Industrial Starch Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: industrial-starch
Industrial Starch Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Industrial Starch market, covering market size, growth forecasts, industry insights, and key trends from 2023 to 2033. It will offer valuable data and insights for stakeholders in the starch industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
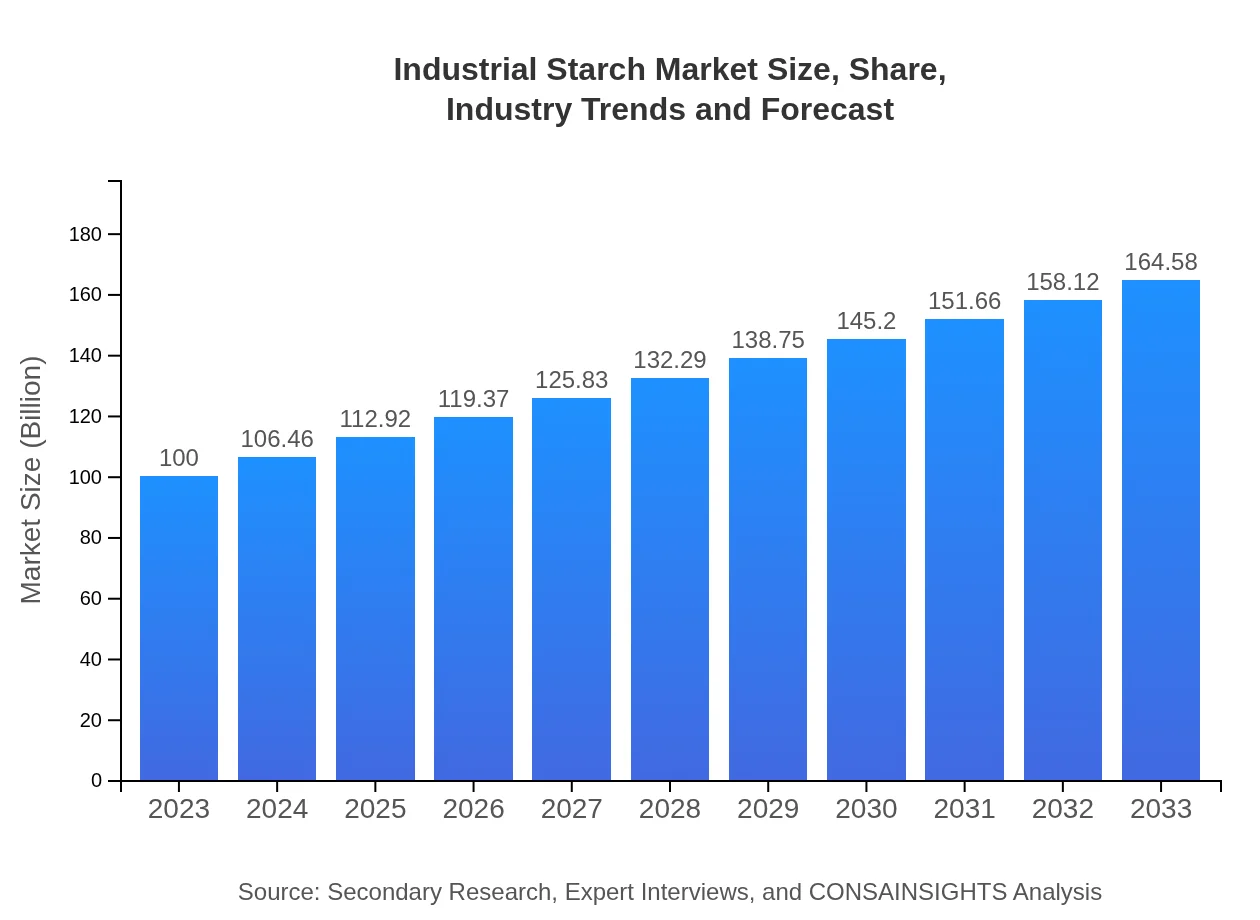
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Inc., Ingredion Incorporated, Tate & Lyle PLC, Roquette Frères, AVEBE |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Industrial Starch Market Overview
Customize Industrial Starch Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industrial Starch market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industrial Starch's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industrial Starch
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Industrial Starch market in 2023?
Industrial Starch Industry Analysis
Industrial Starch Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial Starch Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industrial Starch Market Report:
The European Industrial Starch market is forecasted to grow from $34.12 billion in 2023 to $56.15 billion by 2033, supported by stringent regulations promoting renewable resources and increased consumer focus on bio-based products.Asia Pacific Industrial Starch Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Industrial Starch market is projected to grow from $17.84 billion in 2023 to $29.36 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by the rise in food processing industries and increased consumption of packaged foods.North America Industrial Starch Market Report:
In North America, the market is expected to expand from $35.35 billion in 2023 to $58.18 billion by 2033. This growth is mainly attributed to technological advancements and the growing application of starch in biofuels and pharmaceuticals.South America Industrial Starch Market Report:
The South American market, valued at $4.58 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $7.54 billion by 2033. Key drivers include rising demand in the food and beverage sector and improvements in agricultural output.Middle East & Africa Industrial Starch Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to rise from $8.11 billion in 2023 to $13.35 billion by 2033, driven by fostered agricultural practices and an increase in food processing activities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial Starch Market Analysis By Type
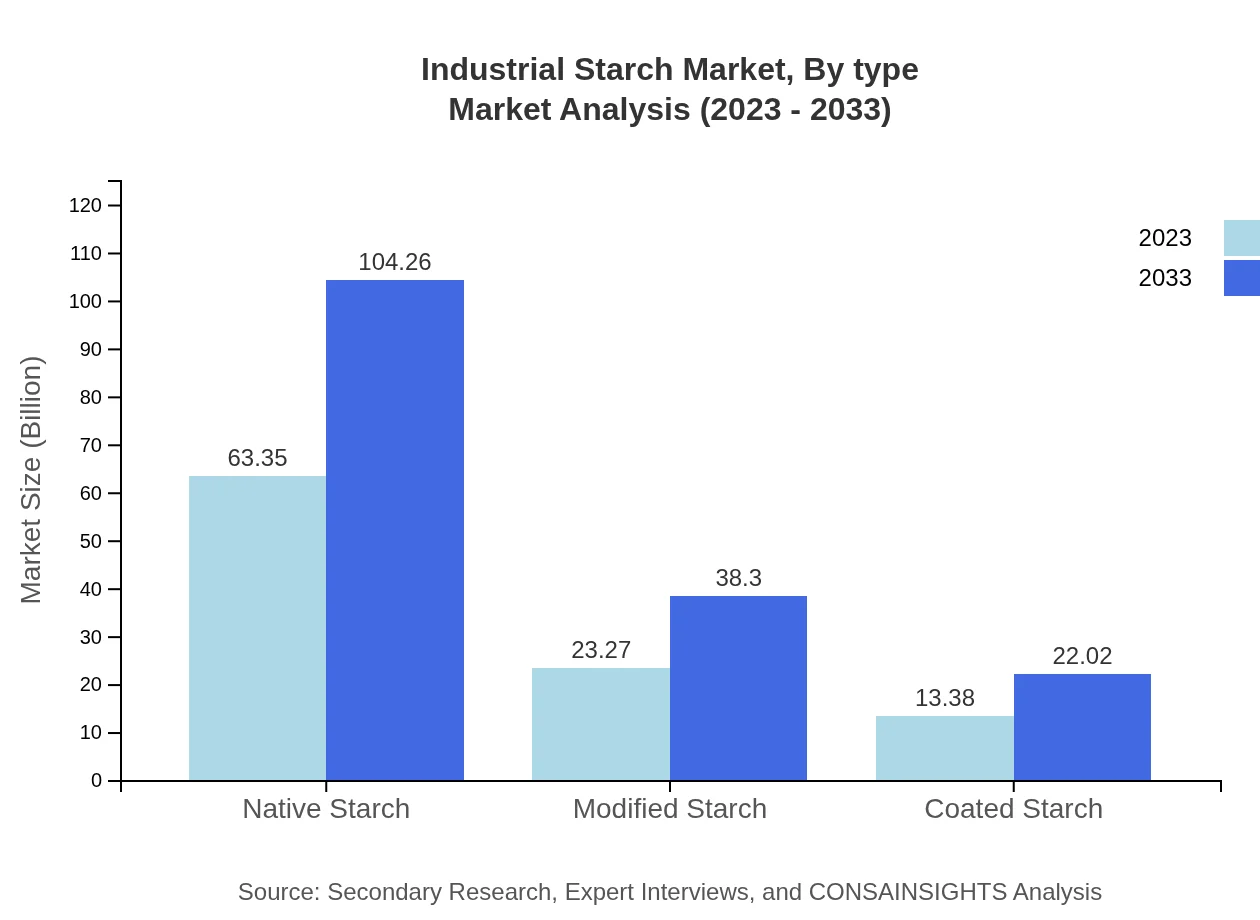
The Industrial Starch market is segmented into native starch, modified starch, and coated starch. Native starch remains dominant, with a market size of $63.35 billion in 2023, projected to reach $104.26 billion by 2033, maintaining a steady market share. Modified starch, valued at $23.27 billion in 2023, is set to grow to $38.30 billion by 2033, reflecting its increased applications in food and industrial processes. Coated starch is also witnessing growth, moving from $13.38 billion in 2023 to $22.02 billion by 2033.
Industrial Starch Market Analysis By Application
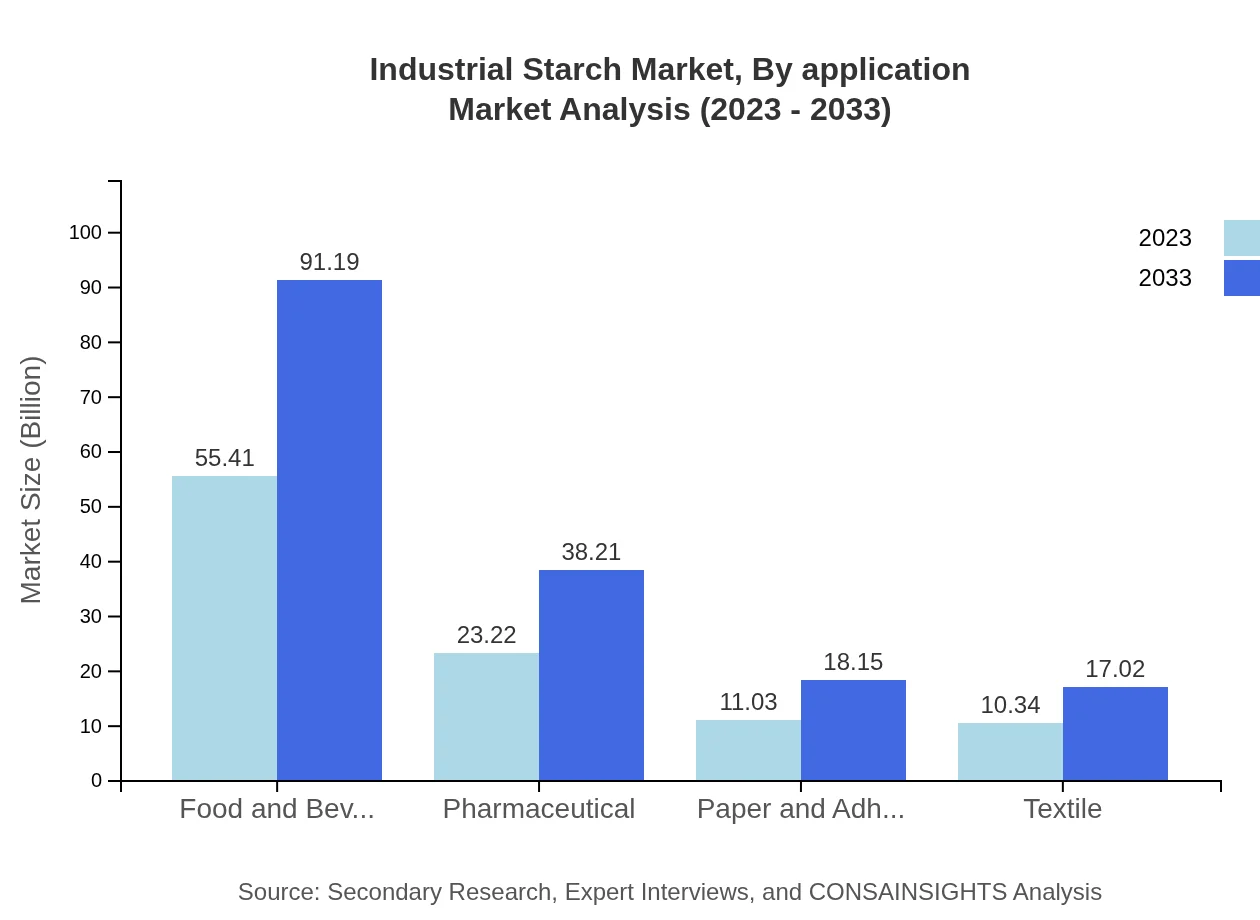
The market is segmented into diverse applications such as food, pharmaceuticals, adhesives, and biofuels. The food industry dominates with a valuation of $55.41 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $91.19 billion, due to growing consumer awareness of health and nutrition. The adhesive industry and pharmaceuticals each show potential for growth, moving from $23.22 billion to $38.21 billion and $11.03 billion to $18.15 billion respectively.
Industrial Starch Market Analysis By End User
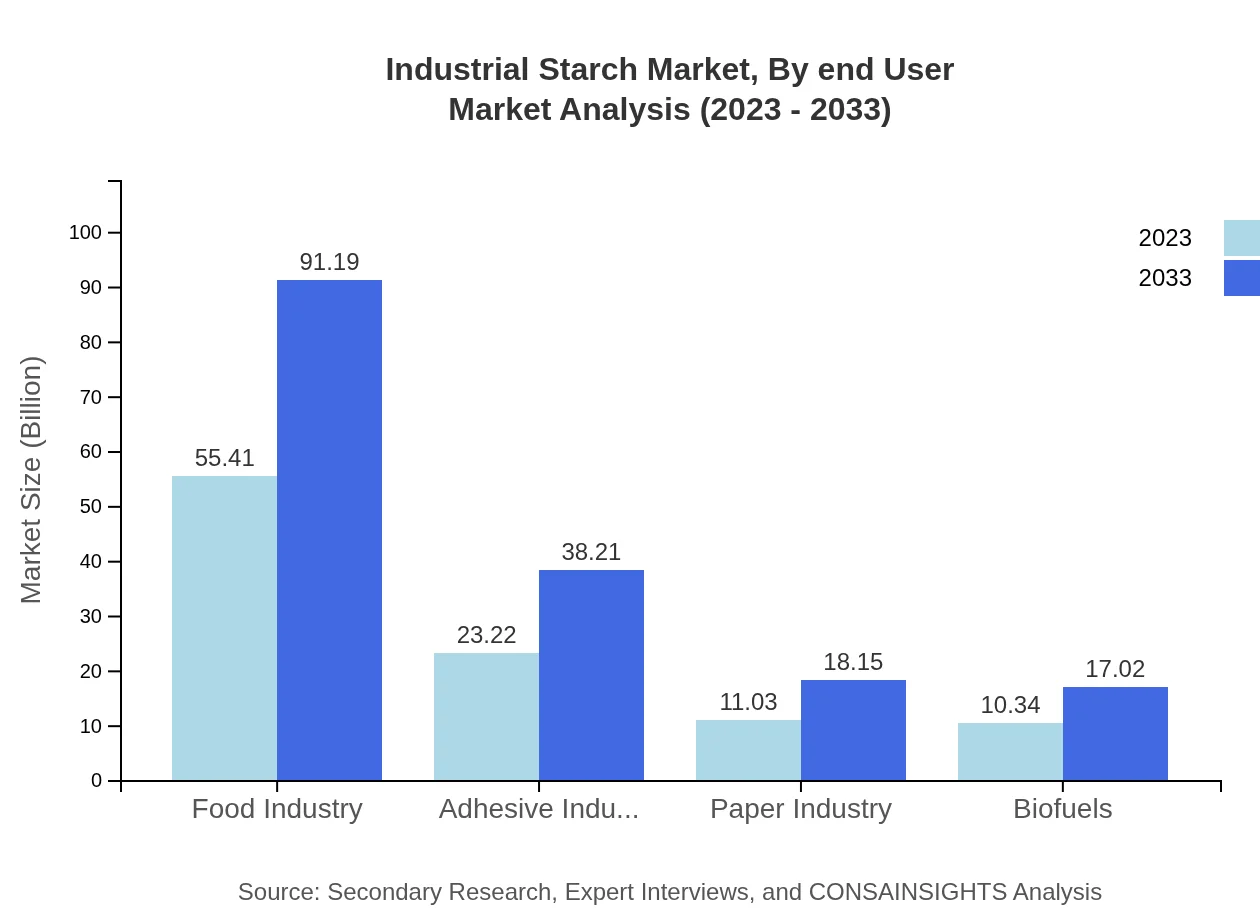
End-users in the Industrial Starch market include food and beverage, pharmaceutical, textile, and biofuel industries. The food and beverage sector leads with $55.41 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $91.19 billion. The pharmaceutical sector, valued at $23.22 billion, is predicted to reach $38.21 billion, reflecting rising demands for excipients and fillers in drug formulations.
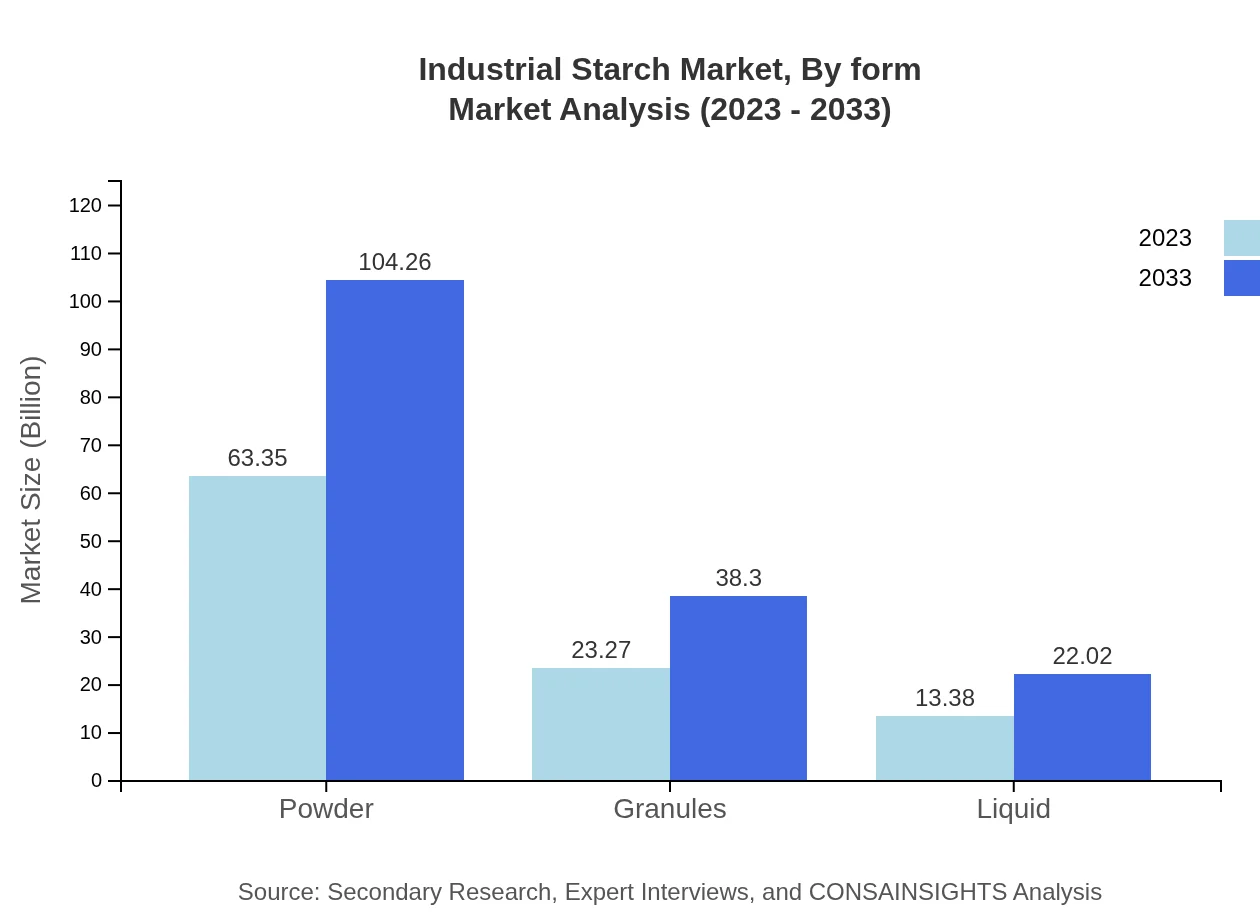
Industrial Starch Market Analysis By Form
Industrial starch is available in various forms, including powder, granules, and liquid. Powder starch dominates the market with a size of $63.35 billion in 2023, expected to reach $104.26 billion by 2033. Granules follow with $23.27 billion to $38.30 billion, while liquid starch accounts for $13.38 billion, anticipated to grow to $22.02 billion by 2033.
Industrial Starch Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Industrial Starch Industry
Cargill, Inc.:
Cargill is a leading global provider of food, agricultural, financial, and industrial products, including starches, ingredients, and co-products.Ingredion Incorporated:
Ingredion is a global ingredient solutions provider, transforming grains, fruits, vegetables, and other plant materials into sweeteners, starches, and nutrition products for various industries.Tate & Lyle PLC:
Tate & Lyle is a global provider of food and beverage ingredients and solutions, known for starches that help improve product quality and performance.Roquette Frères:
Roquette specializes in plant-based ingredients for food, nutrition, and health markets, offering a wide range of starches catering to diverse applications.AVEBE:
AVEBE is a cooperative specializing in potato starch and starch derivatives for food and non-food applications, recognized for high-quality standards.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of industrial Starch?
The industrial starch market is projected to grow from $100 million in 2023 to an estimated value by 2033. The competitive landscape anticipates a CAGR of 5%, indicating steady growth and expanding opportunities in this sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the industrial Starch industry?
Key players in the industrial starch market include global suppliers engaged in the manufacture and distribution of various starch products. Their market strategies focus on innovation, sustainability, and catering to specific industry needs.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the industrial Starch industry?
Growth in the industrial starch industry is driven by rising demand from food, pharmaceutical, and biofuel sectors, along with developments in sustainable production methods and increased applications of starch in non-food industries.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the industrial Starch?
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for industrial starch, expected to grow from $17.84 million in 2023 to $29.36 million by 2033. This growth is attributed to rapid industrialization and urbanization in the region.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the industrial Starch industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the industrial-starch industry. Clients can request tailored analysis to meet specific business needs and gain insights into market dynamics and trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this industrial Starch market research project?
Deliverables from our industrial starch market research project typically include comprehensive reports, regional and segment analysis, market trends, competitive landscape reviews, and projections for future market growth.
What are the market trends of industrial Starch?
Current trends in the industrial starch market include an increased focus on environmentally-friendly production, the integration of advanced technology in manufacturing processes, and expanding applications across various industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and textiles.