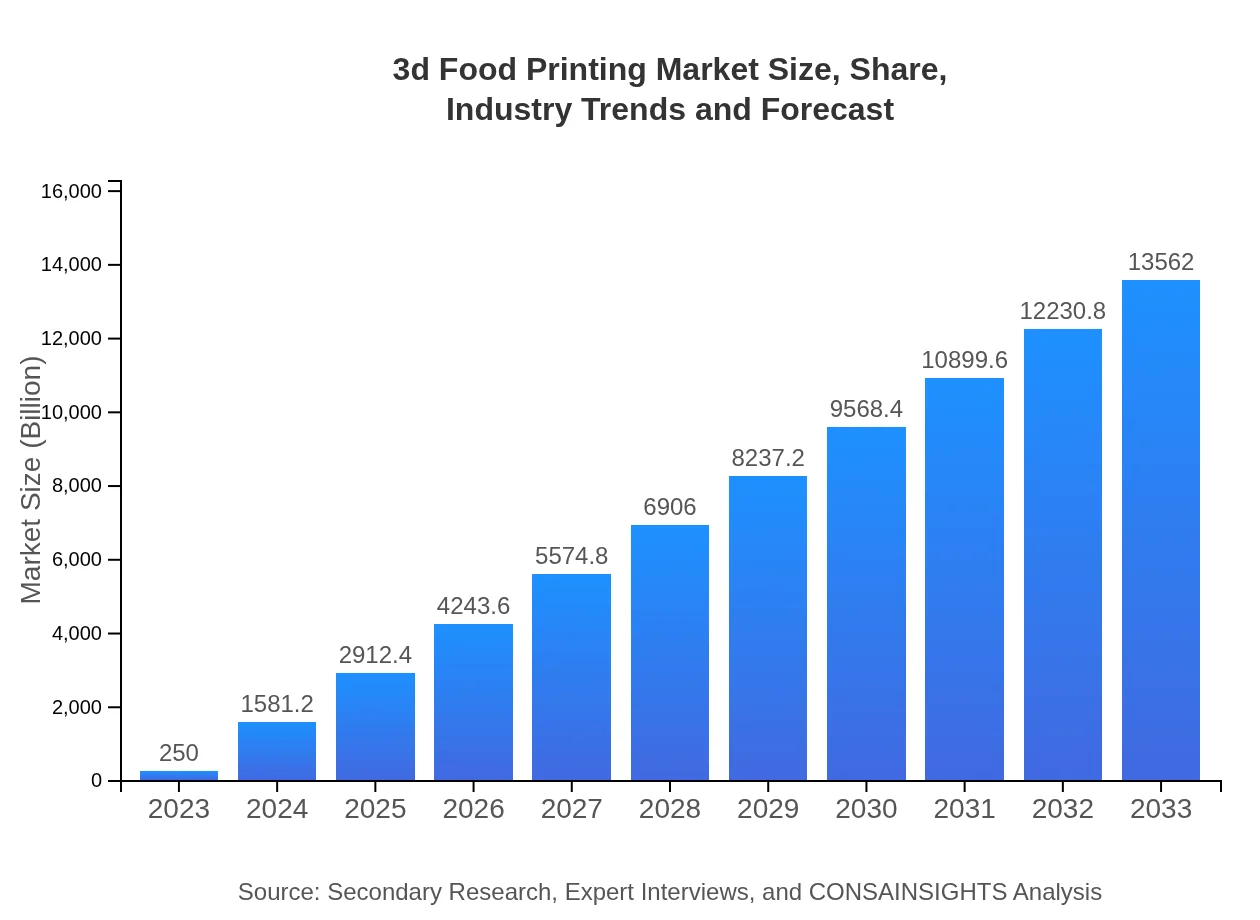
| 2023 Market Size | $250.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 45% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13562.00 Million |
| Top Companies | 3D Systems Corporation, Natural Machines, BeeHex, ByFlow, Redefine Meat |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3d Food Printing Market Overview
Customize 3d Food Printing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Food Printing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Food Printing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Food Printing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 3d Food Printing market in 2023?
3d Food Printing Industry Analysis
3d Food Printing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3d Food Printing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Food Printing Market Report:
Europe's 3D food printing market is valued at $68.60 million in 2023, projected to grow to $3,721.41 million by 2033. Countries in Europe are adopting food printing technology at a rapid rate, influenced by trendsetters in the culinary scene and stringent food regulations encouraging innovation.Asia Pacific 3d Food Printing Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market size for 3D food printing is estimated at $50.80 million in 2023, projected to escalate to $2,755.80 million by 2033. The region's growth is driven by increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and a growing interest in innovative culinary experiences.North America 3d Food Printing Market Report:
North America leads the 3D food printing market with a size of $81.90 million in 2023, expected to reach $4,442.91 million by 2033. The U.S. market drives this growth, supported by high consumer demand for personalized food and notable advancements in food technology.South America 3d Food Printing Market Report:
The South American market for 3D food printing currently stands at $22.23 million in 2023, anticipated to reach $1,205.66 million by 2033. The adoption of advanced food technologies is on the rise, driven by local food manufacturers seeking competitive advantage.Middle East & Africa 3d Food Printing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market currently stands at $26.47 million with growth expected to reach $1,436.22 million by 2033. The growth is fueled by an increasing focus on food technology innovations and the need for efficient food preparation methods.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
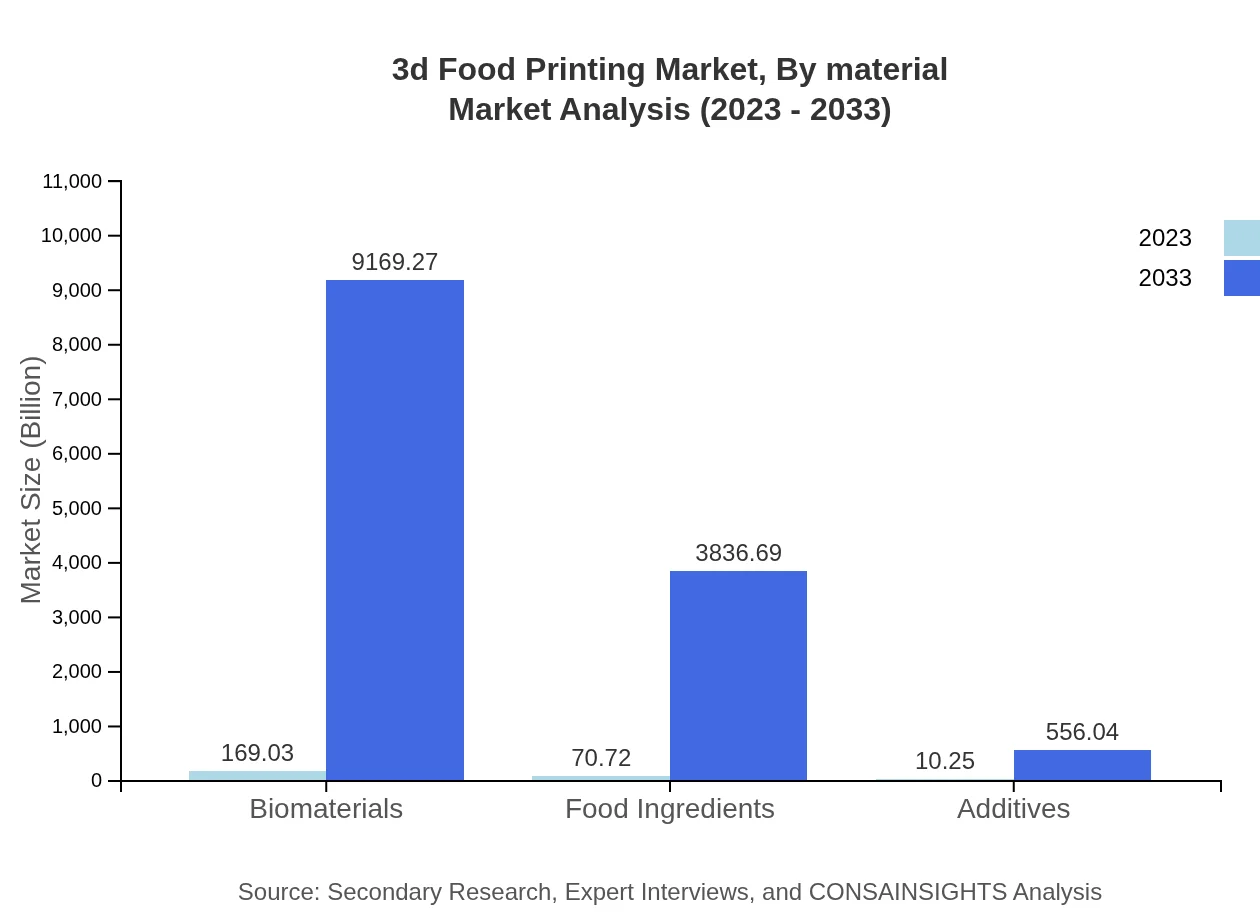
3d Food Printing Market Analysis By Material
The primary materials utilized in 3D food printing include protein-based, carbohydrate-based, and fat-based ingredients. As of 2023, these materials collectively represent a substantial segment of the market, with continuous improvements enhancing their applicability and performance in various culinary applications.
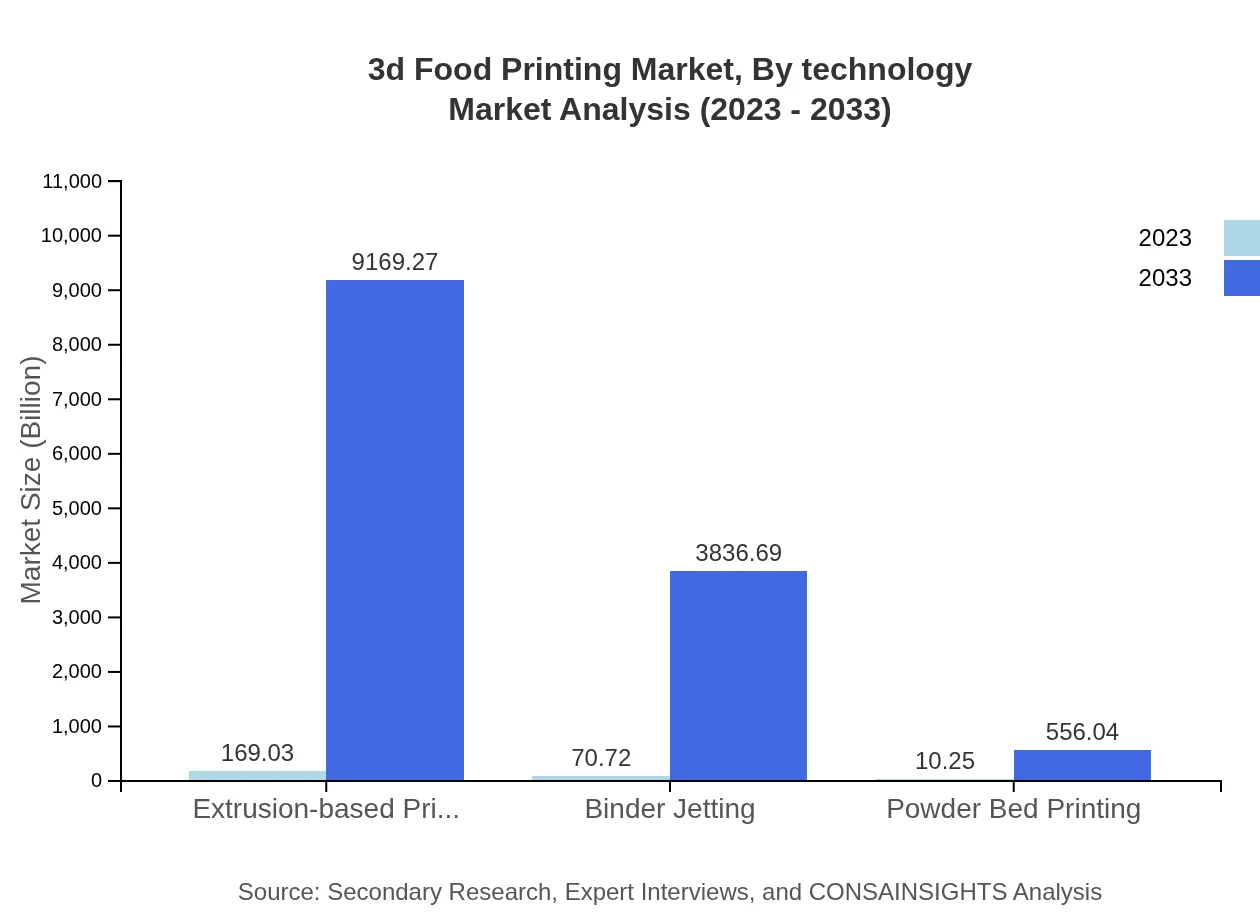
3d Food Printing Market Analysis By Technology
Extrusion-based printing remains the dominant technology, accounting for a significant share of the market. Binder jetting technology is also gaining traction, contributing to the diverse applications of 3D food printing in food customization and high-volume production settings.
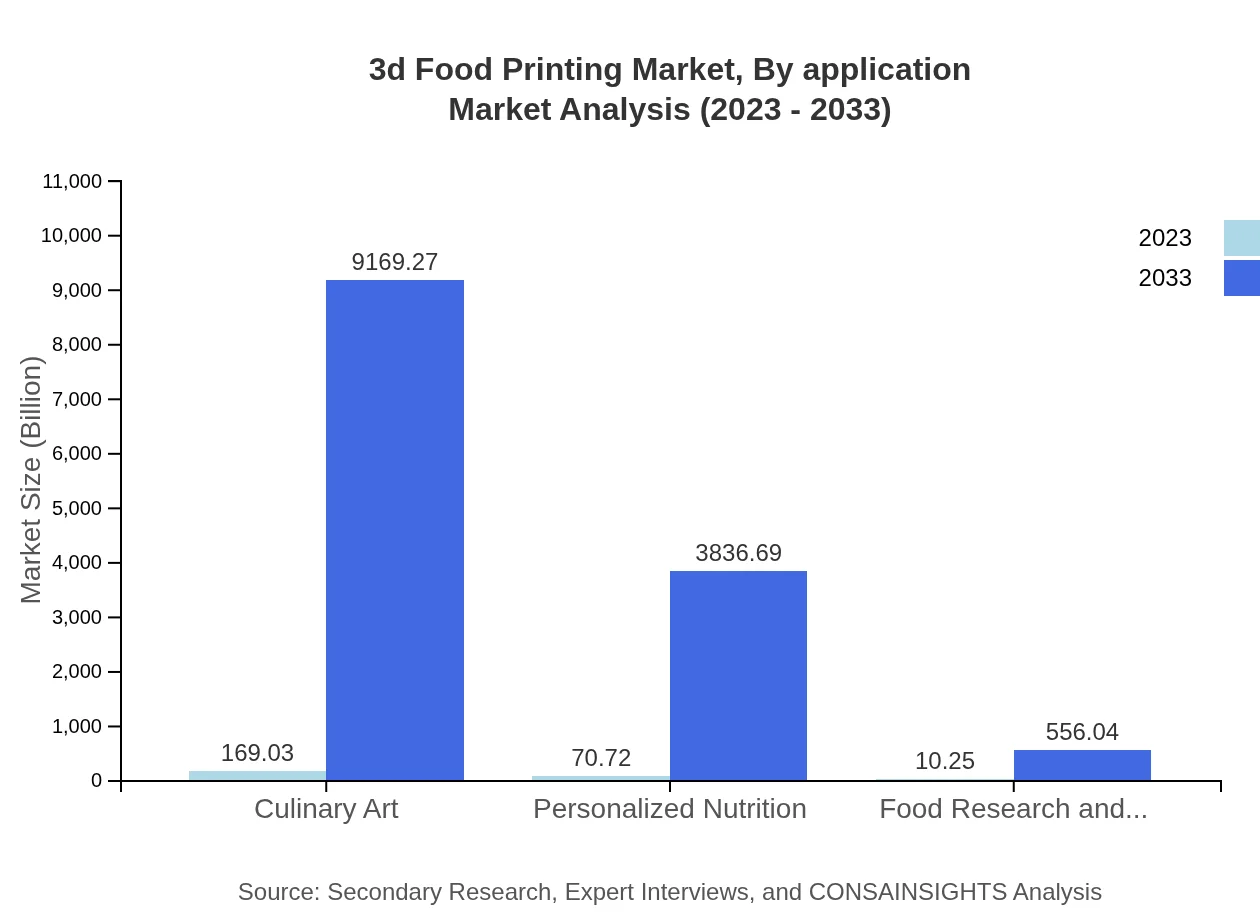
3d Food Printing Market Analysis By Application
The application of 3D food printing spans several domains such as personalized nutrition, food art, and culinary experimentation. The growing trend toward tailor-made diets and health concerns supports accelerated developments within this sector, with potential growth in institutional and commercial settings.
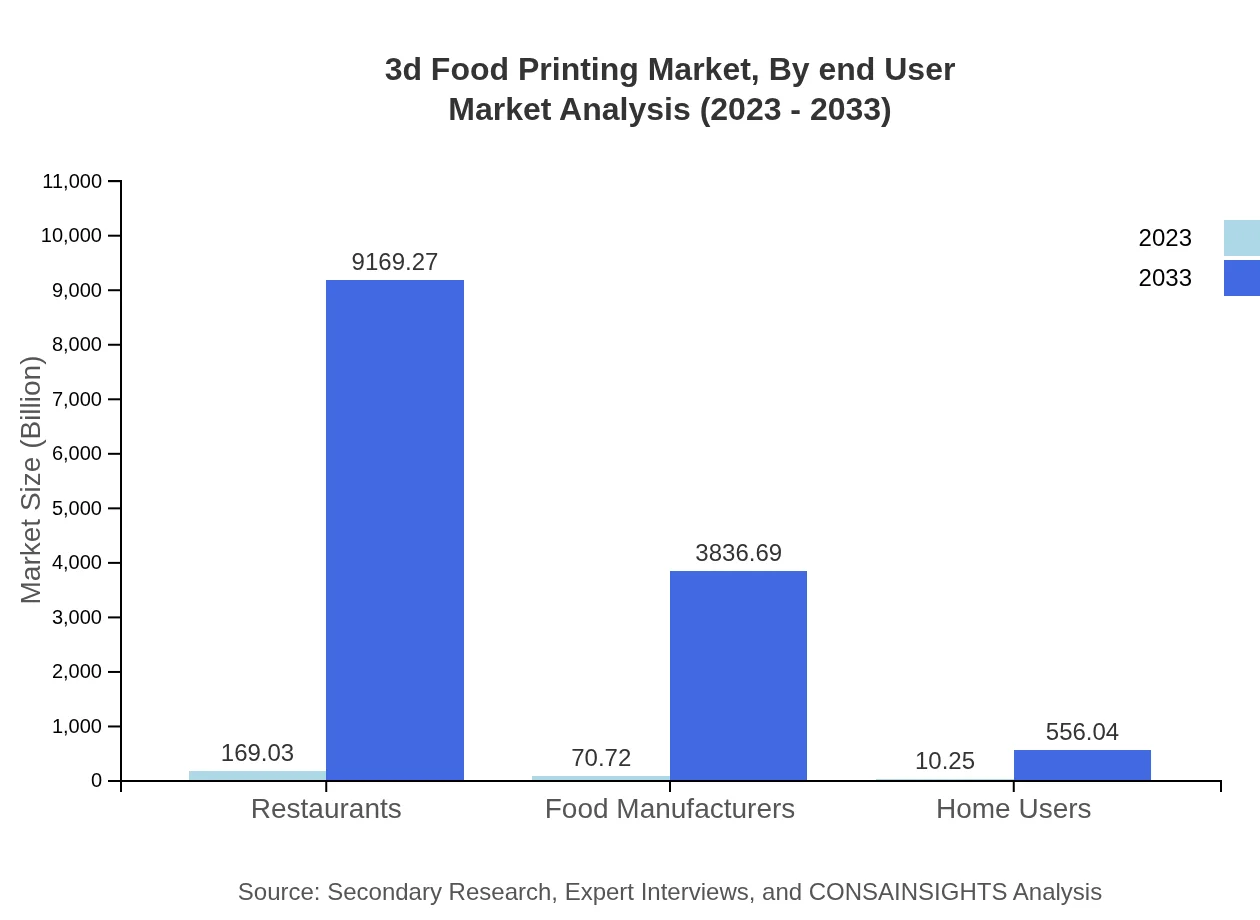
3d Food Printing Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users include restaurants, food manufacturers, and home users. Restaurants account for a significant market share as they adopt bespoke food offerings to enhance customer experiences. Food manufacturers, recognizing the promotional benefits and improved production processes, are increasingly integrating 3D food printing technology.
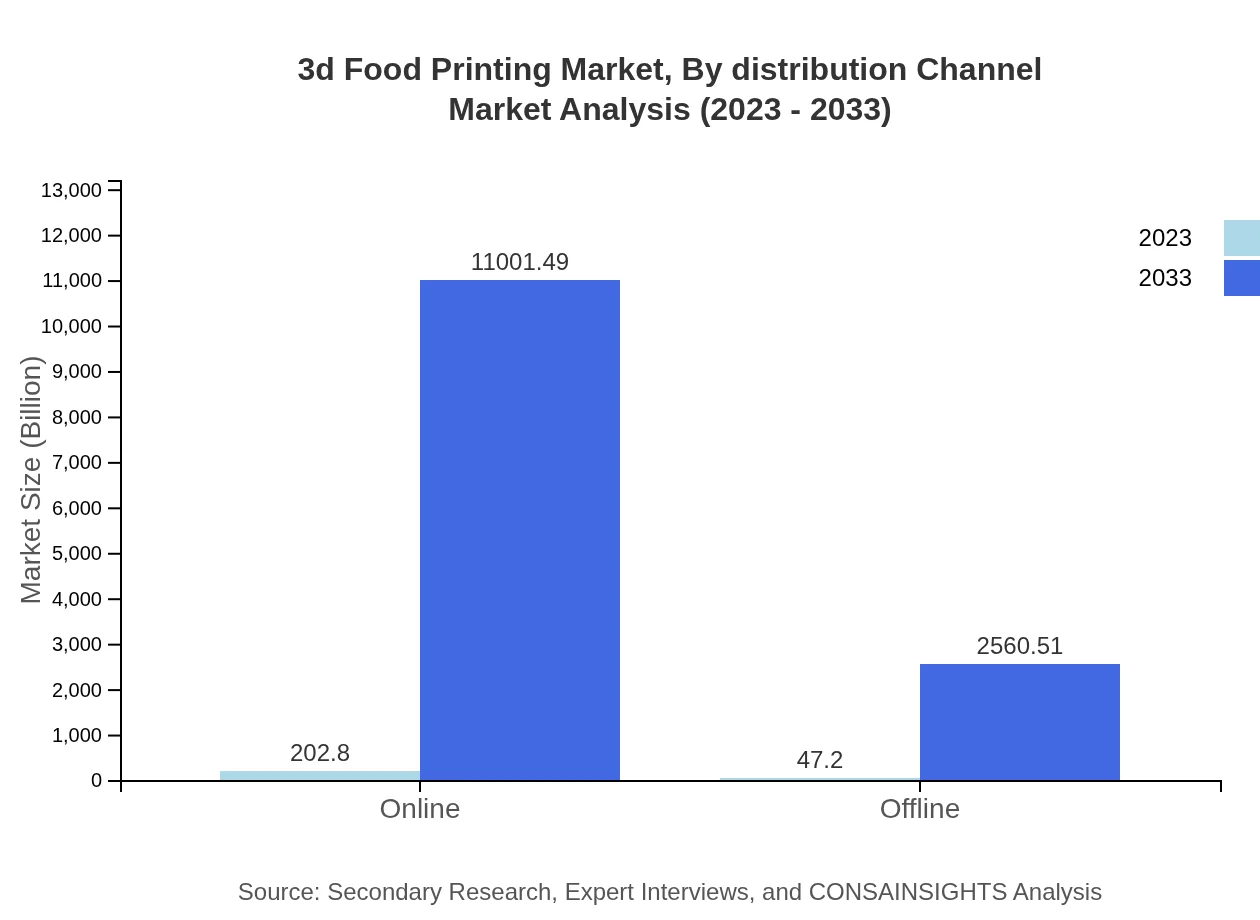
3d Food Printing Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The market's distribution channels comprise online and offline segments. The online distribution channel dominates, reflecting the growing trend of e-commerce in the food sector. With increasing customer trust in purchasing food products online, this channel is expected to grow substantially in the upcoming years.
3d Food Printing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3d Food Printing Industry
3D Systems Corporation:
A pioneer in 3D printing solutions, offering an innovative range of 3D printers specifically focused on the food industry.Natural Machines:
Known for their Foodini machine, which allows users to create personalized meals with a variety of ingredients.BeeHex:
Specializes in developing food printers with applications in both commercial kitchens and space food technology.ByFlow:
Offers the Focus 3D printer, enabling chefs and home users to create intricate food designs tailored to consumer needs.Redefine Meat:
Focuses on plant-based meat alternatives, utilizing 3D printing to improve texture and flavor profiles.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3D Food Printing?
The market size for 3D food printing is currently valued at approximately $250 million. With a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 45%, it is anticipated to see significant expansion over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the 3D food printing industry?
Key players in the 3D food printing market include major companies like Nestle, 3D System Corporation, and DowDuPont, which are at the forefront of technology and innovation, driving advancements in food production.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3D food printing industry?
The growth of 3D food printing is driven by factors such as rising demand for personalized nutrition, advancements in food technology, sustainability concerns, and increasing investments in the food tech sector.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3D food printing market?
North America is the fastest-growing region, with market size projected to grow from $81.90 million in 2023 to approximately $4442.91 million by 2033, reflecting strong innovation and investment.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the 3D food printing industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers customized market report data tailored specifically to the 3D food printing industry, allowing businesses to access in-depth insights and projections.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3D food printing market research project?
Deliverables may include comprehensive reports detailing market analysis, segmentation, competitive landscape, growth forecasts, and actionable insights based on extensive research.
What are the market trends of 3D food printing?
Market trends in 3D food printing indicate a surge in demand for customization, eco-friendly materials, and integration with culinary arts, highlighting the technology's adaptability and potential.