Precision Farming Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: precision-farming
Precision Farming Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive overview of the Precision Farming market, including current trends, market segmentation, and regional insights. Analyzing data from 2023 to 2033, it forecasts growth along with challenges that may arise in this evolving industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
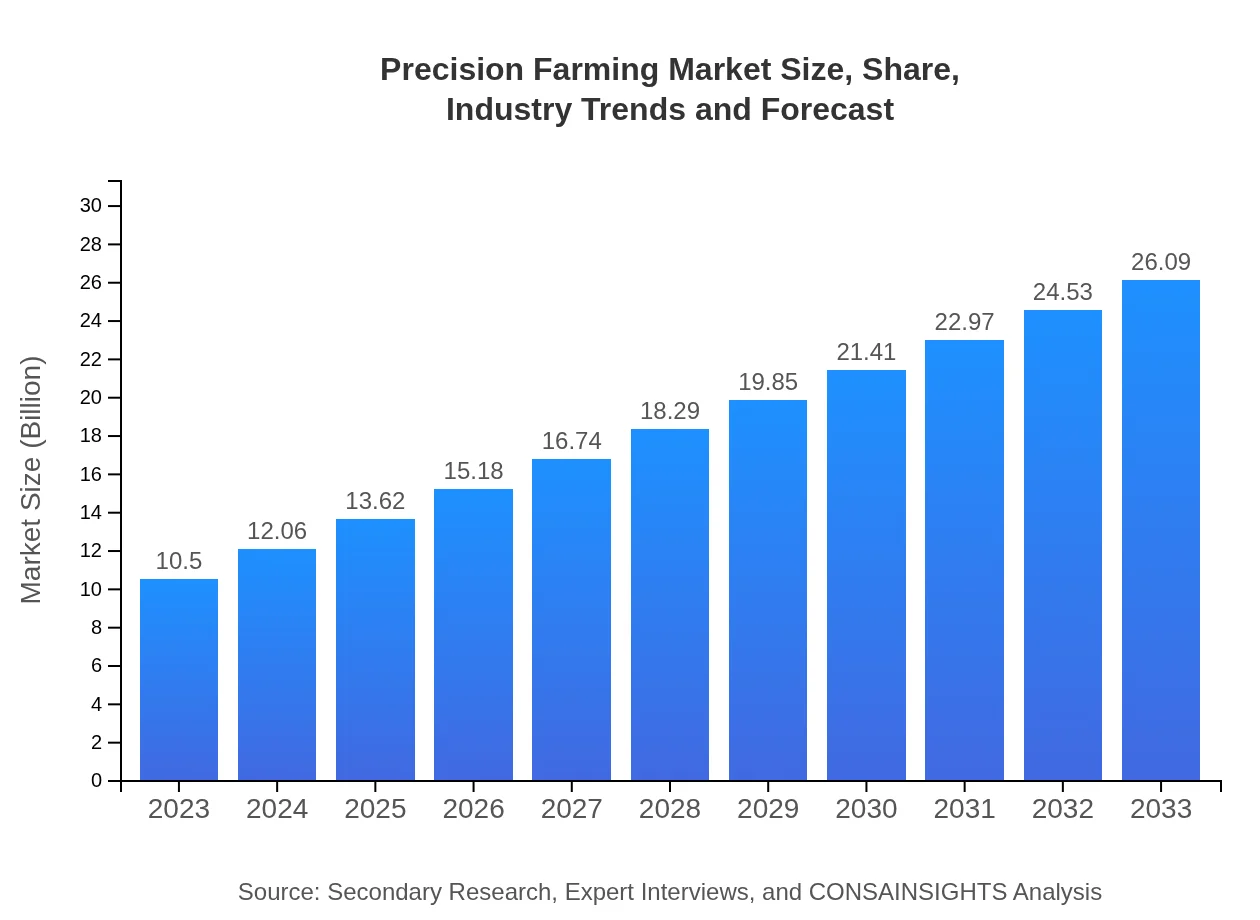
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $26.09 Billion |
| Top Companies | John Deere, Trimble Inc., AG Leader Technology, Raven Industries, Topcon Positioning Systems |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Precision Farming Market Overview
Customize Precision Farming Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Precision Farming market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Precision Farming's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Precision Farming
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Precision Farming market in 2023?
Precision Farming Industry Analysis
Precision Farming Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Precision Farming Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Precision Farming Market Report:
Europe is experiencing rapid growth, with the Precision Farming market expected to rise from $3.05 billion in 2023 to $7.59 billion by 2033. Increased environmental regulations and the EU’s commitment to sustainable agriculture drive the adoption of precision methods in the region.Asia Pacific Precision Farming Market Report:
In 2023, the Precision Farming market in the Asia Pacific is valued at $2.24 billion and is expected to reach $5.57 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increased investments in modern agricultural practices and government policies promoting technology adoption to improve crop production.North America Precision Farming Market Report:
North America stands as a leader in Precision Farming, with a market size of $3.45 billion in 2023 projected to reach $8.56 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include early adoption of technology, a strong farming sector, and high public and private investment in agri-tech.South America Precision Farming Market Report:
South America’s Precision Farming market is projected to grow from $0.70 billion in 2023 to $1.73 billion by 2033. The region’s vast agricultural landscape offers ripe opportunities for growth but faces challenges in technology access and infrastructure.Middle East & Africa Precision Farming Market Report:
In 2023, the Middle East and Africa market size is at $1.06 billion, expected to expand to $2.63 billion by 2033. The region faces significant agricultural challenges that precision farming can address, including water scarcity and the need for increased productivity.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Precision Farming Market Analysis By Technology
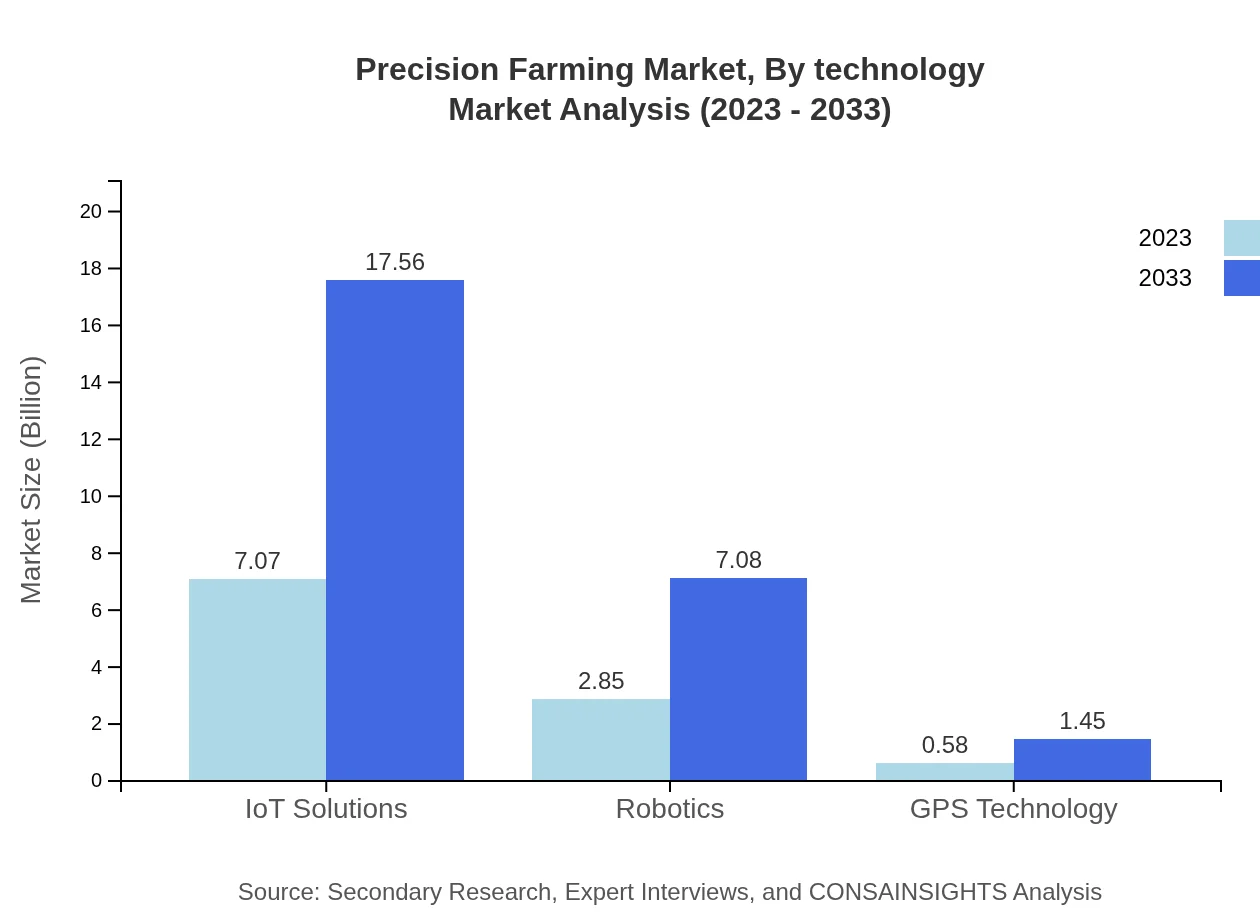
The IoT Solutions segment is a leader, with a market size reaching $7.07 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $17.56 billion by 2033, highlighting significant adoption of connected devices. Robotics in precision farming is also growing, with values of $2.85 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $7.08 billion by 2033. GPS technology, while smaller, is becoming more critical with performance increasing from $0.58 billion in 2023 to $1.45 billion by 2033. Field Monitoring, Crop Management, Livestock Management, Weather Forecasting, and other innovations play pivotal roles, meeting the growing demand for efficient agricultural practices.
Precision Farming Market Analysis By Application
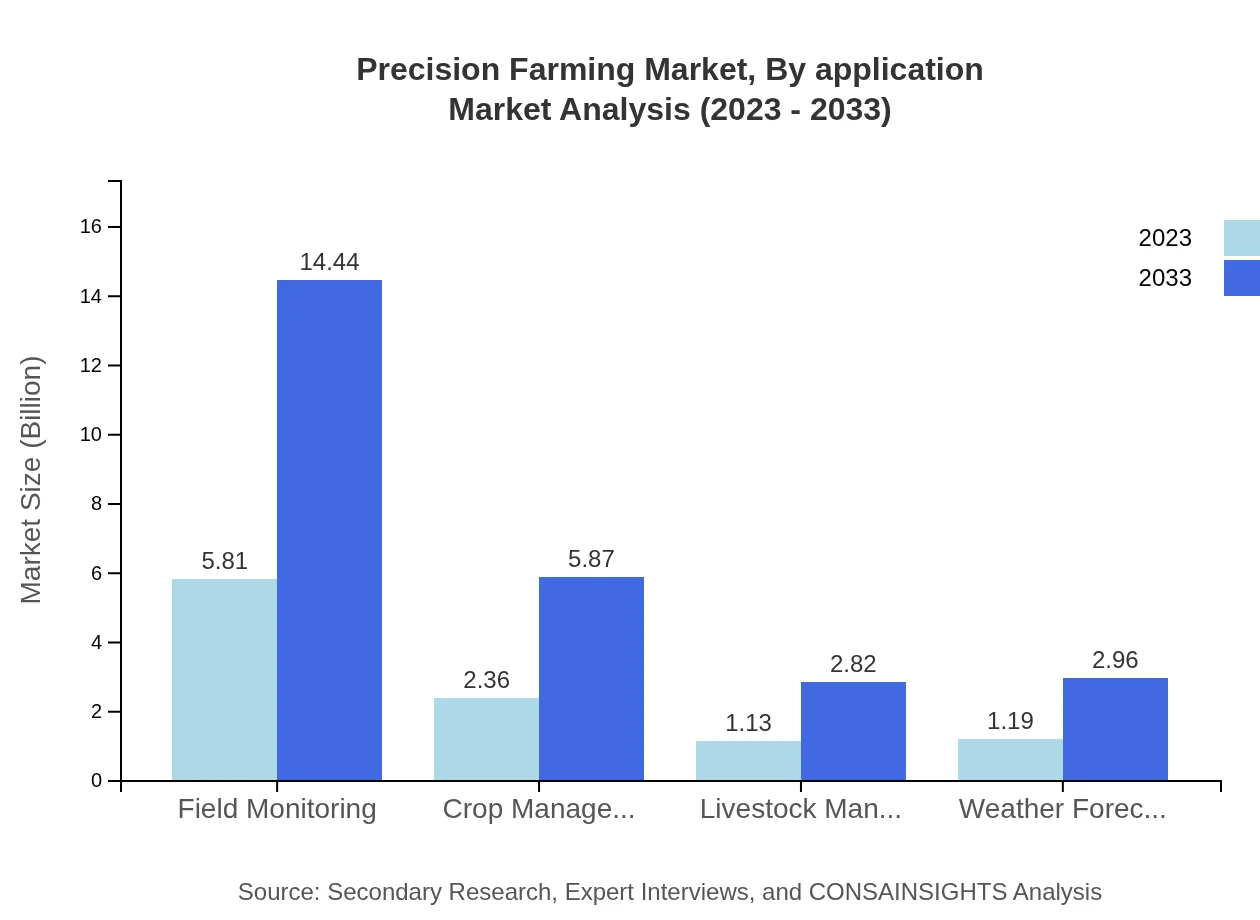
Segmented by applications, Field Monitoring leads with substantial market share driven by its critical role in maximizing crop yields. In 2023, it holds $5.81 billion and is projected to reach $14.44 billion by 2033. Crop Management follows closely, growing from $2.36 billion in 2023 to $5.87 billion by 2033, reflecting critical investment in data-driven farming solutions. Livestock Management, Weather Forecasting, and applications aimed at addressing Organic Farming and Conventional Farming needs are also relevant segments in this growing industry.
Precision Farming Market Analysis By Farming Type
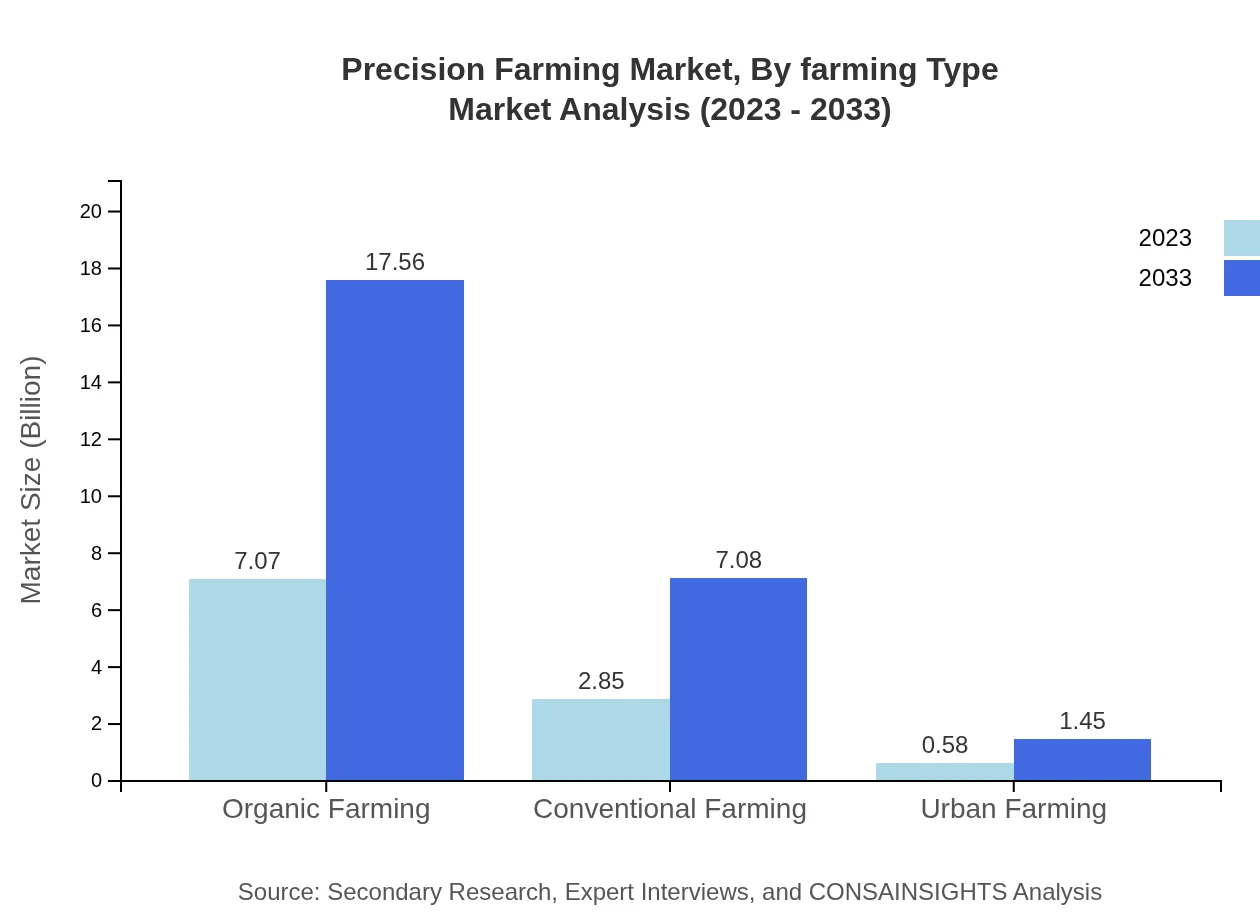
The Precision Farming market is also segmented by farming types, notably Organic Farming and Conventional Farming. Organic Farming occupies a substantial market share, expecting to grow from $7.07 billion in 2023 to $17.56 billion by 2033. In contrast, Conventional Farming is set for growth from $2.85 billion in 2023 to $7.08 billion by 2033. Urban Farming is a smaller but promising segment, growing from $0.58 billion to $1.45 billion by 2033, driven by increasing urbanization and the need for local food production.
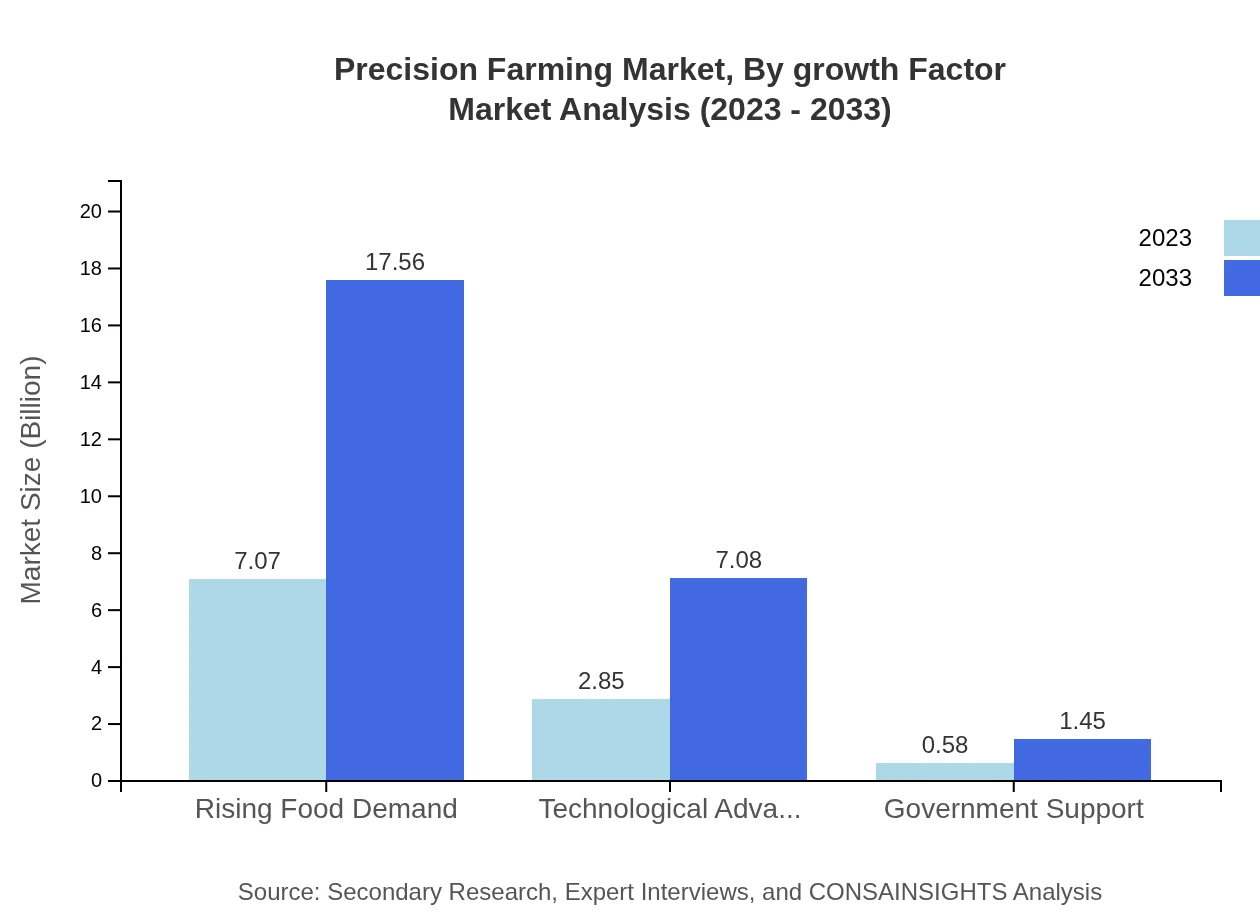
Precision Farming Market Analysis By Growth Factor
The market's growth factors include Rising Food Demand, Technological Advancements, and Government Support. Rising Food Demand is a significant growth factor with a value of $7.07 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $17.56 billion by 2033. Technological Advancements follow suit, expecting to increase from $2.85 billion to $7.08 billion during the same period. Government Support plays a notable role as well, estimated to grow from $0.58 billion in 2023 to $1.45 billion by 2033, as initiatives promote the adoption of smarter farming practices.
Precision Farming Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Precision Farming Industry
John Deere:
A major player in agricultural machinery, John Deere is at the forefront of precision farming, providing advanced equipment and technology solutions for maximizing farm productivity.Trimble Inc.:
Trimble is a leader in geospatial technology serving the agriculture sector with precision GPS solutions, enhancing field mapping and crop management practices.AG Leader Technology:
AG Leader offers precision farming solutions that provide farmers with tools for better decision-making based on data analytics.Raven Industries:
Specializing in technology to improve crop yields and empower farmers, Raven Industries focuses on field computers and precision application systems.Topcon Positioning Systems:
Topcon offers innovative solutions in agricultural technology, enhancing productivity through precision positioning and measuring systems.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of precision Farming?
The precision farming market is valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 9.2% through 2033. This growth reflects increasing adoption of advanced agricultural technologies, resulting in optimized resource management and better yield outcomes.
What are the key market players or companies in this precision Farming industry?
Several key players dominate the precision farming landscape, including John Deere, Trimble, Ag Leader Technology, and AG Leader. These companies leverage innovative technologies to deliver comprehensive solutions that enhance agricultural productivity.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the precision farming industry?
Growth in the precision farming sector is driven by factors such as rising food demand, technological advancements, and government support initiatives. Adopting smart farming techniques significantly boosts yield and reduces resource waste.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the precision farming?
North America is currently experiencing the fastest growth in the precision farming market, projected to grow from $3.45 billion in 2023 to $8.56 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by advanced agricultural practices and technology implementation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the precision Farming industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the precision farming industry. Clients can request specific analyses based on their unique needs and strategic objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this precision Farming market research project?
From the precision farming market research project, you can expect comprehensive data reports, trend analyses, market forecasts, competitive landscape insights, and segment performance evaluations for informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of precision farming?
Key market trends in precision farming include increased implementation of IoT solutions, advancements in robotics, and enhanced field monitoring techniques. These trends signify a shift towards integrated technological solutions for agricultural efficiency.