Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: industrial-and-factory-automation
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report explores the Industrial And Factory Automation market, providing insights into size, segmentation, technology trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to deliver valuable information for stakeholders, investors, and industry professionals to understand market dynamics and future developments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
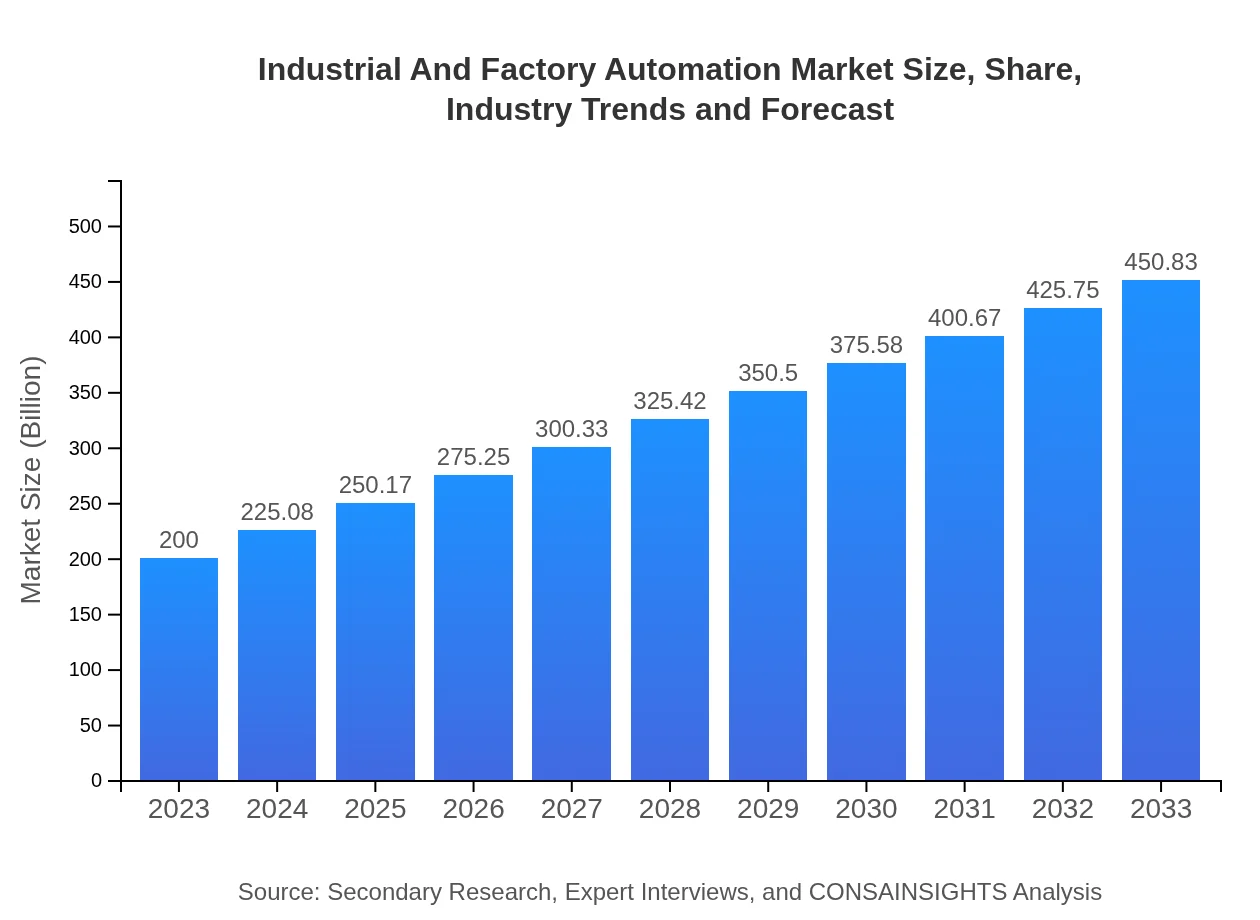
| 2023 Market Size | $200.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $450.83 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Inc., ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Overview
Customize Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industrial And Factory Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industrial And Factory Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industrial And Factory Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Industrial And Factory Automation market in 2023 and 2033?
Industrial And Factory Automation Industry Analysis
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report:
Europe’s market is expected to grow significantly, with a size of $63.40 billion in 2023 to $142.91 billion by 2033. The European Union’s commitment to Industry 4.0 and sustainability initiatives boosts investments in automation technologies, especially in manufacturing and process industries.Asia Pacific Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Industrial And Factory Automation market size for 2023 is approximately $32.36 billion, projected to grow to $72.94 billion by 2033. This growth is primarily driven by rapid industrialization, increasing labor cost, and significant investments in smart manufacturing technologies.North America Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report:
North America is a leading market in Industrial And Factory Automation, with a market size of $74.62 billion in 2023, projected to reach $168.21 billion by 2033. The region's strong emphasis on technological advancements, high adoption rates of automation solutions, and a robust automotive sector drive significant growth.South America Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report:
The South American market is expected to grow from $9.96 billion in 2023 to $22.45 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate fueled by the need for productivity improvements in local industries and the integration of advanced automation technologies.Middle East & Africa Industrial And Factory Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is on a growth trajectory, increasing from $19.66 billion in 2023 to $44.32 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to diverse industrial development projects and the rising need for efficient manufacturing systems throughout the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
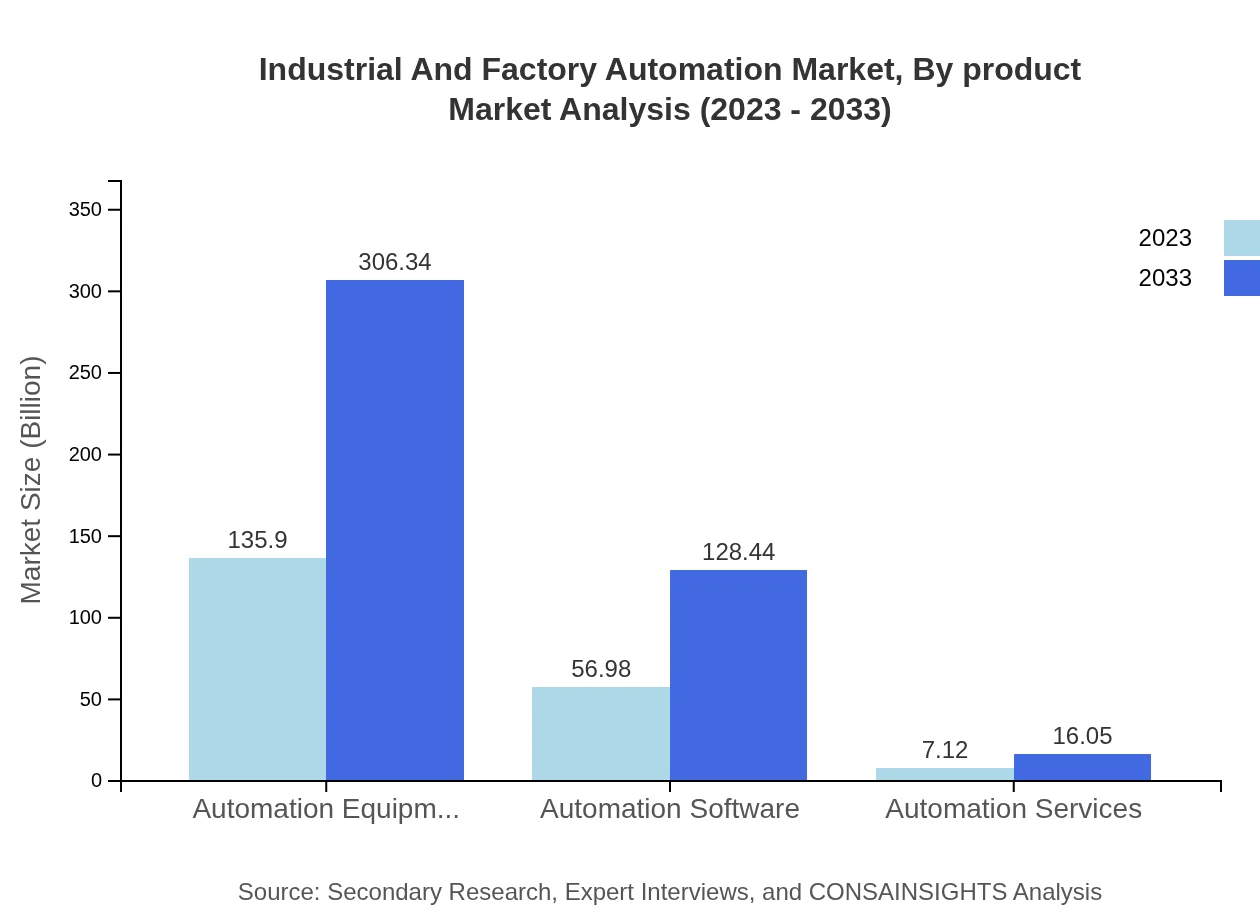
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Analysis By Product
In 2023, Automation Equipment dominates the market size at $135.90 billion, growing to $306.34 billion by 2033, accounting for a share of 67.95%. Automation Software and Services hold significant positions too, with sizes of $56.98 billion and $7.12 billion respectively in 2023. The demand for robust automation solutions continues to drive the market for all product segments.
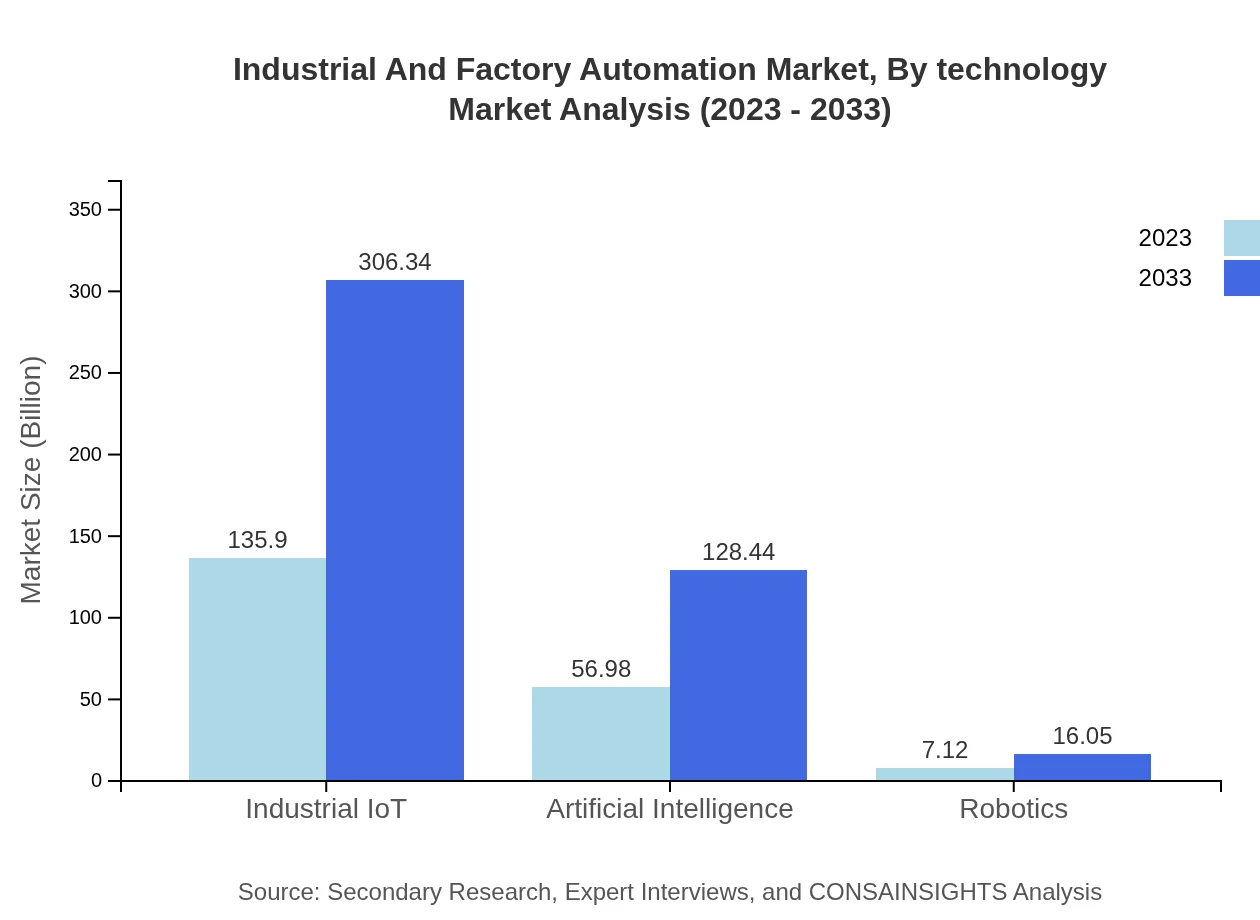
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Analysis By Technology
Key technological segments include Industrial IoT, Artificial Intelligence, and Robotics. Industrial IoT, valued at $135.90 billion in 2023, exhibits substantial market growth, highlighting the trend towards interconnected manufacturing systems. Artificial Intelligence is projected to grow from $56.98 billion in 2023 to $128.44 billion by 2033, reinforcing its significance in predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
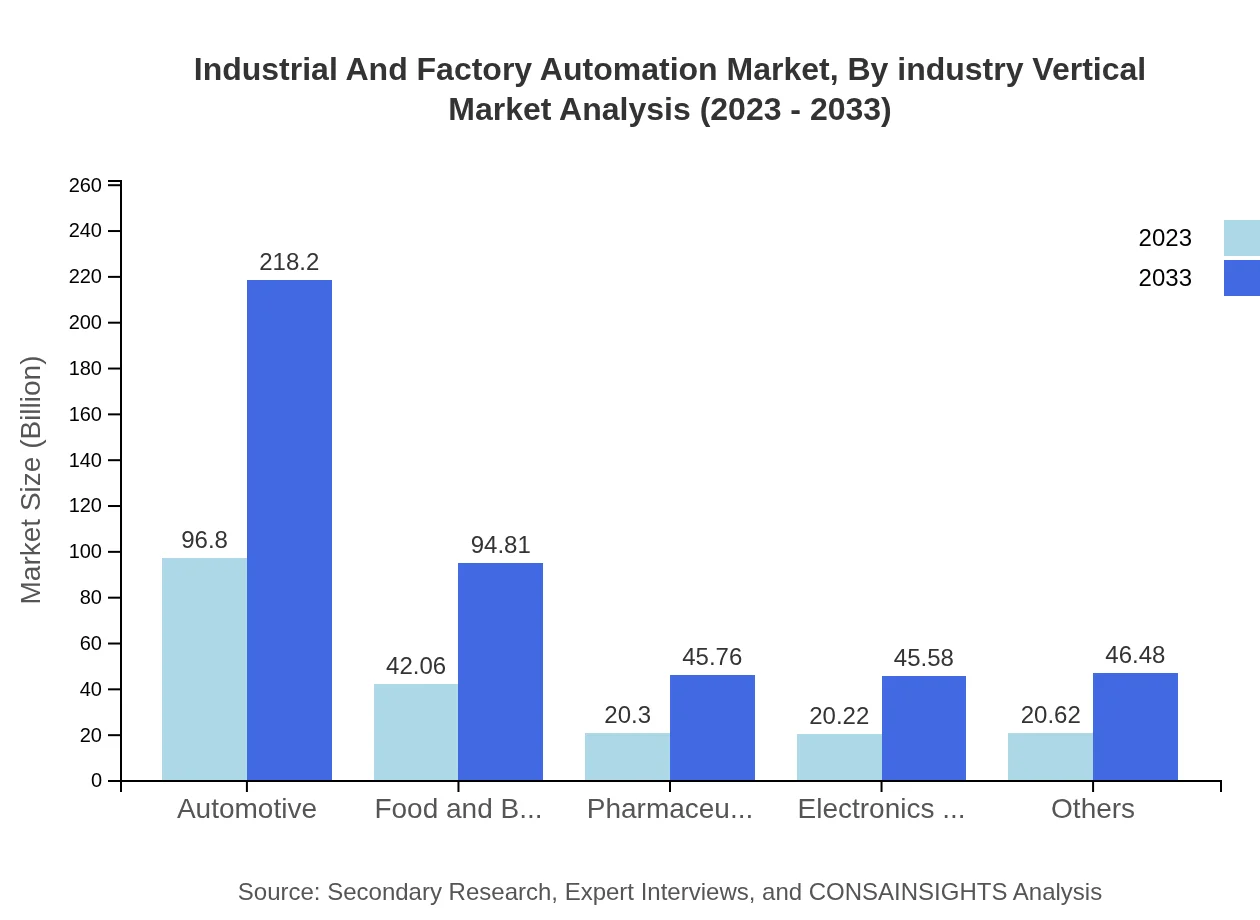
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Analysis By Industry Vertical
The Automotive sector is a leading vertical, expected to increase from $96.80 billion in 2023 to $218.20 billion by 2033, driven by automation in vehicle assembly and production. The Food and Beverage and Pharmaceutical sectors also show remarkable growth prospects, with increasing reliance on automation for quality control and efficient production processes.
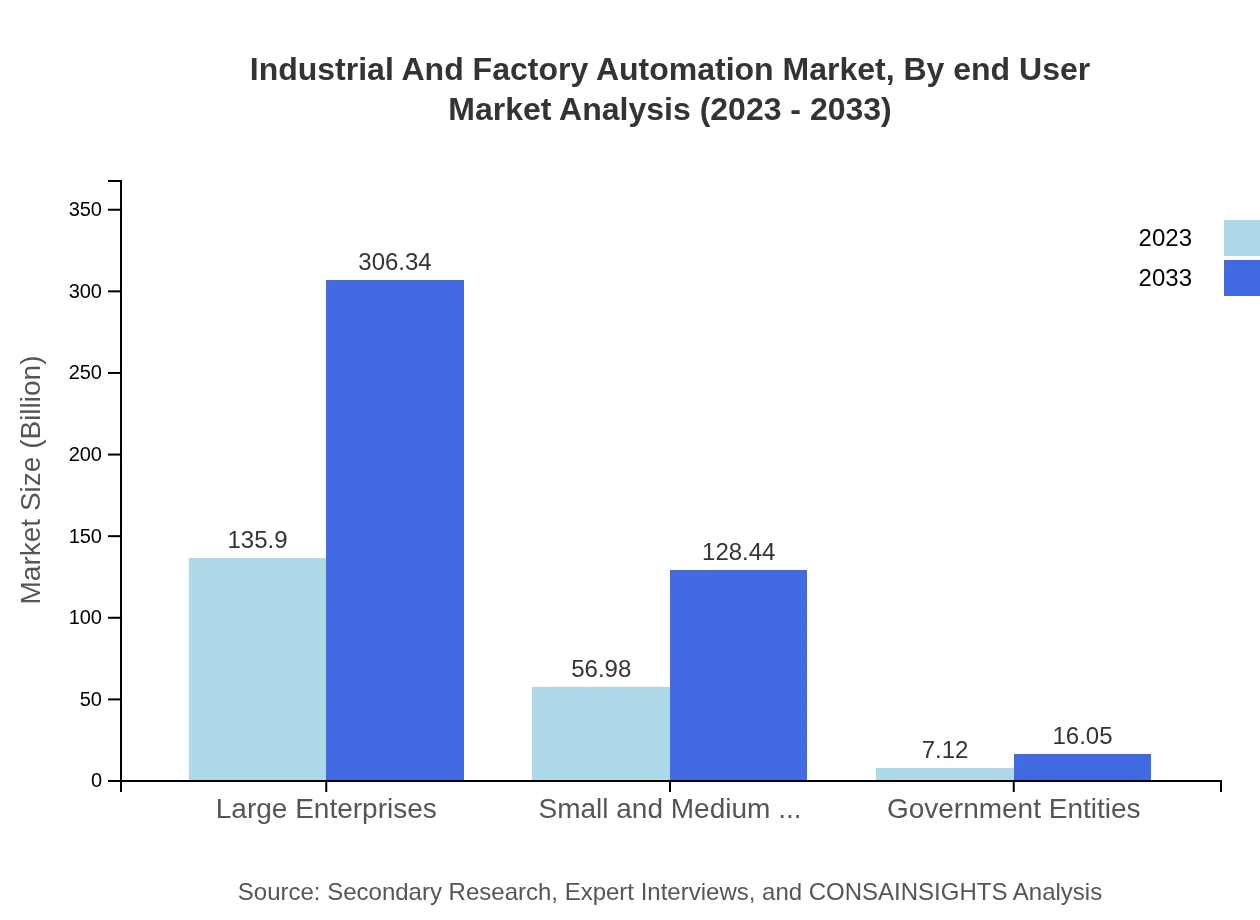
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Analysis By End User
End-users in the market include Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), and Government Entities. Large Enterprises encompass a significant market size, reflecting extensive investments in automation technologies, while SMEs and Government Entities are also growing segments.
Industrial And Factory Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Industrial And Factory Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
A leading global technology company that provides industry, energy, healthcare, and infrastructure solutions, known for its innovative automation technologies.Rockwell Automation, Inc.:
Specializes in industrial automation and information technology, Rockwell Automation offers a range of products and services designed to improve manufacturing productivity.ABB Ltd.:
A multinational corporation that offers electrification, automation, and digitalization solutions, recognized for its strong focus on innovation in factory automation.Schneider Electric SE:
A global specialist in energy management and automation, Schneider Electric offers integrated solutions across multiple industry segments, driving efficiency and sustainability.Honeywell International Inc.:
Provides automation and control solutions with innovative technologies and services designed to increase operational efficiency in various industries.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of industrial And Factory Automation?
The global industrial and factory automation market is projected to reach approximately $200 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% from the current market size. This growth reflects increasing adoption of automation technologies across various industries.
What are the key market players or companies in this industrial And Factory Automation industry?
Key players in the industrial and factory automation industry include Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric, and Mitsubishi Electric. These companies lead the market through innovative solutions and extensive portfolios in automation technologies.
What are the primary factors driving growth in the industrial And Factory Automation industry?
Growth in the industrial and factory automation sector is primarily driven by the need for increased operational efficiency, the integration of IoT and AI technologies, labor shortages, and the demand for higher product quality and precision in manufacturing processes.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the industrial And Factory Automation market?
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for industrial and factory automation, with projected growth from $32.36 billion in 2023 to $72.94 billion in 2033, benefiting from rapid industrialization and technological advancements.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the industrial And Factory Automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored specifically to the needs of clients in the industrial and factory automation industry. This includes detailed insights, forecasts, and analyses to support strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this industrial And Factory Automation market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables including market size analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, segment data, and strategic recommendations tailored to the industrial and factory automation market.
What are the market trends of industrial And Factory Automation?
Current market trends in industrial and factory automation indicate a growing emphasis on smart factories, Industry 4.0 technologies, the integration of robotics, and increased reliance on data analytics for operational improvements and predictive maintenance.