Rolling Stock Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: rolling-stock
Rolling Stock Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Rolling Stock market from 2023 to 2033, focusing on market size, trends, segmentation, regional insights, and future forecasts. It provides valuable insights for stakeholders looking to understand market dynamics in the coming years.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
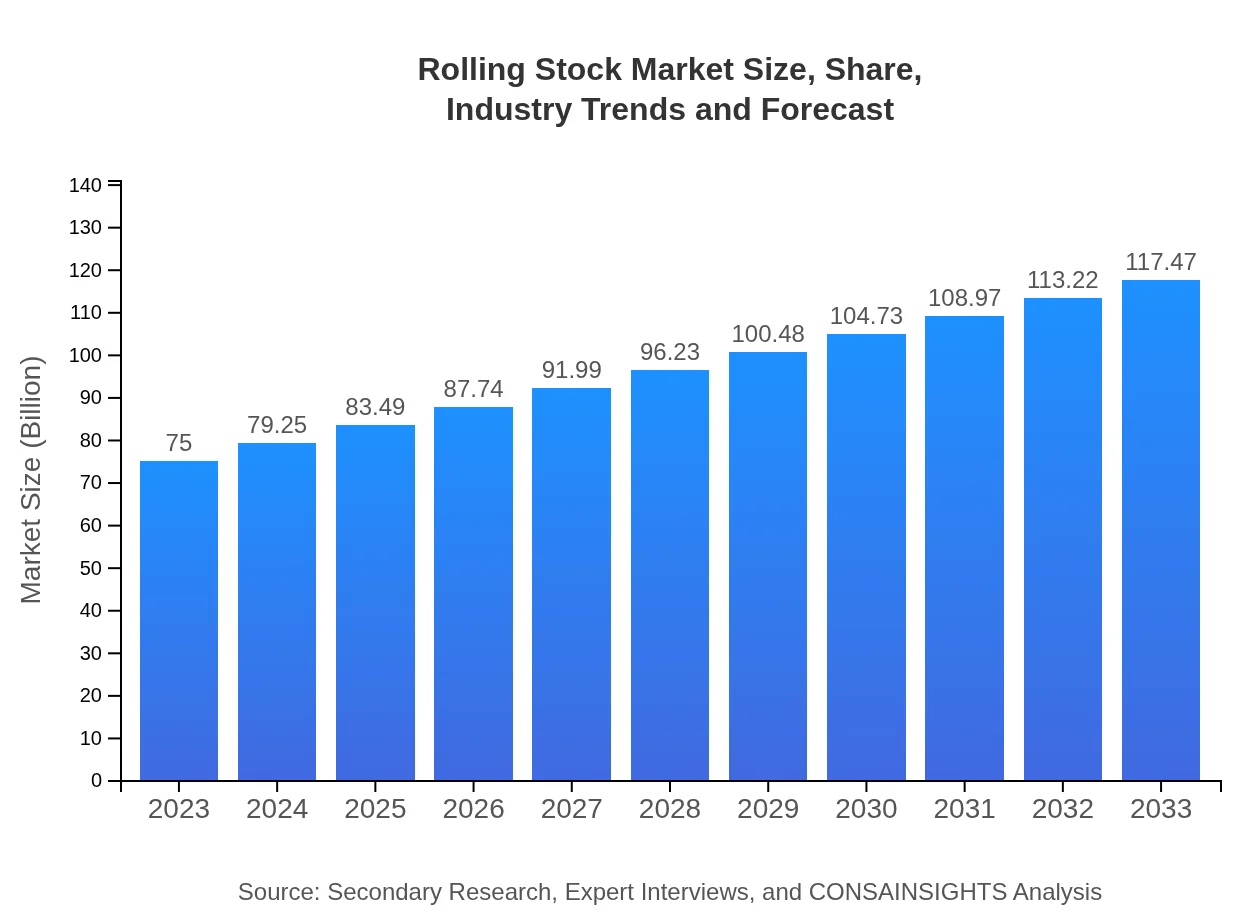
| 2023 Market Size | $75.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $117.47 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Alstom SA, Bombardier AEROSPACE, CRRC Corporation Limited |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Rolling Stock Market Overview
Customize Rolling Stock Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Rolling Stock market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Rolling Stock's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Rolling Stock
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Rolling Stock market in 2023?
Rolling Stock Industry Analysis
Rolling Stock Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Rolling Stock Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Rolling Stock Market Report:
Europe's market was valued at $24.99 billion in 2023, growing to about $39.14 billion by 2033. The trend is driven by stringent environmental regulations, investments in high-speed rail projects, and the transition towards electrification and automation in the rail sector.Asia Pacific Rolling Stock Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's rolling stock market was valued at approximately $14.25 billion, expected to grow to around $22.32 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rapid urbanization, significant government investments in rail infrastructure, and increasing demand for efficient public transportation solutions that align with sustainable practices.North America Rolling Stock Market Report:
North America's rolling stock market was valued at approximately $24.53 billion in 2023, with expectations to reach around $38.41 billion by 2033. The region benefits from long-standing rail systems and increased freight transport, alongside a shift towards cleaner energy and technology integration.South America Rolling Stock Market Report:
The South American market, valued at $6.53 billion in 2023, is projected to increase to $10.23 billion by 2033. Challenges remain in the form of economic disparities and infrastructure constraints, yet the push for improved rail connectivity and the adoption of modern rolling stock are driving markets in key countries.Middle East & Africa Rolling Stock Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa rolling stock market was estimated at $4.70 billion in 2023, expected to reach $7.37 billion by 2033. Investment in railway infrastructure and urban development projects in the Gulf region enhance demand for modern rolling stock solutions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
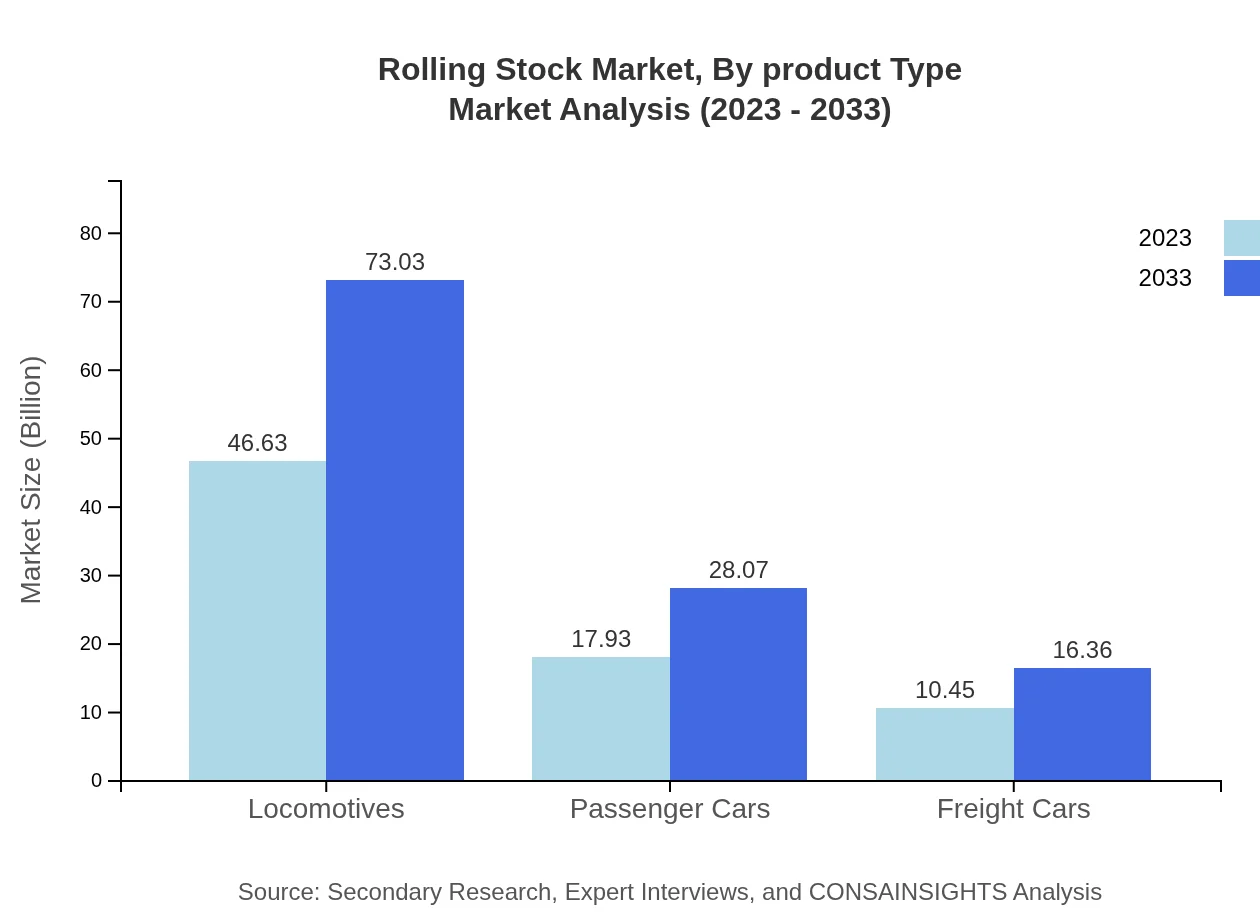
Rolling Stock Market Analysis By Product Type
The rolling stock market showcases diverse product types, including locomotives, passenger cars, and freight cars. In 2023, locomotives constitute approximately $46.63 billion and are expected to grow to around $73.03 billion by 2033. Passenger and freight cars also show promising growth, with values progressing from $17.93 billion to $28.07 billion for passenger cars and $10.45 billion to $16.36 billion for freight cars during the same period.
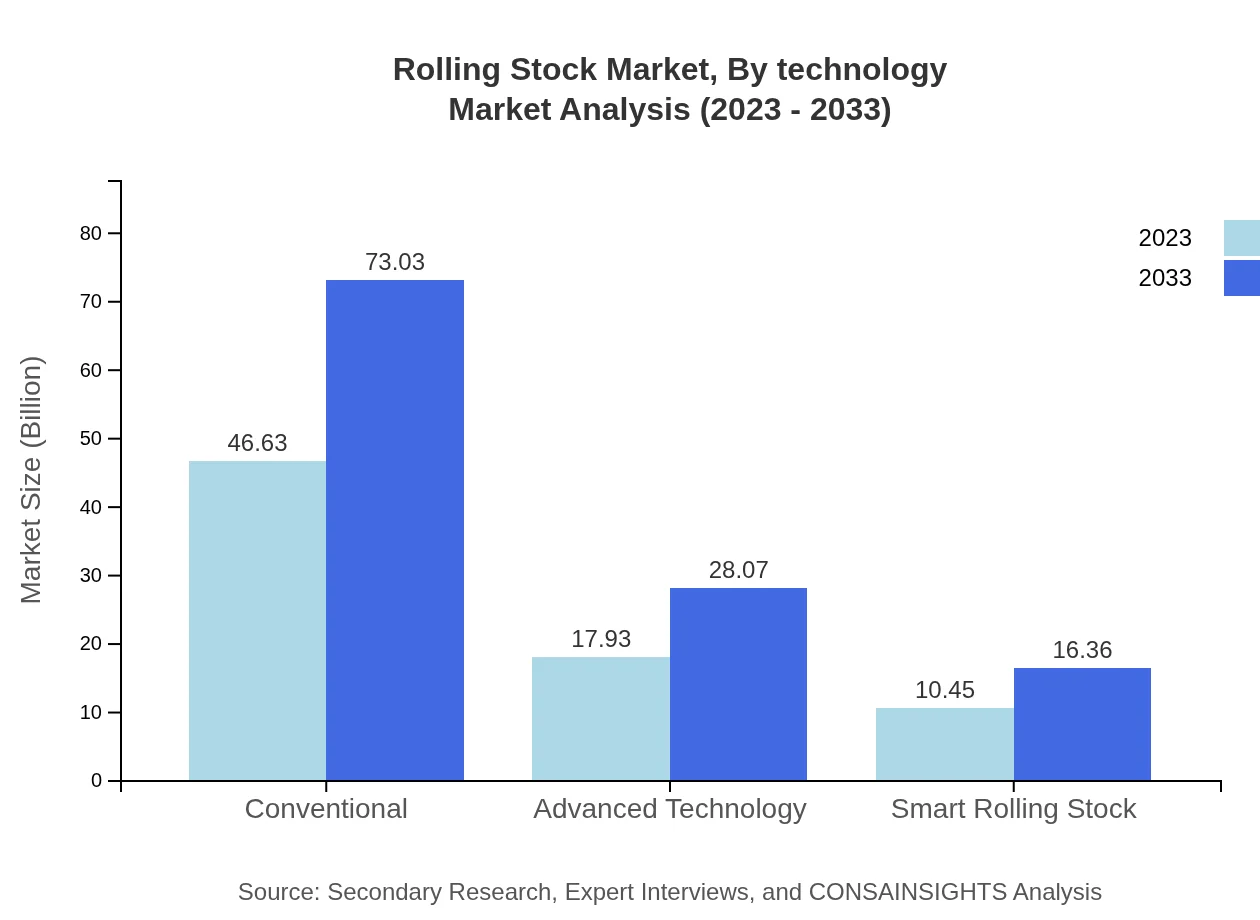
Rolling Stock Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancement plays a crucial role in the rolling stock market, with segments including conventional systems and advanced technology solutions. The market for advanced technologies, including smart rolling stock, is estimated to grow significantly, transitioning from $17.93 billion in 2023 to $28.07 billion by 2033.
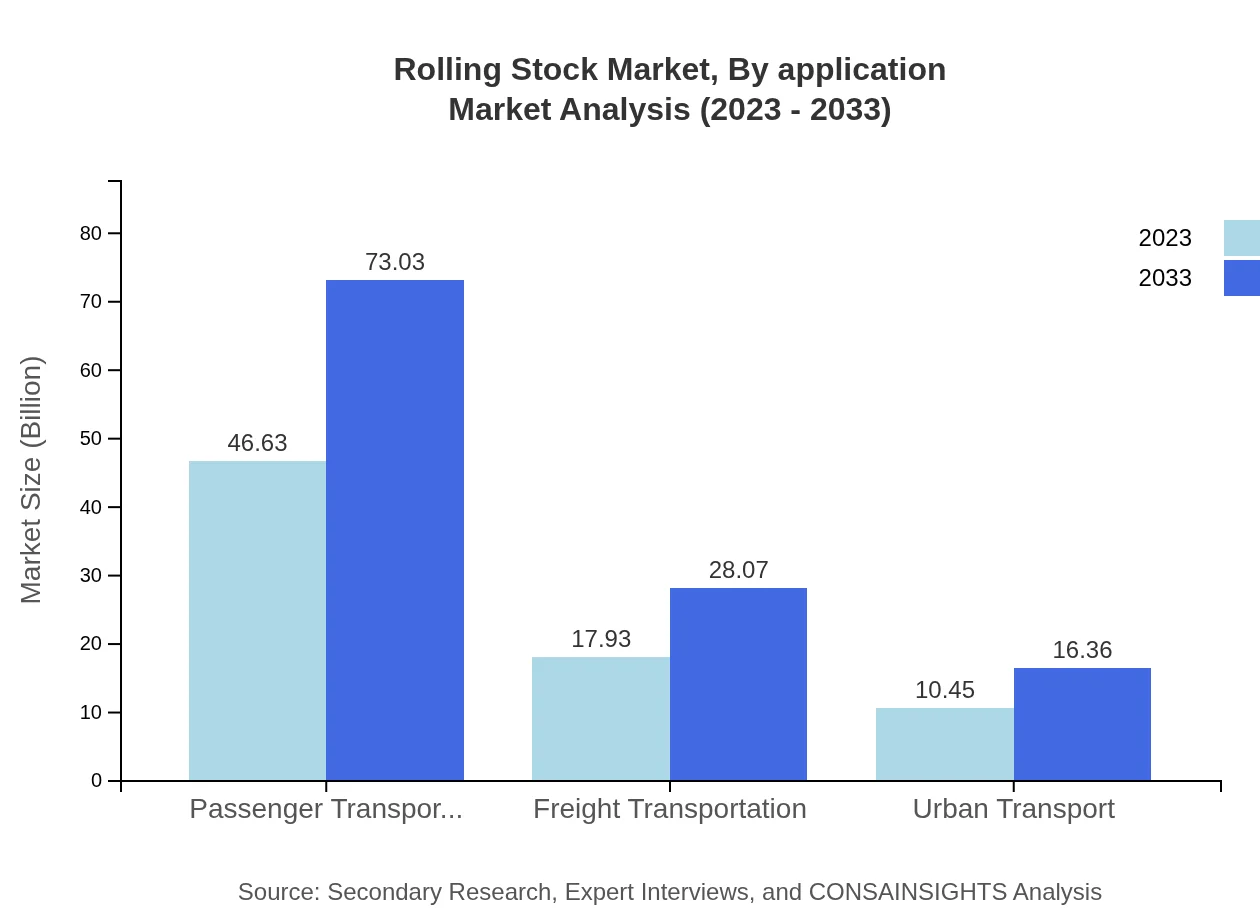
Rolling Stock Market Analysis By Application
The rolling stock market spans various applications, primarily passenger transportation and freight transportation. Passenger transport remains dominant, with a market size of $46.63 billion in 2023, projected to increase to $73.03 billion by 2033, driven by urbanization and increased mobility. Freight transport also sees growth, moving from $17.93 billion to $28.07 billion in the same timeframe.
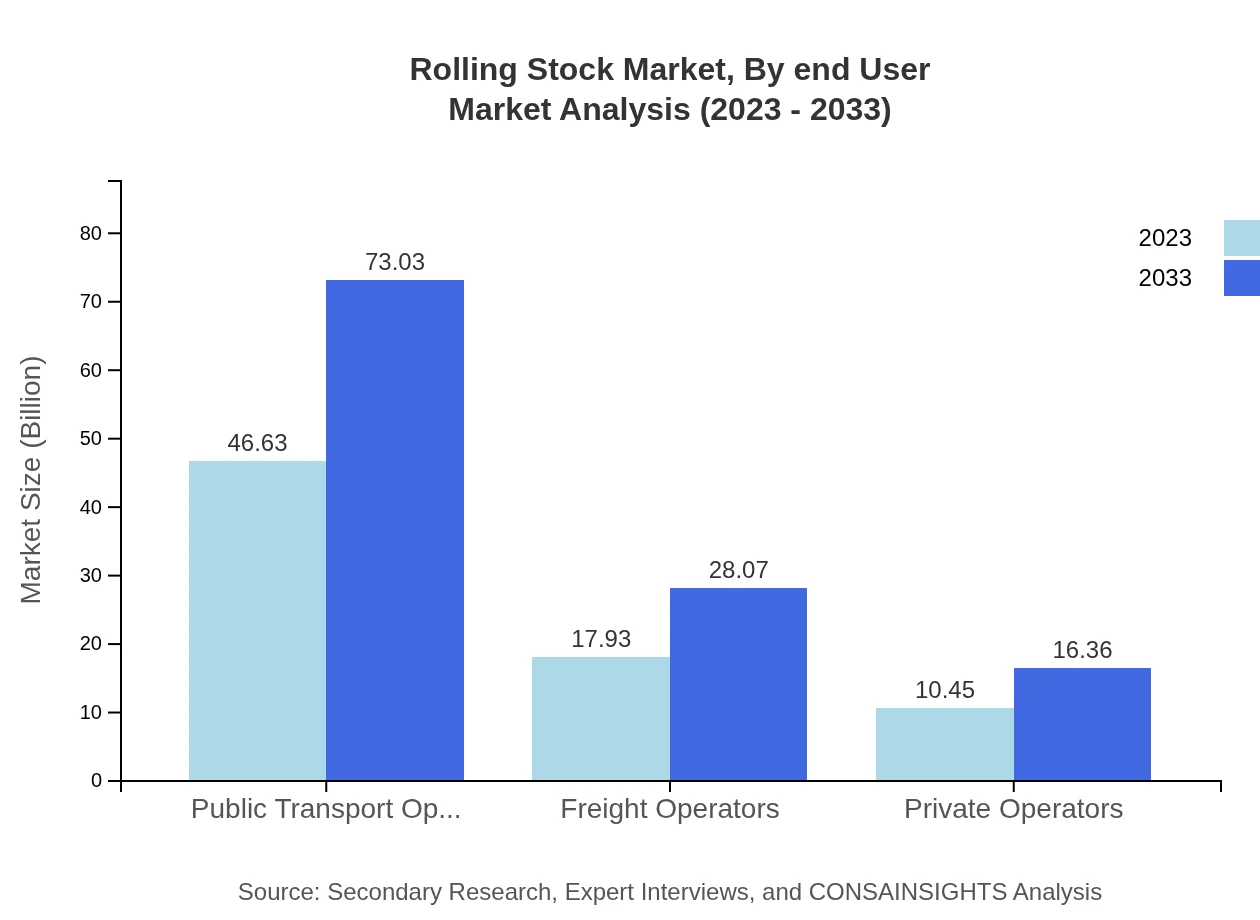
Rolling Stock Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users in the rolling stock industry consist of public transport operators, freight operators, and private operators. Public transport operators are the largest segment, with revenues around $46.63 billion in 2023, indicating strong demand. The freight operator segment is also growing, increasing from $17.93 billion in 2023 to $28.07 billion by 2033.
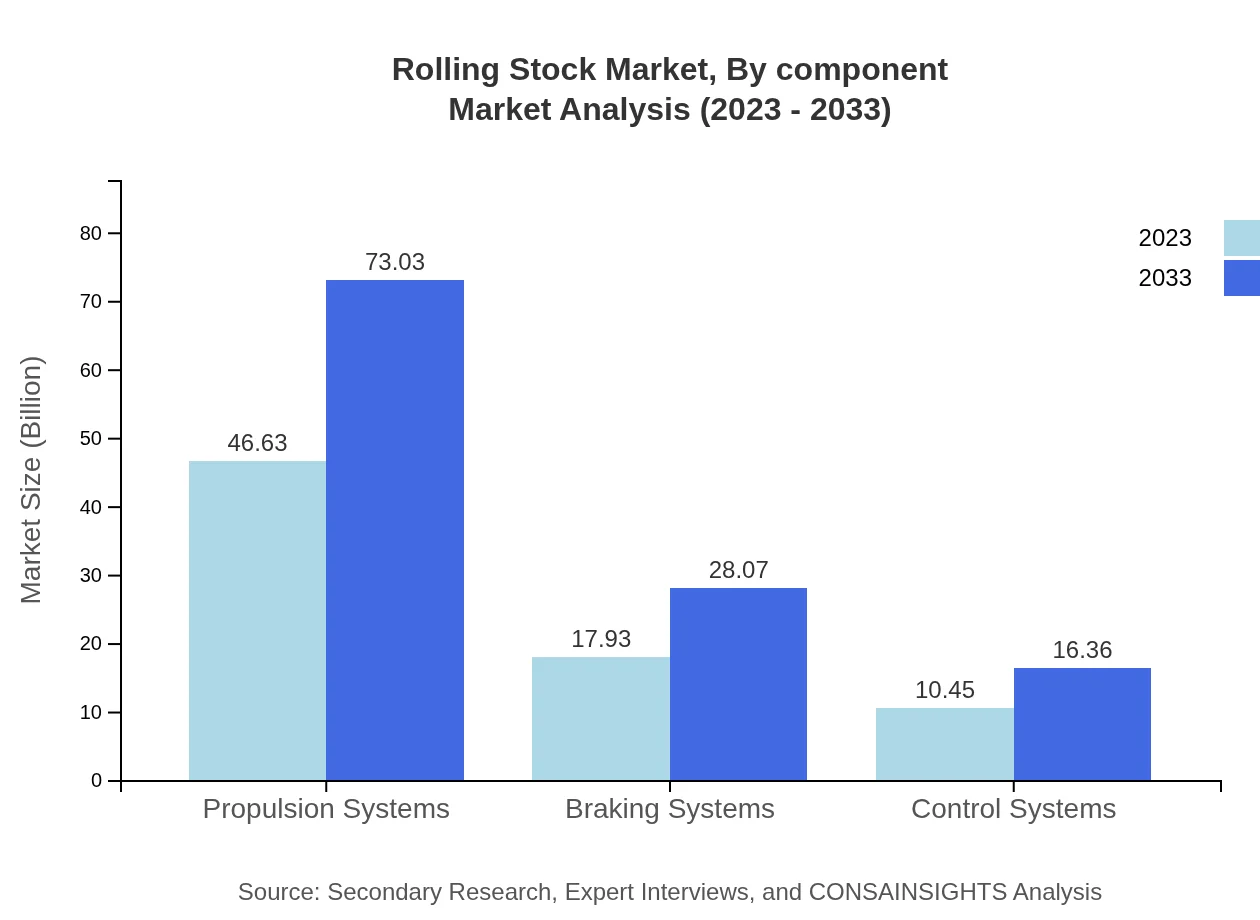
Rolling Stock Market Analysis By Component
Rolling stock components encompass propulsion systems, braking systems, and control systems. Propulsion systems are substantial, with a market value of $46.63 billion projected to grow significantly by 2033. Braking and control systems also represent vital segments, contributing equally to functionality and safety in the overall rolling stock market.
Rolling Stock Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Rolling Stock Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a leading player in the rolling stock market, known for its innovative rail vehicles and technologies. The company's focus on sustainability and modernization enhances its competitive edge in both the passenger and freight sectors.Alstom SA:
Alstom SA is recognized for its commitment to high-speed trains and innovative rail solutions, impacting the global rolling stock market significantly. The company emphasizes electric train technology and digital rail solutions.Bombardier AEROSPACE:
Bombardier is a notable name in the rail transport sector, manufacturing various types of rolling stock, including passenger and freight trains. Innovation and global presence bolster its market position.CRRC Corporation Limited:
The largest rolling stock manufacturer in China, CRRC plays a significant role in the global market, emphasizing technology and efficiency in its extensive portfolio.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of rolling Stock?
The global rolling stock market is valued at approximately $75 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.5% through 2033, indicating steady growth as demand for advanced transport solutions increases.
What are the key market players or companies in this rolling Stock industry?
Key players in the rolling stock market include major manufacturers and service providers who play pivotal roles in the production and maintenance of trains and rail equipment globally, enhancing operational efficiencies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the rolling stock industry?
Growth in the rolling stock industry is driven by urbanization, increased freight transportation needs, government initiatives for transportation infrastructure, and the integration of advanced technologies in rail systems.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the rolling stock?
Europe is the fastest-growing region in the rolling stock market, projected to expand from $24.99 billion in 2023 to $39.14 billion by 2033, reflecting significant investment in railway upgrades and expansion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the rolling stock industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the rolling stock industry, allowing stakeholders to gain insights specific to their needs, which enhances strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this rolling stock market research project?
Expect detailed insights including market size, growth rates, competitive analysis, trends, forecasts, and actionable recommendations specific to various segments of the rolling stock industry.
What are the market trends of rolling stock?
Current market trends in rolling stock include increasing digitalization, sustainability initiatives, the rise of smart transportation solutions, and a focus on enhancing safety and efficiency in rail networks.