Cloud Security In Banking Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cloud-security-in-banking
Cloud Security In Banking Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cloud Security in Banking market, encompassing key insights, industry trends, forecasts, and growth opportunities from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
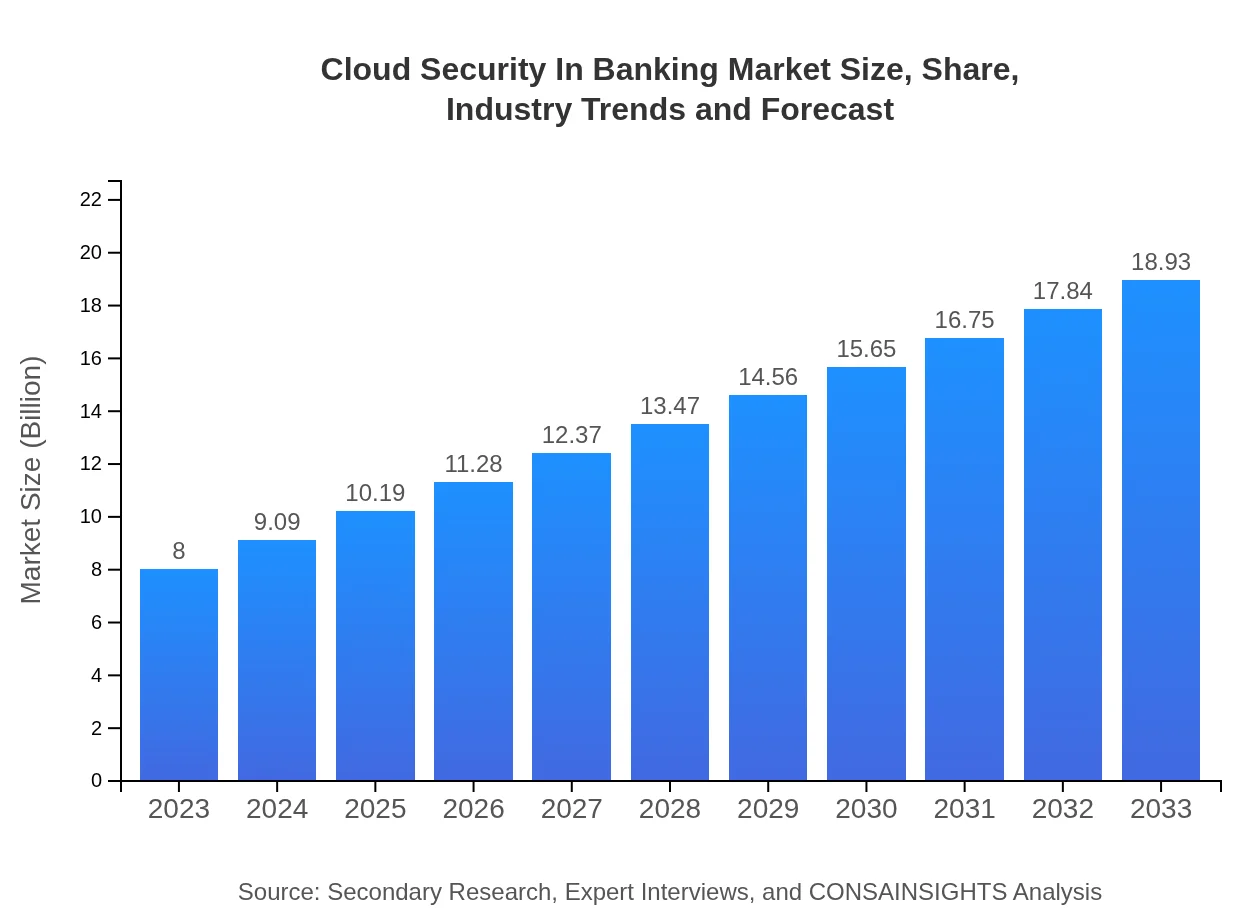
| 2023 Market Size | $8.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.93 Billion |
| Top Companies | IBM Security, Microsoft Azure, Cisco Systems, McAfee, Oracle Cloud |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cloud Security In Banking Market Overview
Customize Cloud Security In Banking Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cloud Security In Banking market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cloud Security In Banking's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cloud Security In Banking
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cloud Security In Banking market?
Cloud Security In Banking Industry Analysis
Cloud Security In Banking Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cloud Security In Banking Market Report:
In Europe, the market size was approximately $2.69 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $6.36 billion by 2033. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR is a major driver, encouraging banks to adopt rigorous cloud security measures to safeguard customer data.Asia Pacific Cloud Security In Banking Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Cloud Security in Banking market was valued at $1.50 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $3.55 billion by 2033. Factors driving this growth include increased investments in digital banking and a heightened focus on cybersecurity among financial institutions to combat rising cyber threats.North America Cloud Security In Banking Market Report:
North America remains a key market for Cloud Security in Banking, with a value of $2.61 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $6.18 billion by 2033. The growth is accelerated by the presence of established financial institutions, regulatory mandates, and significant investments in advanced cybersecurity technologies.South America Cloud Security In Banking Market Report:
South America has shown a burgeoning interest in cloud security, with the market estimated at $0.78 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $1.84 billion by 2033. The growing adoption of cloud-based infrastructures aligns with the region's need to enhance data protection amidst increasing regulatory scrutiny.Middle East & Africa Cloud Security In Banking Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is smaller but increasingly important, expected to grow from $0.42 billion in 2023 to $1.00 billion by 2033. The rise in digital banking and governmental initiatives to bolster cybersecurity frameworks are expected to drive market growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
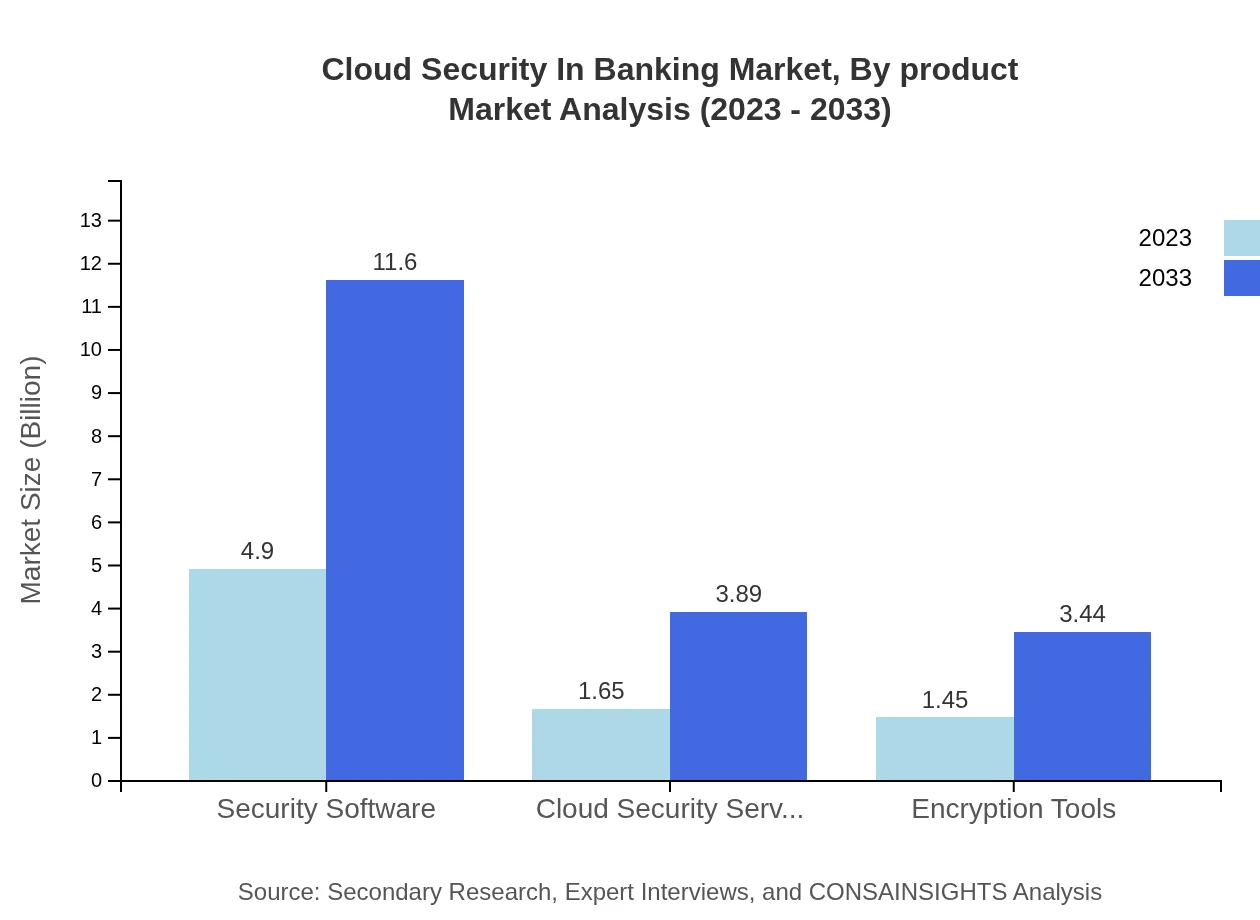
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis By Product
The product segmentation highlights security software as a significant component, valued at $4.90 billion in 2023, set to grow to $11.60 billion by 2033. Cloud security services and encryption tools are also significant, with respective market sizes of $1.65 billion and $1.45 billion in 2023. The rising complexity of cyber threats emphasizes the importance of robust security tools in the banking sector.
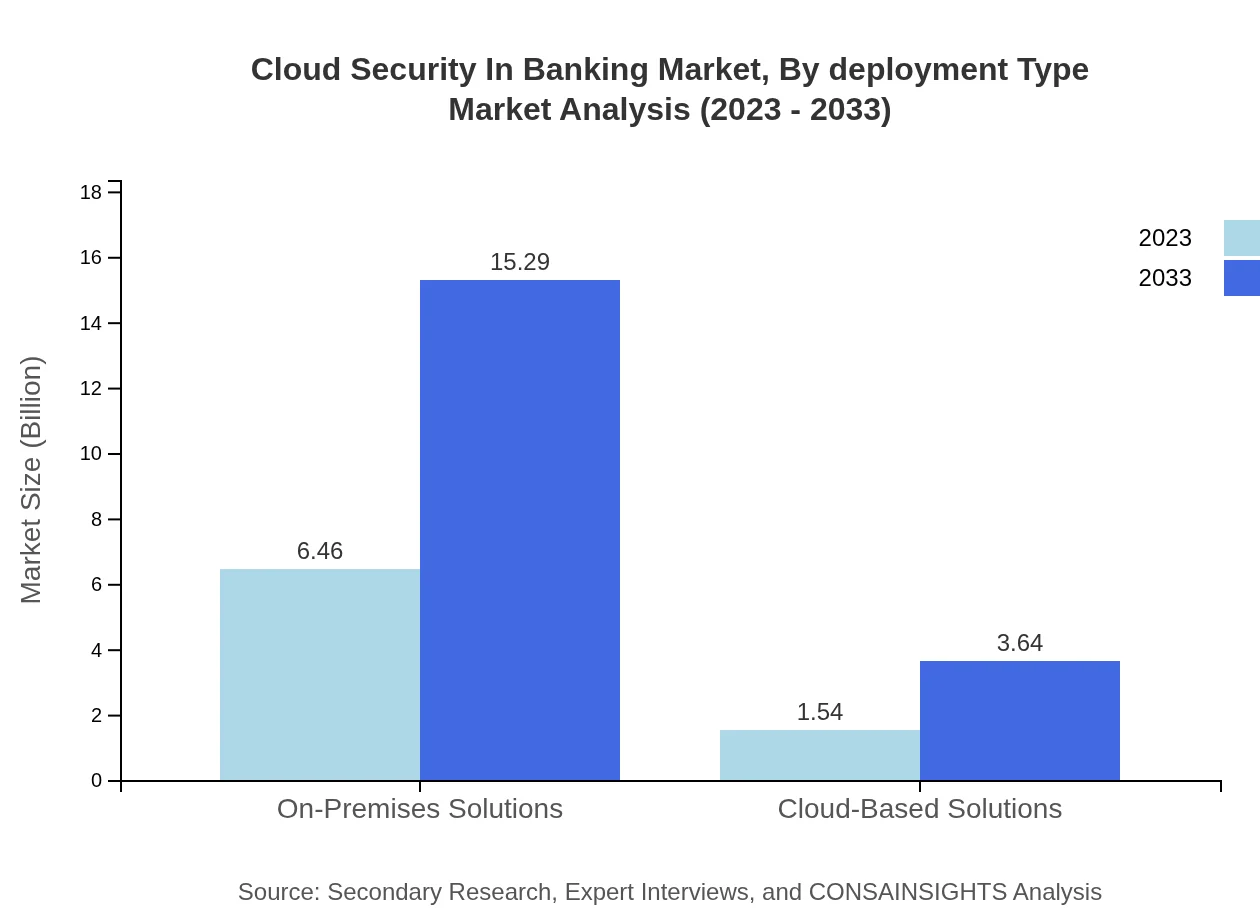
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Deployment types include on-premises and cloud-based solutions. On-premises solutions dominate, valued at $6.46 billion in 2023, while cloud-based solutions are anticipated to grow from $1.54 billion to $3.64 billion by 2033. The shift towards cloud solutions reflects the banking sector's move towards increased scalability and flexibility.
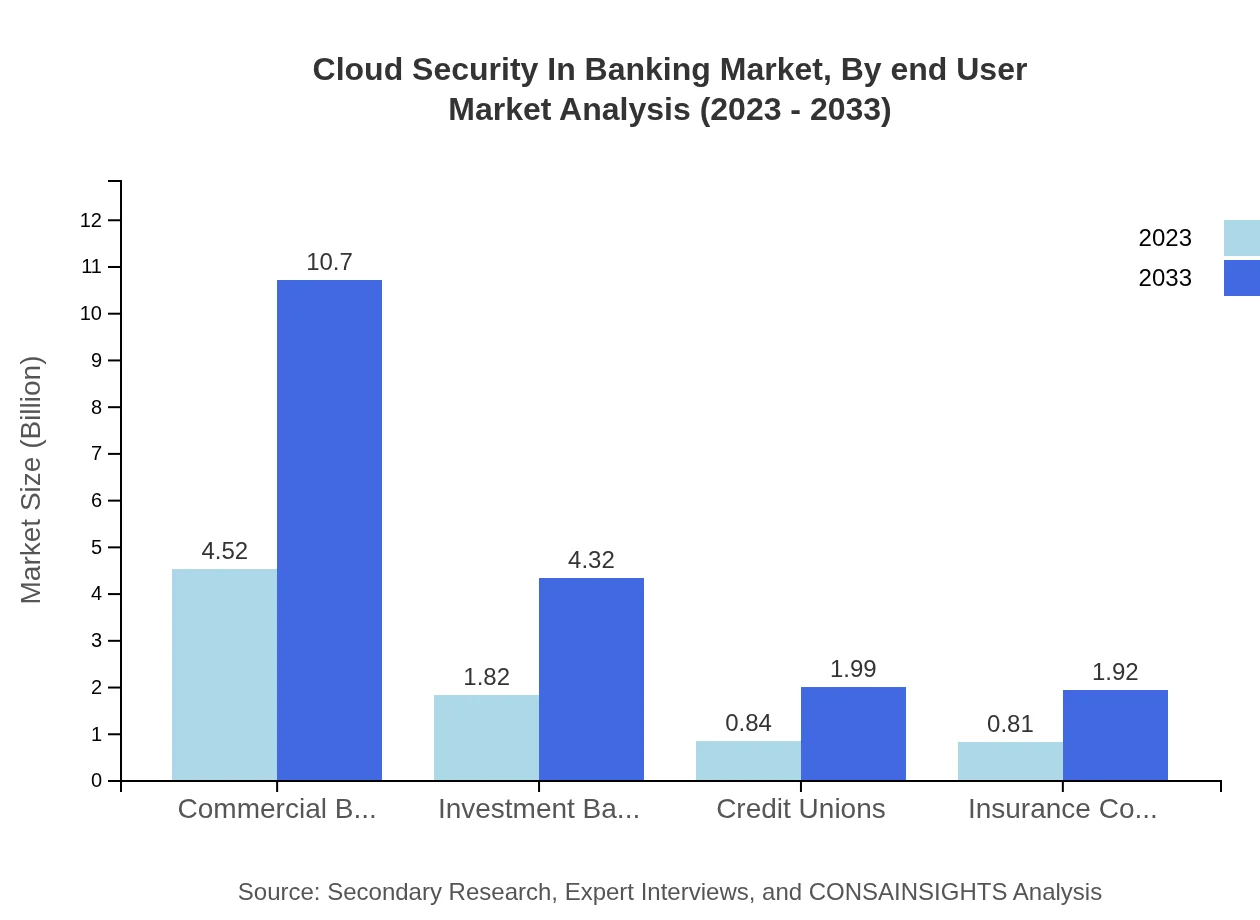
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis By End User
The banking sector's end-users comprise commercial banks, investment banks, credit unions, and insurance companies. Commercial banks lead the market with a size of $4.52 billion in 2023, while investment banks and credit unions hold 22.81% and 10.52% shares, respectively. This segmentation highlights the differing security requirements and adoption rates across various banking types.
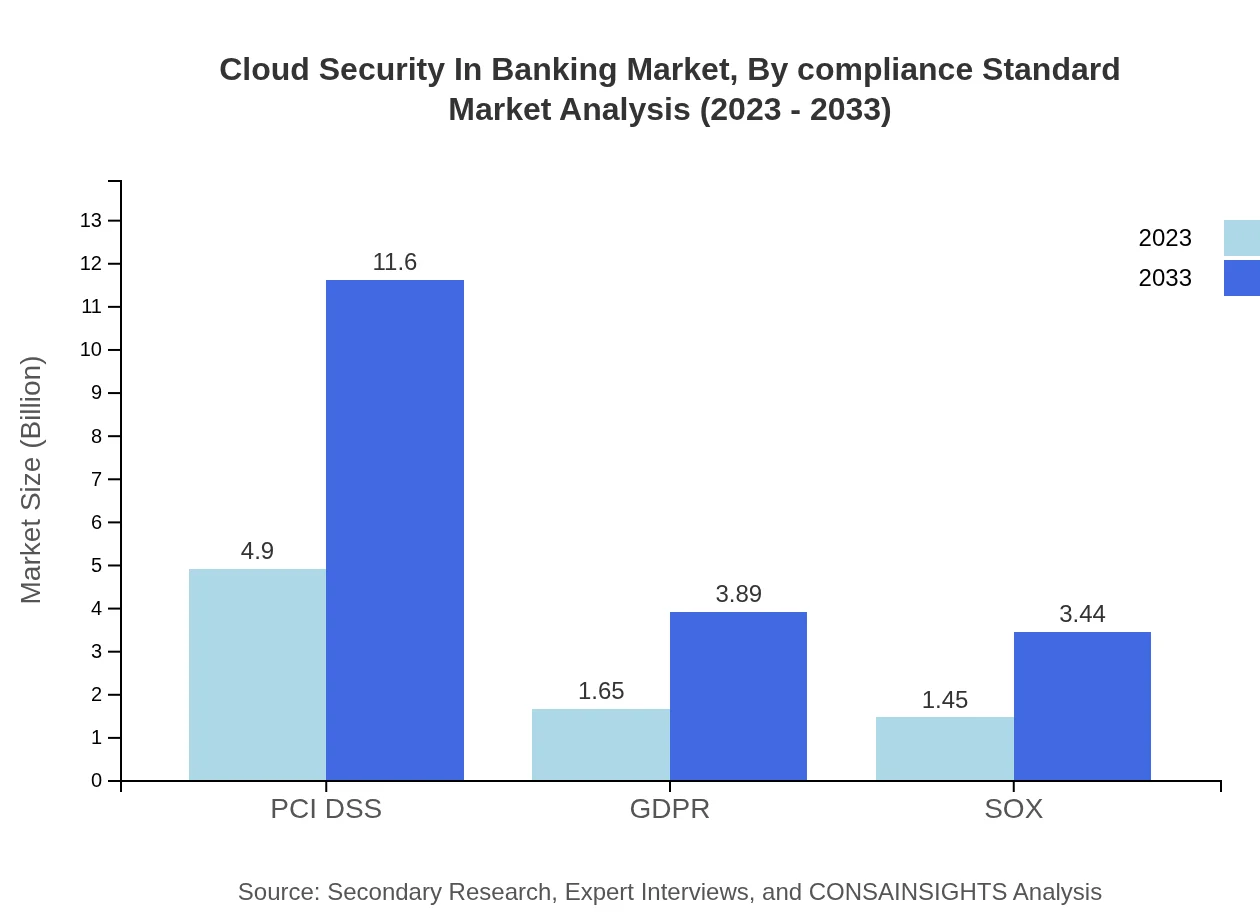
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis By Compliance Standard
Key compliance standards impacting the market include PCI DSS, GDPR, and SOX. The PCI DSS segment dominates with a market size of $4.90 billion in 2023, emphasizing the critical need for payment data protection. The growing emphasis on compliance-driven security solutions will shape future investments in cloud security among banks.
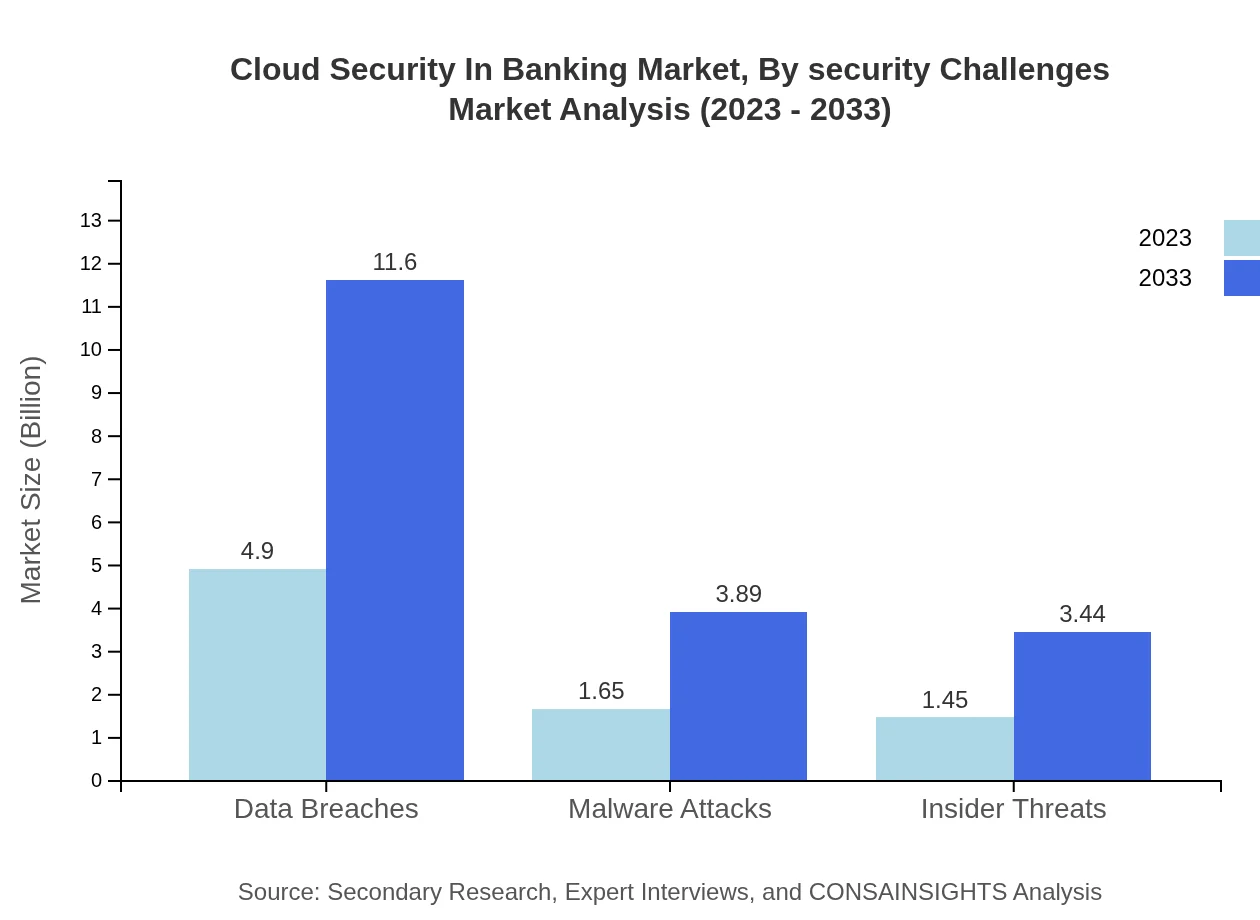
Cloud Security In Banking Market Analysis By Security Challenges
Common security challenges include combating data breaches, malware attacks, and insider threats. The data breach segment represents a notable challenge with a size of $4.90 billion in 2023, as banks increasingly face sophisticated cyber threats. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for sustaining customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Cloud Security In Banking Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cloud Security In Banking Industry
IBM Security:
IBM offers a diverse range of cloud security solutions tailored to the banking sector, emphasizing analytics-driven insights and advanced threat detection capabilities.Microsoft Azure:
Microsoft Azure provides integrated cloud security solutions that cater specifically to banks, ensuring compliance and data protection in complex digital environments.Cisco Systems:
Cisco's security solutions focus on protecting financial institutions from cyber threats with advanced security technologies and secure cloud environments.McAfee:
McAfee offers a comprehensive portfolio of security applications that are instrumental in safeguarding sensitive banking data against evolving cyber threats.Oracle Cloud:
Oracle delivers robust cloud security solutions, focusing on data protection and compliance, enabling banks to transition securely to cloud infrastructures.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Cloud Security in Banking?
The Cloud Security in Banking market is projected to reach approximately $8 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7%. This growth reflects increasing demands for enhanced security measures in the banking sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the Cloud Security in Banking industry?
Key players in the Cloud Security in Banking market include established firms that specialize in cybersecurity, cloud services, and banking technologies, contributing to the industry's evolving landscape through innovation and comprehensive security solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Cloud Security in Banking industry?
Major growth drivers include the escalating incidents of cyber threats, regulatory requirements for data protection, and the increasing adoption of cloud technology in banking operations, each pushing financial institutions to enhance their security frameworks.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Cloud Security in Banking?
The fastest-growing region in the Cloud Security in Banking market is projected to be North America, with the market size expected to increase from $2.61 billion in 2023 to $6.18 billion by 2033, reflecting significant investment in security solutions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Cloud Security in Banking industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the Cloud Security in Banking industry, tailored to meet specific client needs and enabling stakeholders to make informed market decisions based on precise insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this Cloud Security in Banking market research project?
Deliverables from the Cloud Security in Banking market research project typically include comprehensive reports, market trend analyses, competitive landscape assessments, and projections that aid strategic planning and decision-making processes.
What are the market trends of Cloud Security in Banking?
Current market trends in Cloud Security in Banking indicate a shift towards integration of advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning, increased regulatory compliance, and a growing focus on multi-cloud security strategies as banks evolve their operations.