Pipeline Network Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: pipeline-network
Pipeline Network Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Pipeline Network market, including current trends, future evaluations, and the competitive landscape through 2033, illustrating market size, segmentation, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
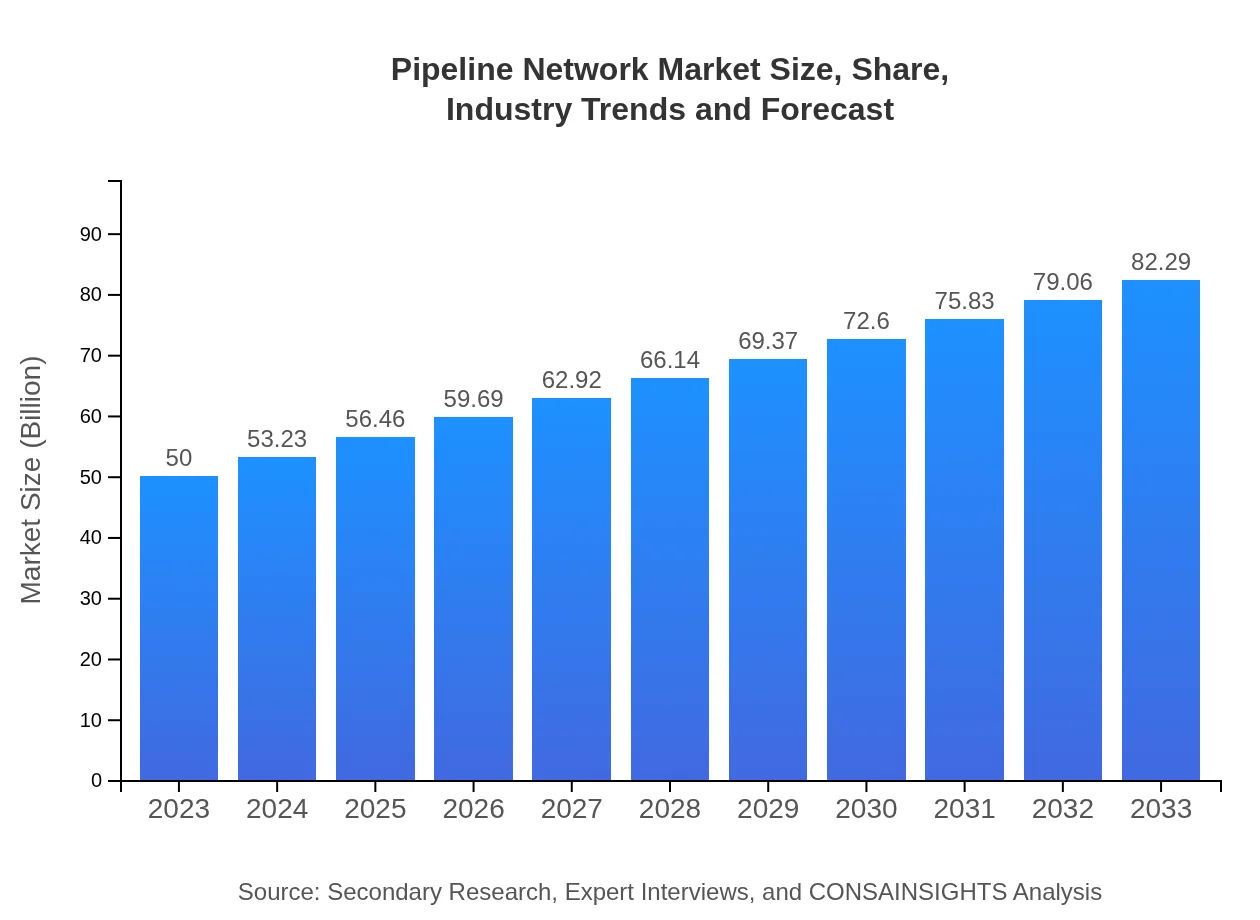
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $82.29 Billion |
| Top Companies | TransCanada Corporation, Enbridge Inc., Kinder Morgan, Royal Dutch Shell |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Pipeline Network Market Overview
Customize Pipeline Network Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Pipeline Network market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Pipeline Network's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Pipeline Network
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Pipeline Network market in 2023?
Pipeline Network Industry Analysis
Pipeline Network Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Pipeline Network Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Pipeline Network Market Report:
The European market, initially valued at $12.39 billion in 2023, is estimated to expand to $20.40 billion by 2033, fueled by stringent environmental regulations and a shift towards renewable energy pipelines.Asia Pacific Pipeline Network Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's pipeline network market is valued at approximately $9.99 billion, projected to reach $16.45 billion by 2033, driven by accelerated urbanization and energy demands from emerging markets.North America Pipeline Network Market Report:
North America boasts a substantial pipeline network market of $19.07 billion in 2023, expected to achieve $31.39 billion by 2033, largely due to extensive oil and gas operations and ongoing infrastructure upgrades.South America Pipeline Network Market Report:
The South American market, starting at $3.89 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to $6.40 billion by 2033. Key growth factors include resource extraction in countries like Brazil and Argentina and infrastructure improvements.Middle East & Africa Pipeline Network Market Report:
With a market worth $4.64 billion in 2023, the Middle East and Africa region is projected to grow to $7.64 billion by 2033, benefiting from large-scale oil and gas projects and investments in water infrastructure.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
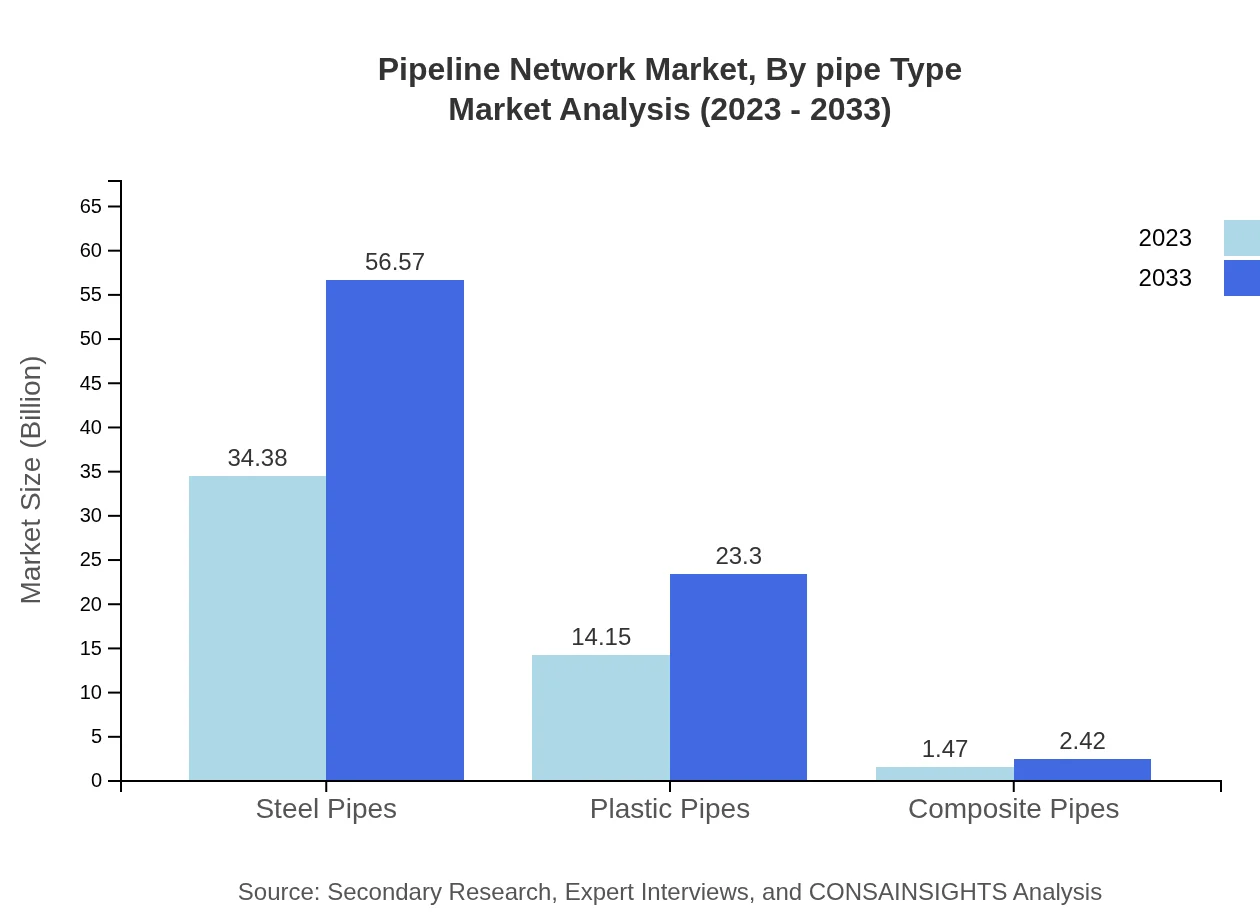
Pipeline Network Market Analysis By Pipe Type
Key types of pipes driving the pipeline network are steel pipes, plastic pipes, composite pipes, traditional pipelines, smart pipelines, and eco-friendly pipelines. Steel pipes dominate the market with a size of $34.38 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $56.57 billion by 2033, accounting for 68.75% of the market share. Plastic pipes, while smaller at $14.15 billion in 2023, show a promising increase to $23.30 billion by 2033, holding 28.31% market share.
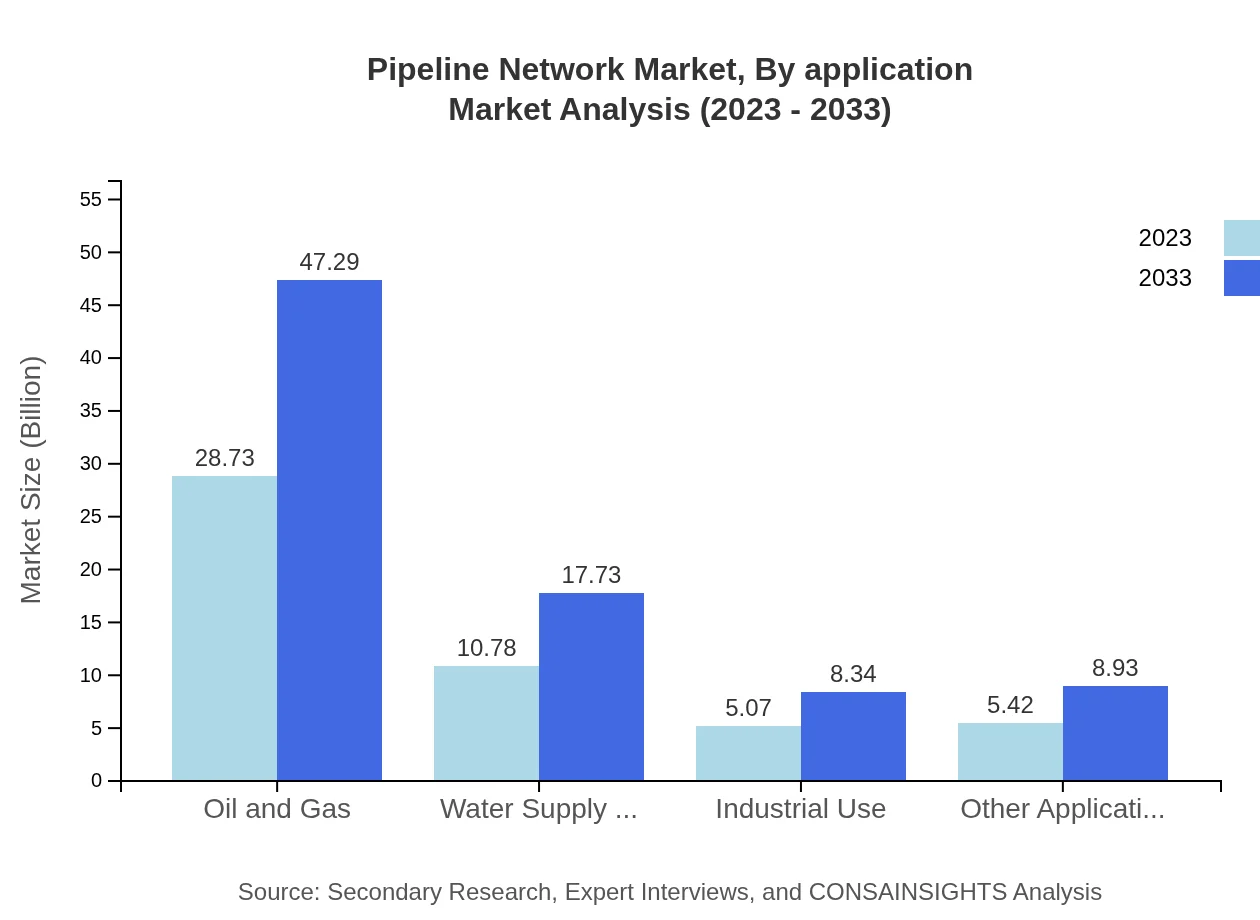
Pipeline Network Market Analysis By Application
Applications of pipeline networks include oil and gas extraction, municipalities, construction, manufacturing, and more. In 2023, oil and gas extraction leads with a market size of $28.73 billion (57.47% share), expected to rise to $47.29 billion by 2033. Municipalities account for $10.78 billion in 2023, with expectations of reaching $17.73 billion by 2033.
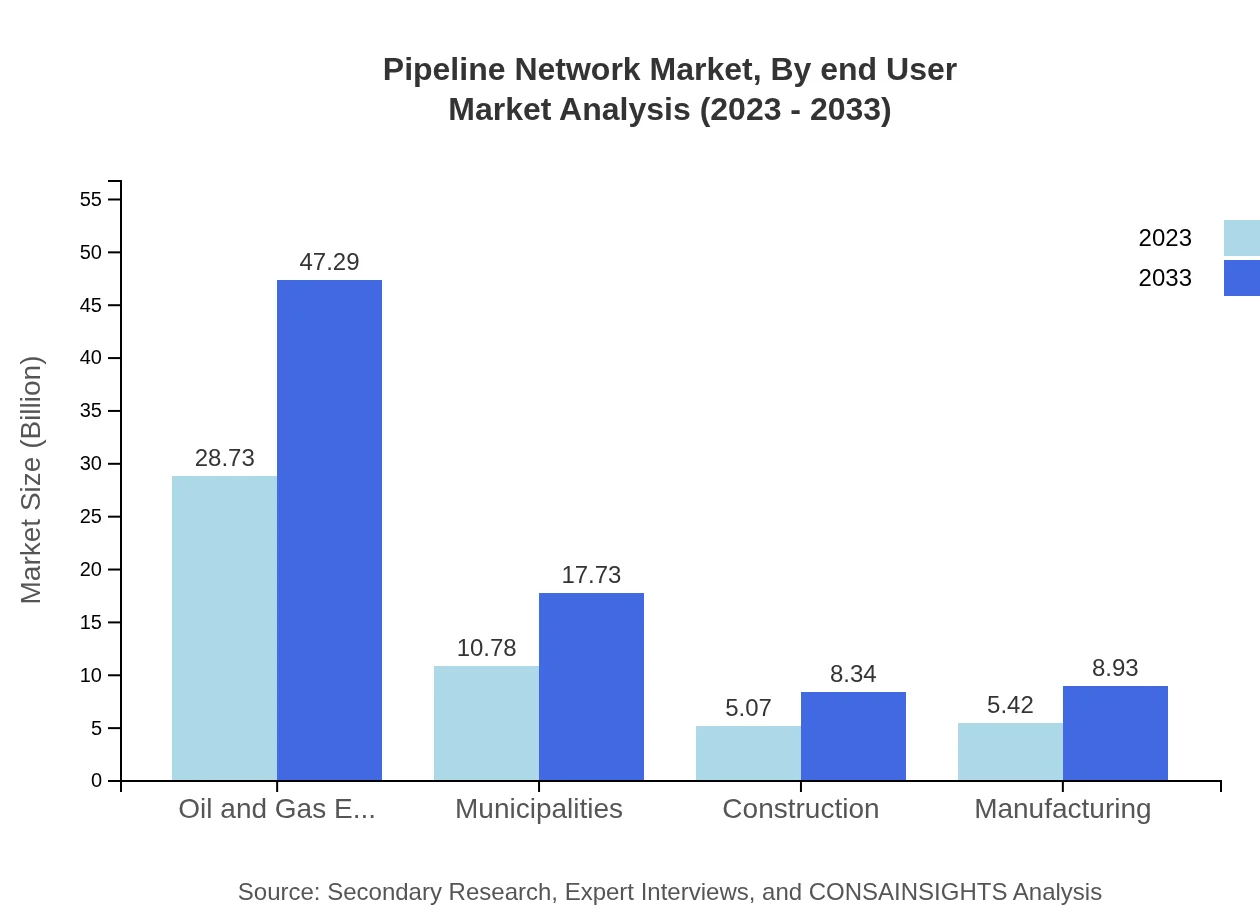
Pipeline Network Market Analysis By End User
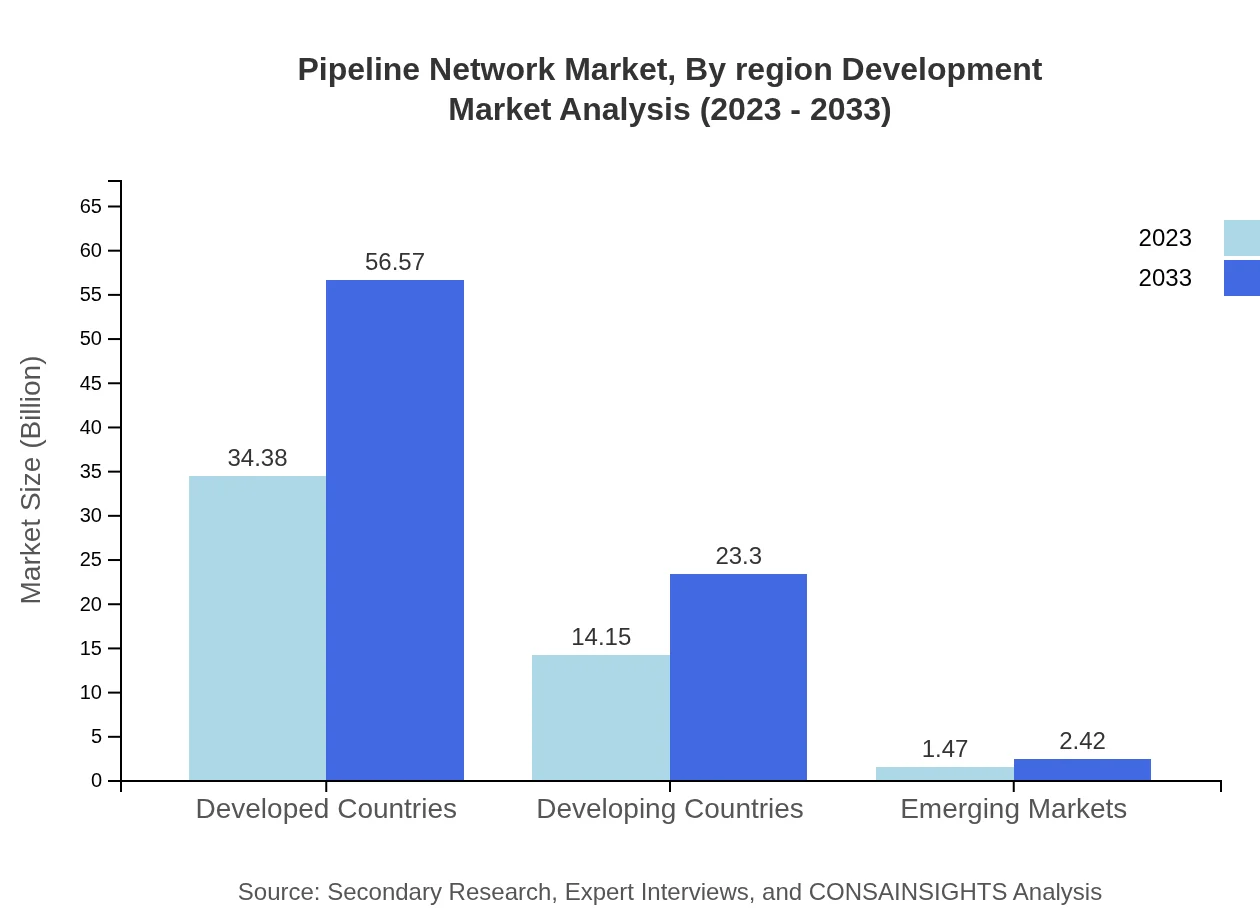
End-users for pipeline networks include developed and developing countries, with developed markets holding substantial shares. In 2023, developed countries account for $34.38 billion, growing to $56.57 billion by 2033, sustaining a share of 68.75%. In contrast, developing countries, starting at $14.15 billion, anticipate growth to $23.30 billion.
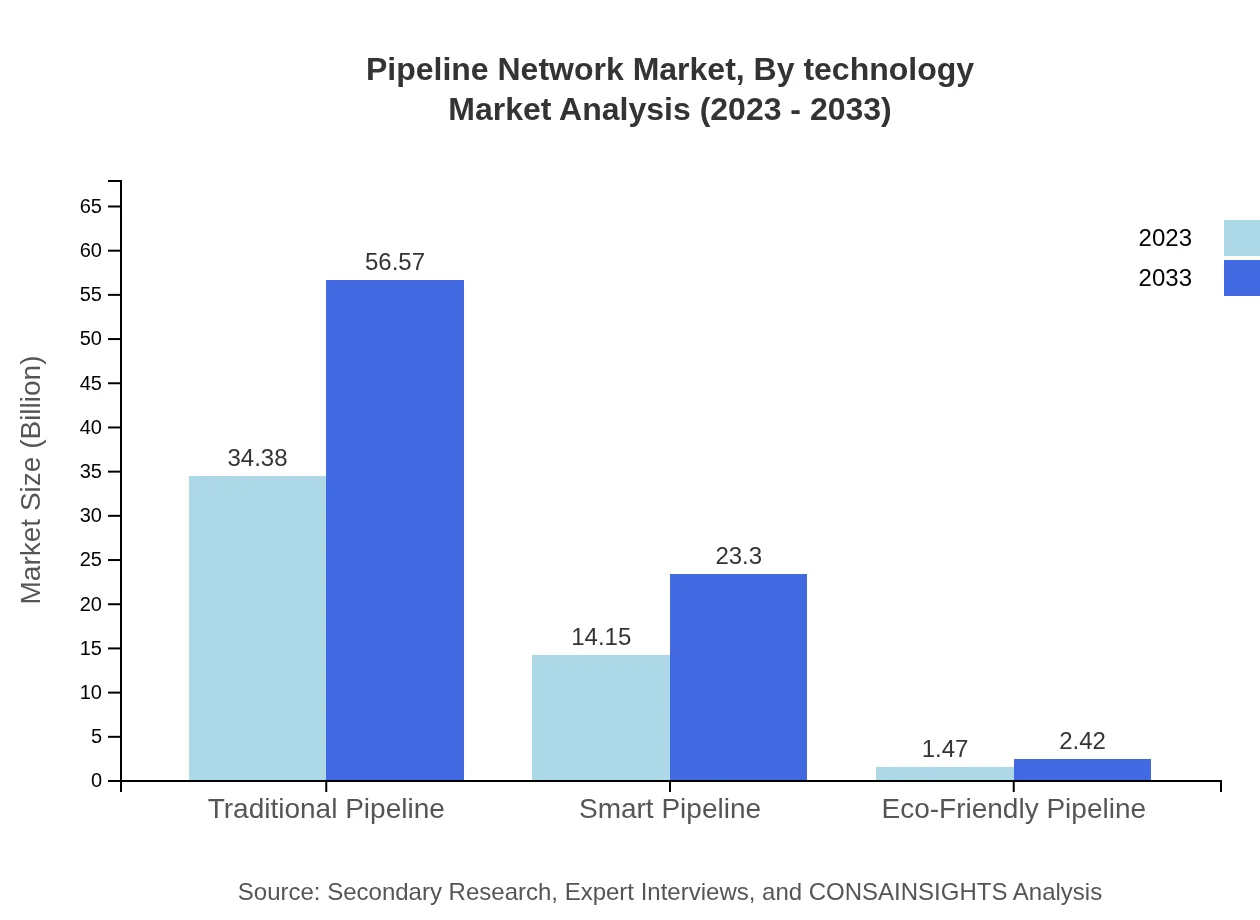
Pipeline Network Market Analysis By Technology
Innovations in pipeline technology, especially smart pipeline systems, have transformed operational robustness. Smart pipelines, valued at $14.15 billion in 2023, are projected to grow to $23.30 billion by 2033. Eco-friendly solutions also emerge as a vital segment, albeit with smaller market figures, growing from $1.47 billion to $2.42 billion, showing increasing interest in sustainability.
Pipeline Network Market Analysis By Region Development
Regional development focus is vital, as different regions prioritize pipelines catering to their unique energy and resource demands. Developed regions largely invest in upgrading existing pipelines, while developing areas focus on new installations to facilitate growth, leading to a balanced, progressive market landscape.
Pipeline Network Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Pipeline Network Industry
TransCanada Corporation:
A leading North American multinational energy company with extensive involvement in natural gas and crude oil transportation.Enbridge Inc.:
A Canadian company specializing in the transportation of crude oil and natural gas, recognized for its expansive pipeline network and commitment to renewable energy.Kinder Morgan:
One of the largest energy infrastructure companies in North America, primarily engaged in the transportation of natural gas, crude oil, and CO2.Royal Dutch Shell:
A global group of energy and petrochemical companies, deeply engaged in the supply of liquefied natural gas pipelines.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of pipeline Network?
The global pipeline network market is estimated to reach a size of approximately $50 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5% from its current valuation.
What are the key market players or companies in this pipeline Network industry?
The pipeline network industry features key players including major oil and gas enterprises, utility companies, and pipeline manufacturers, each contributing significantly to the market's growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the pipeline Network industry?
Growth in the pipeline network industry is driven by increasing energy demand, infrastructural investments across regions, and advancements in pipeline technology that enhance efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the pipeline Network?
The fastest-growing region for the pipeline network market is North America, predicted to expand from $19.07 billion in 2023 to $31.39 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the pipeline Network industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored for the pipeline network industry, addressing specific client needs and insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this pipeline Network market research project?
Expect detailed market analysis reports, regional insights, competitive landscape studies, and growth forecasts, all tailored for the pipeline network sector.
What are the market trends of pipeline Network?
Current trends in the pipeline network market include increasing adoption of smart pipelines, emphasis on eco-friendly pipeline materials, and innovative construction technologies.