Food Automation Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: food-automation
Food Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Food Automation market from 2023 to 2033, including market trends, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts. It covers critical data, insights on growth projections, challenges, and primary players influencing this industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
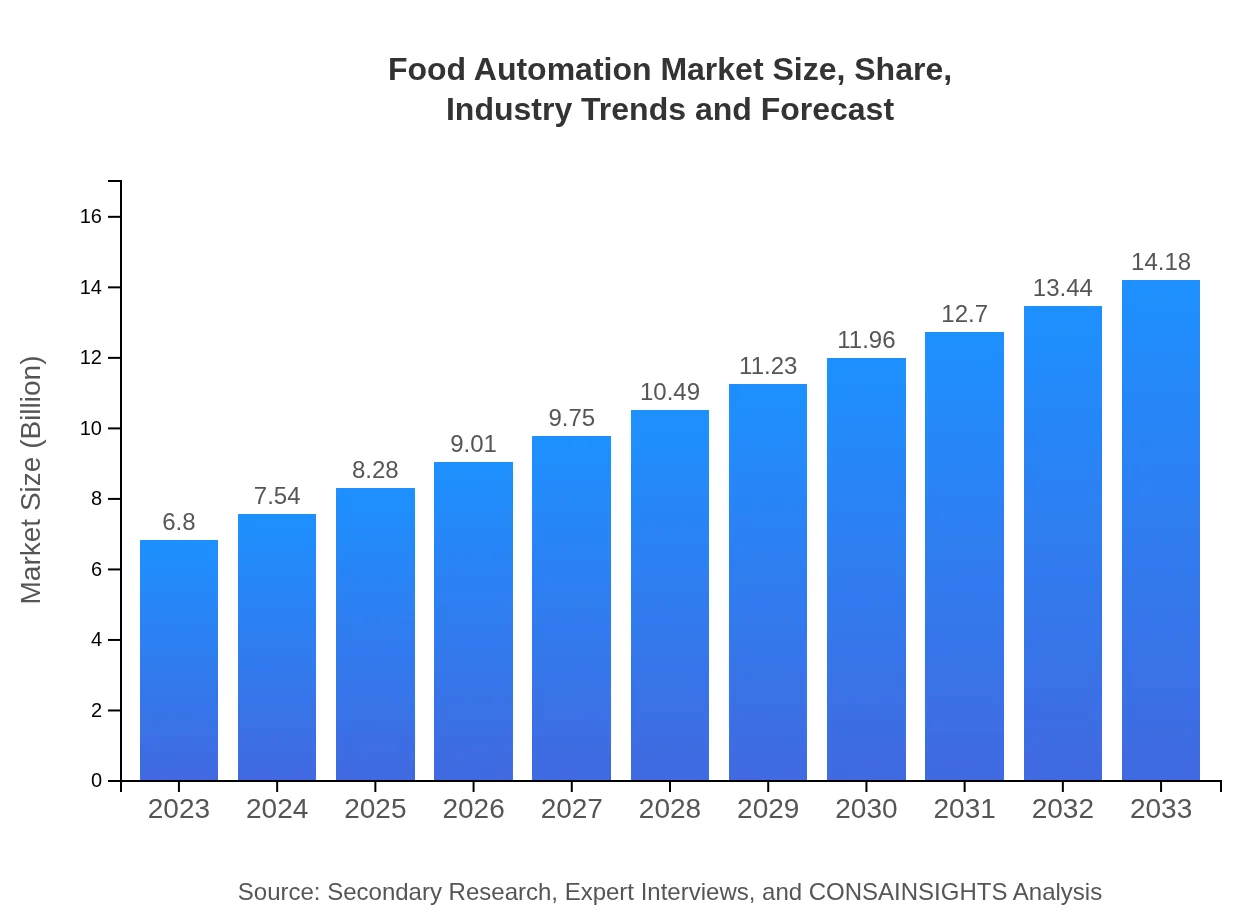
| 2023 Market Size | $6.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $14.18 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, ABB Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Food Automation Market Overview
Customize Food Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Food Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Food Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Food Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Food Automation market in 2023?
Food Automation Industry Analysis
Food Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Food Automation Market Report:
Europe presents a robust market with an estimated size of $2.01 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $4.18 billion by 2033. Regulatory pressures and a push towards sustainability are strong drivers of market growth.Asia Pacific Food Automation Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Food Automation market is estimated at $1.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $2.87 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in food standards and quality assurance systems.North America Food Automation Market Report:
In North America, the Food Automation market is estimated to be $2.39 billion in 2023, with expectations to rise to $4.98 billion by 2033. Strong technological adoption and the presence of key market players bolster growth.South America Food Automation Market Report:
The South American market for Food Automation is valued at $0.30 billion in 2023, with projections reaching $0.62 billion by 2033. Factors such as population growth and urbanization trends contribute to the upward trajectory.Middle East & Africa Food Automation Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is valued at $0.73 billion for 2023, expected to expand to $1.53 billion by 2033. The focus on improving food supply chains is a primary growth facilitator in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
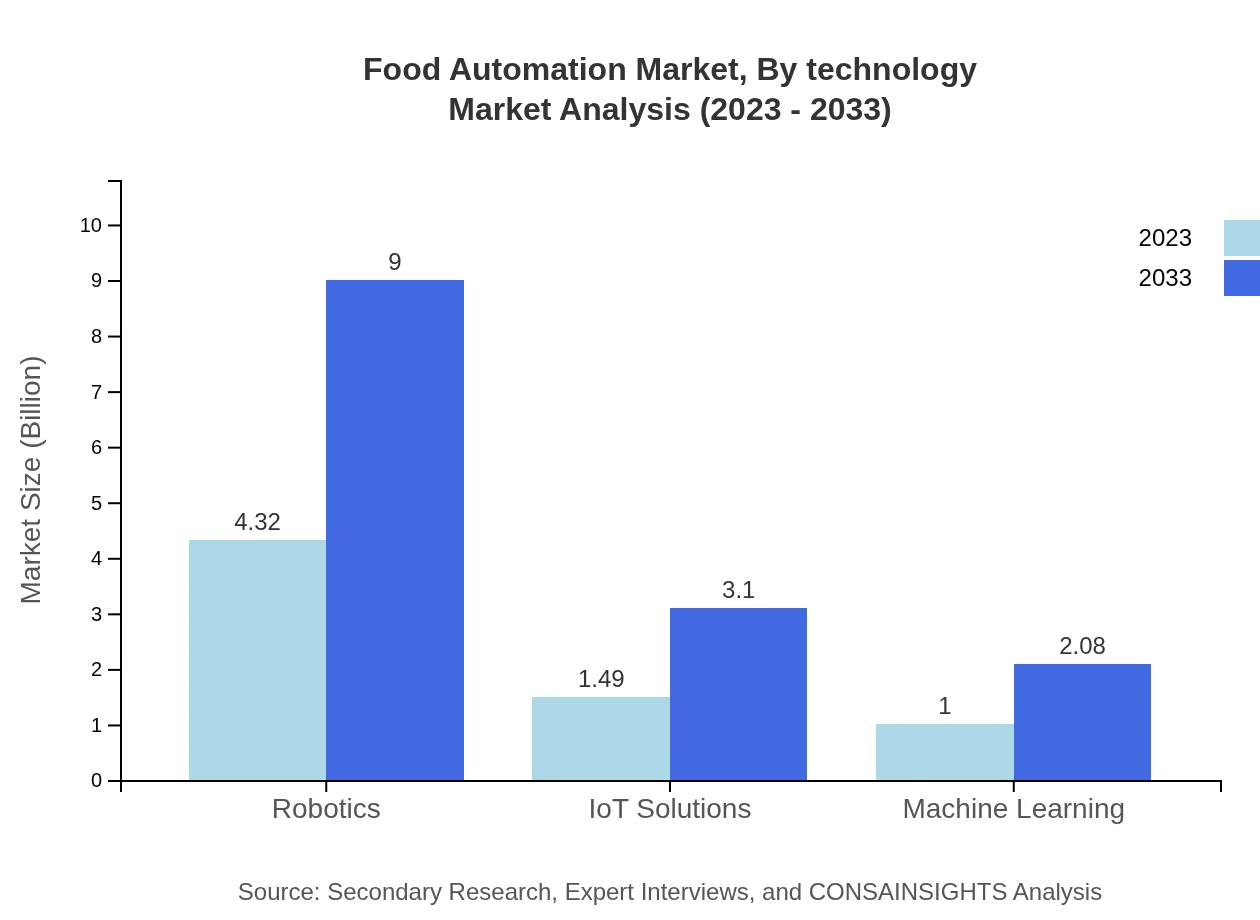
Food Automation Market Analysis By Technology
This segment includes innovations in robotics, IoT solutions, machine learning, and fully automated systems. Robotics and IoT have shown significant growth, driven by the introduction of smart food processing systems and automated handling, which increase production efficiency.
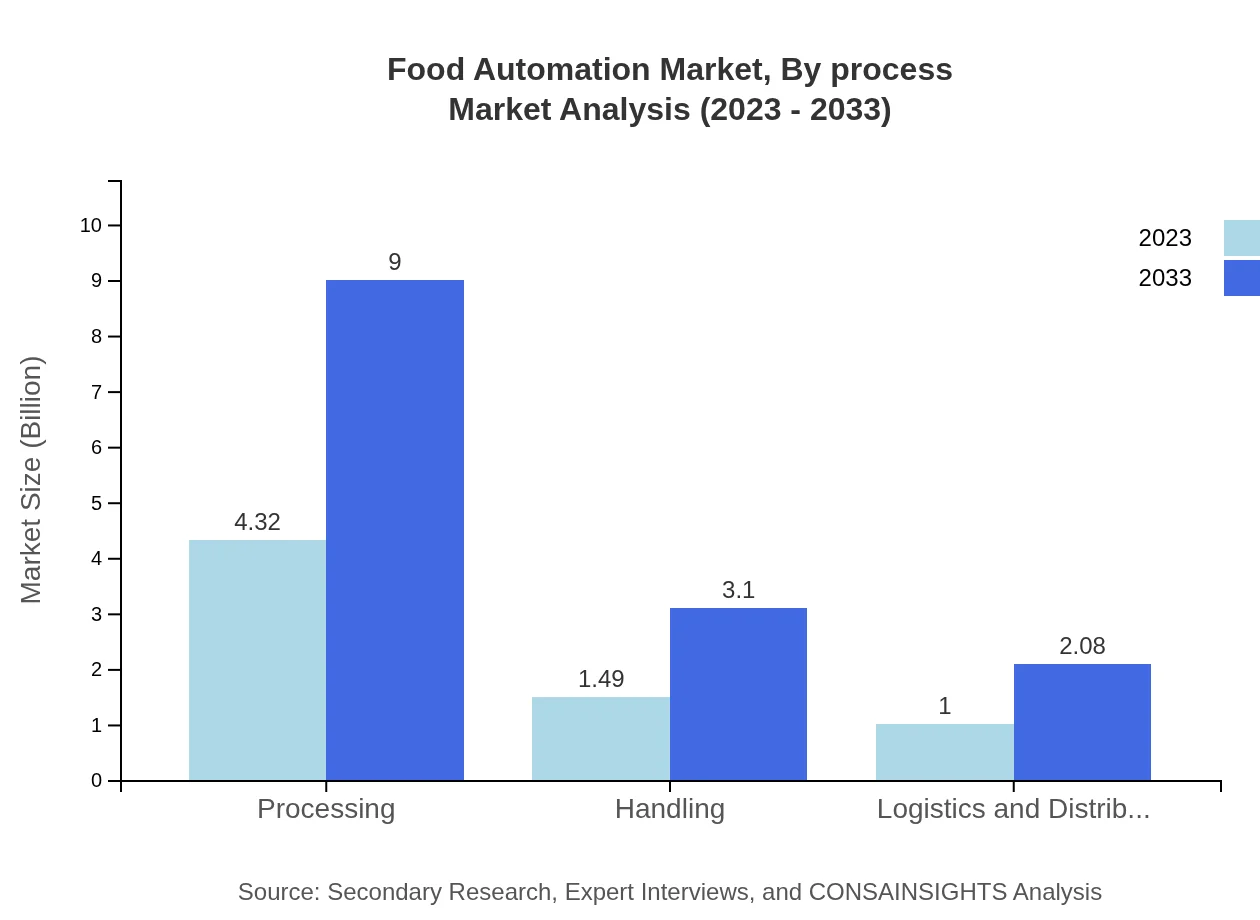
Food Automation Market Analysis By Process
The processing segment dominates, projected to reach $9.00 billion by 2033 from $4.32 billion in 2023. The handling and logistics segments are also significant, with growth driven by demand for efficiency and reduced labor costs.
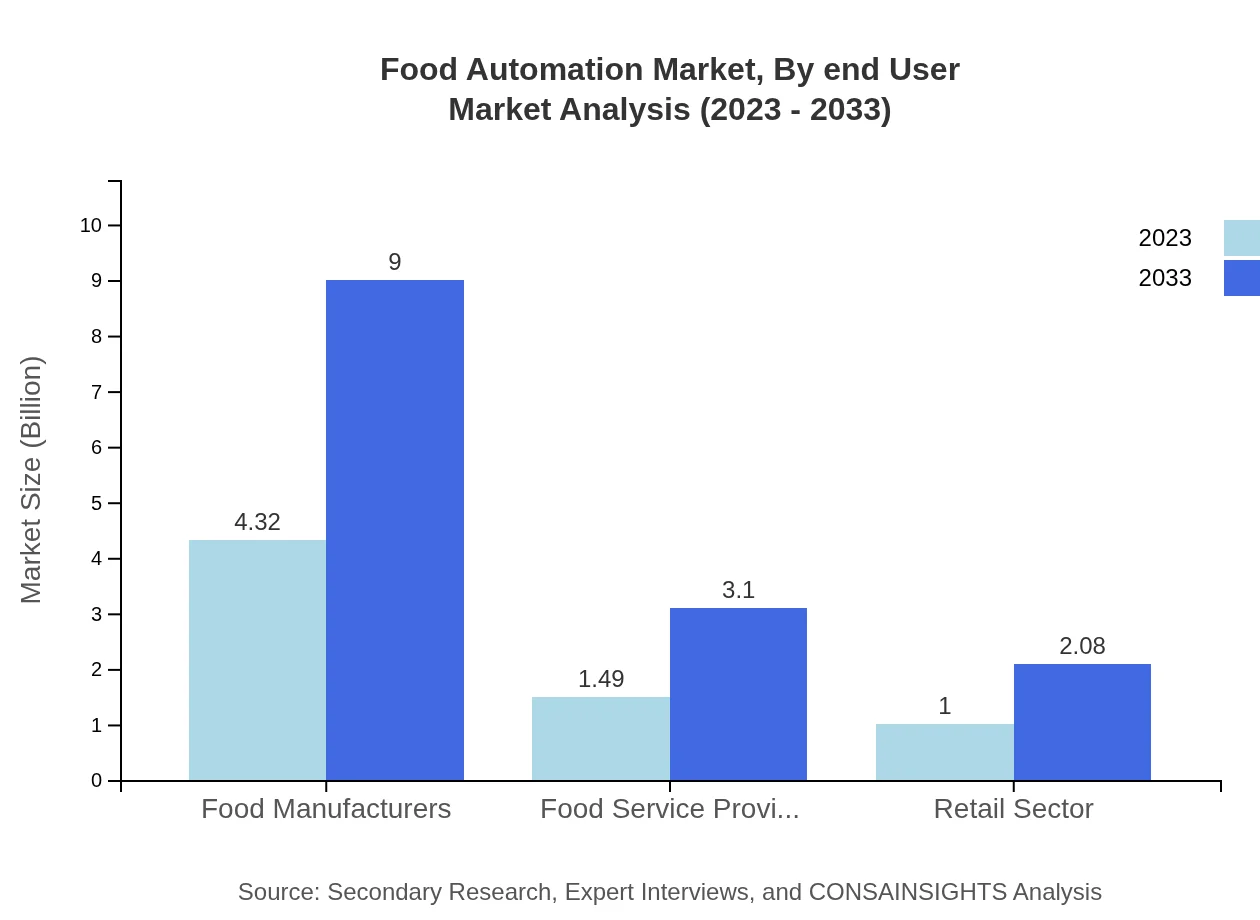
Food Automation Market Analysis By End User
Food manufacturers and food service providers are the largest contributors, each showcasing a consistent market share. The growing emphasis on automation is reshaping operational frameworks to increase productivity while meeting regulatory requirements.
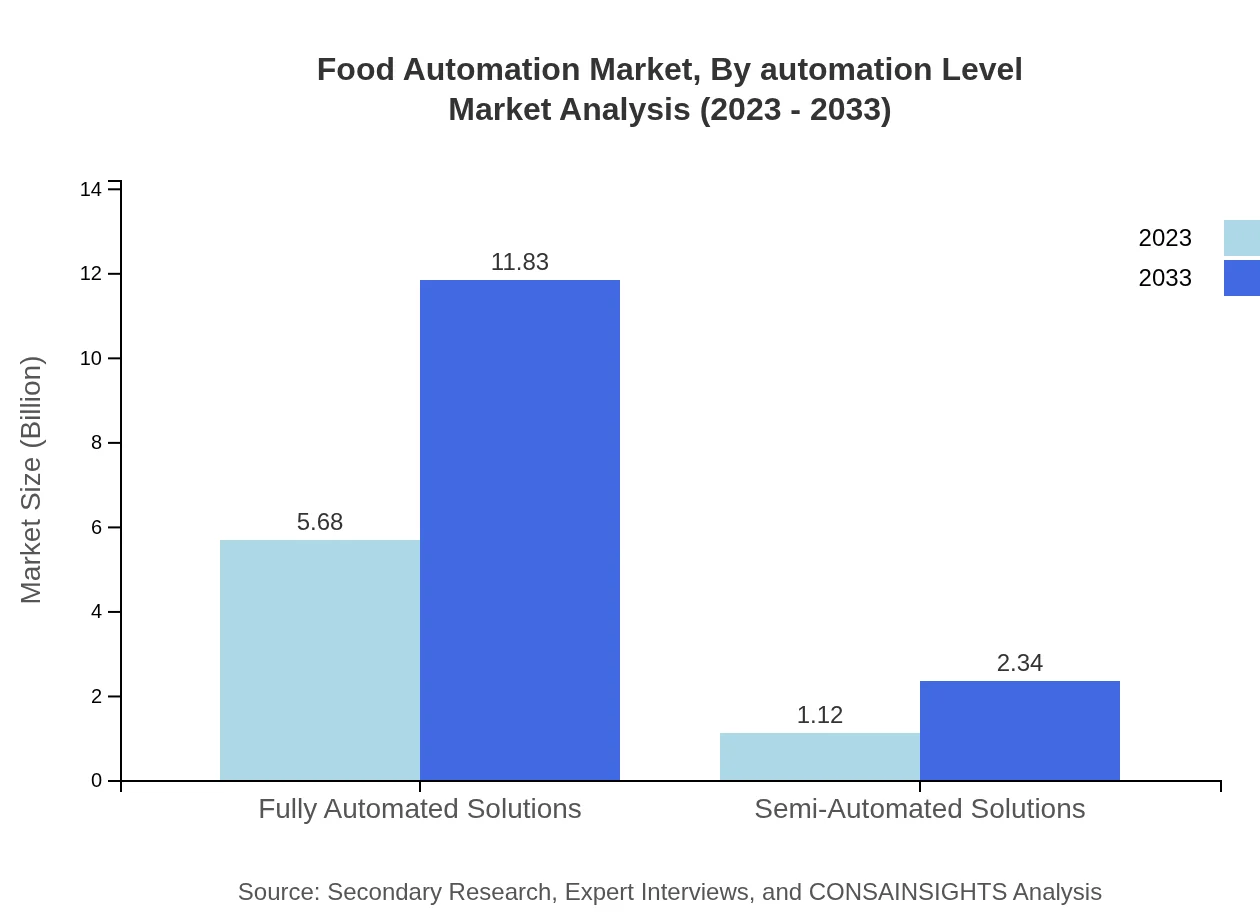
Food Automation Market Analysis By Automation Level
Fully automated solutions represent the largest market share at 83.47% in 2023, reflecting a significant push toward comprehensive automation in food production and handling processes.
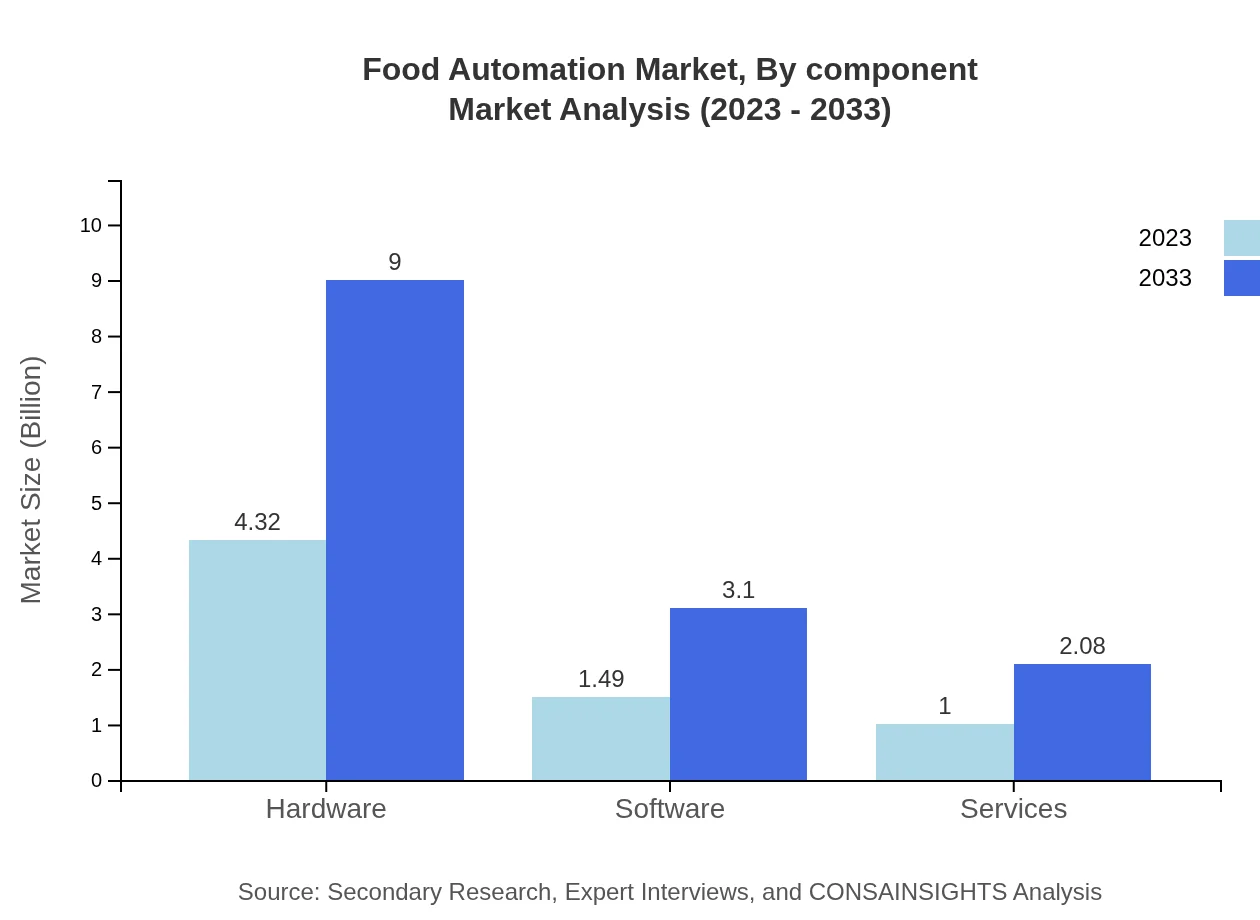
Food Automation Market Analysis By Component
The market is dominated by hardware solutions, followed by software and services. With the increasing integration of smart technologies, software solutions are gaining traction, driven by a rising demand for analytics.
Food Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Food Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
A leading global technology company known for its extensive range of solutions in automation and digitization within the food and beverage industry.Rockwell Automation:
A prominent provider of industrial automation and digital transformation solutions, Rockwell Automation helps food manufacturers optimize production processes.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is known for its automation and robotics solutions, which enhance the efficiency and safety of food production lines.Mitsubishi Electric:
Mitsubishi Electric provides advanced automation systems that enable food manufacturers to implement tailored automation solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of food Automation?
As of 2023, the food automation market is valued at approximately $6.8 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4%. By 2033, the market is expected to expand significantly, reflecting advancements in automation technology.
What are the key market players or companies in this food automation industry?
The food automation industry features major players including Rockwell Automation, Siemens AG, and ABB. These companies specialize in providing solutions like robotics, IoT solutions, and software aimed at enhancing food processing and manufacturing efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the food Automation industry?
Growth in the food automation sector is driven by the increasing demand for efficiency in food processing, labor shortages, advancements in robotics, and the adoption of IoT technologies. Additionally, consumer preferences for quality and safety boost automation efforts.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the food automation?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the food automation market, expected to grow from $1.37 billion in 2023 to $2.87 billion by 2033. Europe and North America follow closely with significant growth projections as well.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the food automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs within the food automation industry. Clients can request insights on demographics, segmentation, and trends to suit their strategic objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this food automation market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables including market size analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape reviews, segmentation data, and insights on market trends, offering a thorough understanding of the food automation sector.
What are the market trends of food automation?
Key trends in food automation include increased investment in fully automated solutions, growth of IoT applications in processing, and rising reliance on machine learning for efficiency. Sustainability and safety protocols are also becoming critical in automation advancements.