String Inverter Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: string-inverter
String Inverter Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the String Inverter market from 2023 to 2033, detailing market size, industry analysis, segmentation, regional insights, technology trends, and forecasts to provide comprehensive insights into market dynamics and future trajectories.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
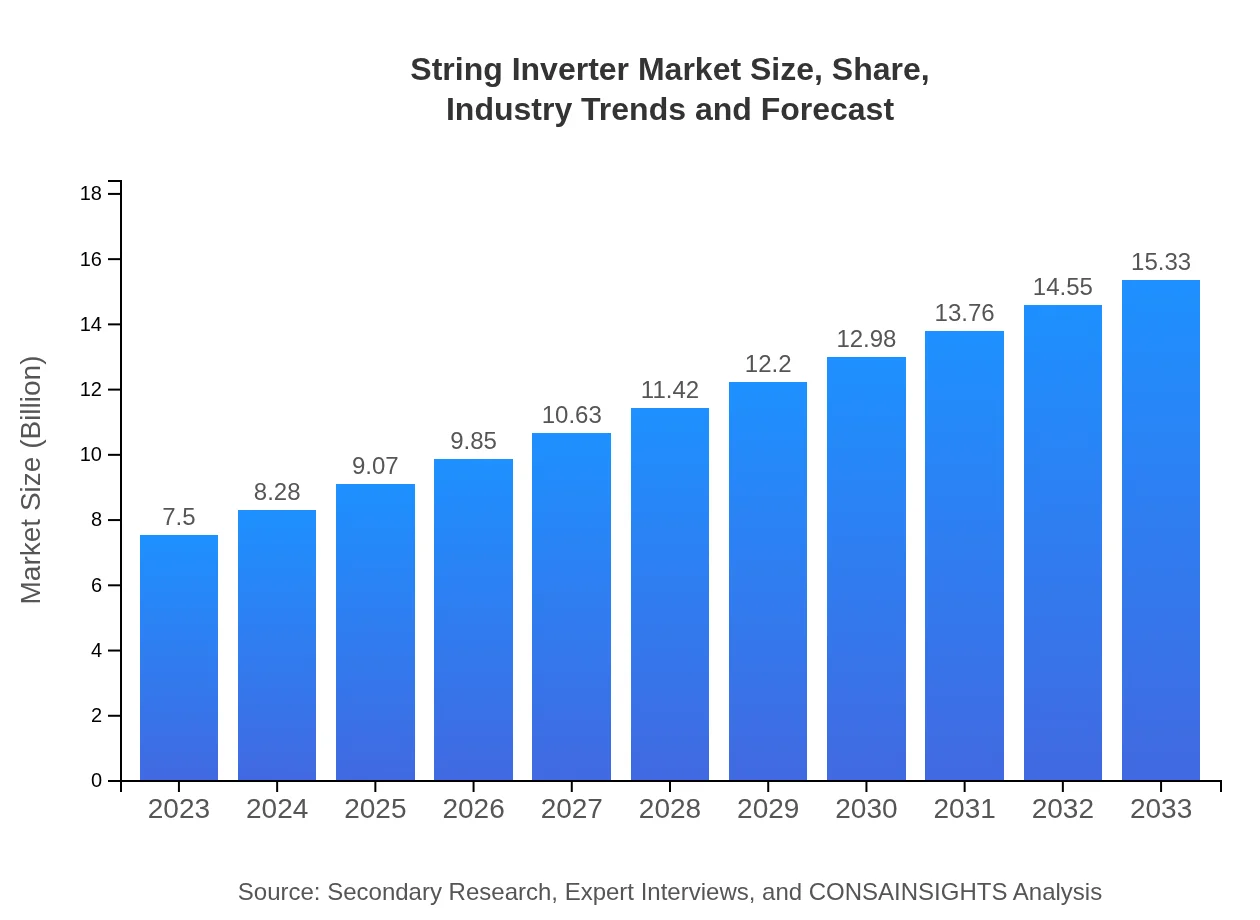
| 2023 Market Size | $7.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $15.33 Billion |
| Top Companies | SMA Solar Technology AG, Fronius International GmbH, SolarEdge Technologies, Inc., Enphase Energy, ABB Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
String Inverter Market Overview
Customize String Inverter Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of String Inverter market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand String Inverter's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in String Inverter
What is the Market Size & CAGR of String Inverter market in 2023?
String Inverter Industry Analysis
String Inverter Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
String Inverter Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe String Inverter Market Report:
Europe’s market for String Inverters is also expanding, valued at $2.46 billion in 2023 and anticipated to double to approximately $5.04 billion by 2033, fueled by stringent environmental regulations and stronger consumer awareness regarding renewable energy solutions.Asia Pacific String Inverter Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth in the String Inverter market, with a market value of $1.36 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $2.79 billion by 2033. Countries like China and India are at the forefront, driven by government policies favoring solar energy adoption and increased infrastructure development.North America String Inverter Market Report:
North America holds a substantial share of the market, with its value at $2.62 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $5.35 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads this region, driven by technological innovation and strong policy support for solar energy.South America String Inverter Market Report:
In South America, the String Inverter market is projected to rise from $0.58 billion in 2023 to $1.19 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are significant players, with increasing investments in renewable energy projects powered by the ongoing energy crisis.Middle East & Africa String Inverter Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are witnessing gradual growth, with the market value expected to increase from $0.47 billion in 2023 to $0.97 billion by 2033, as numerous countries are investing in solar energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, especially in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
String Inverter Market Analysis By Product Type
The String Inverter sector can be divided into several product types with distinct performance characteristics. In 2023, the market size for String Inverters is around $1.95 billion, anticipated to grow to $3.99 billion by 2033, highlighting the growing demand for this product in multiple applications.
String Inverter Market Analysis By Application
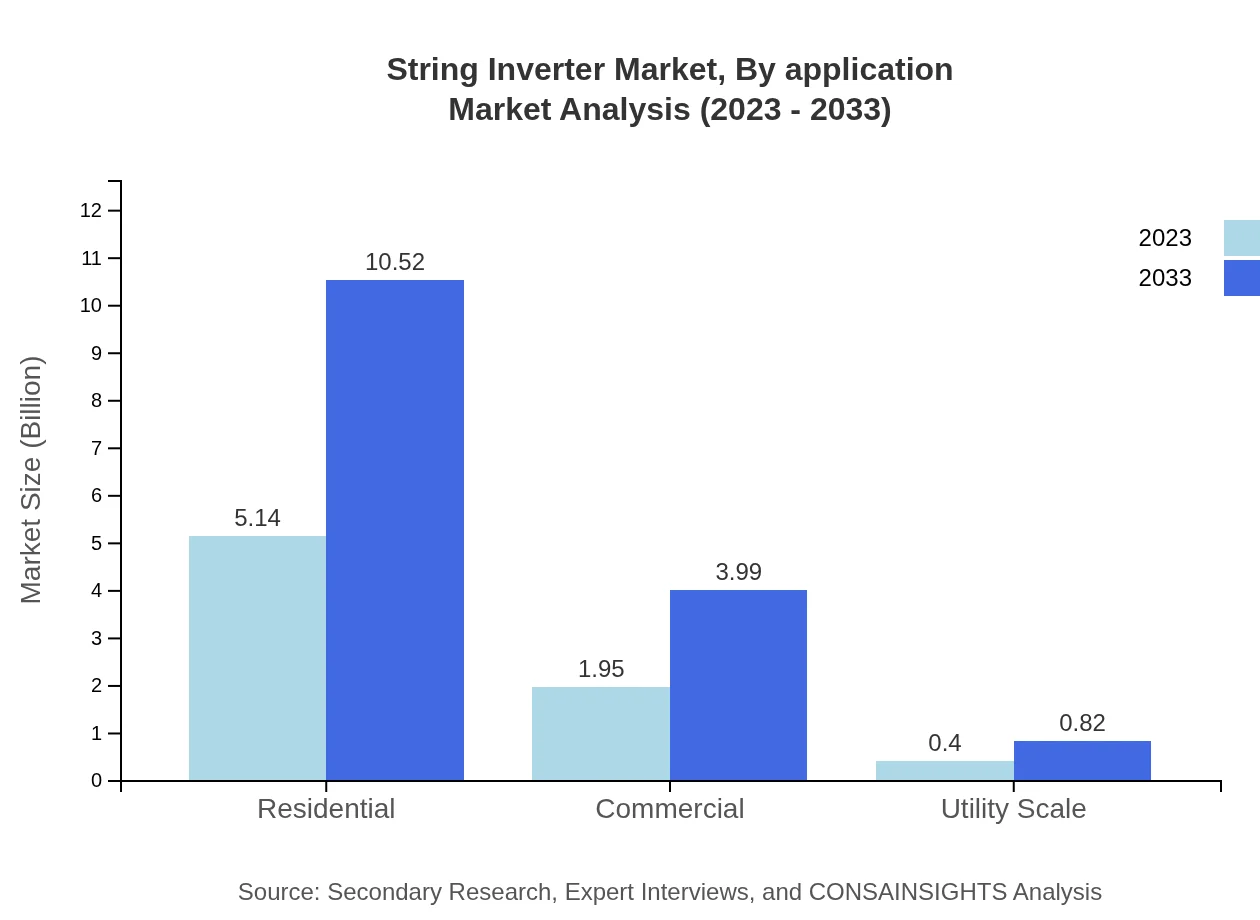
In 2023, residential applications dominate the String Inverter market, accounting for a substantial share of 68.6%. As renewable energy sources become mainstream, the residential segment is expected to grow significantly, reaching 10.52 in the next decade, supporting eco-friendly practices.
String Inverter Market Analysis By Technology
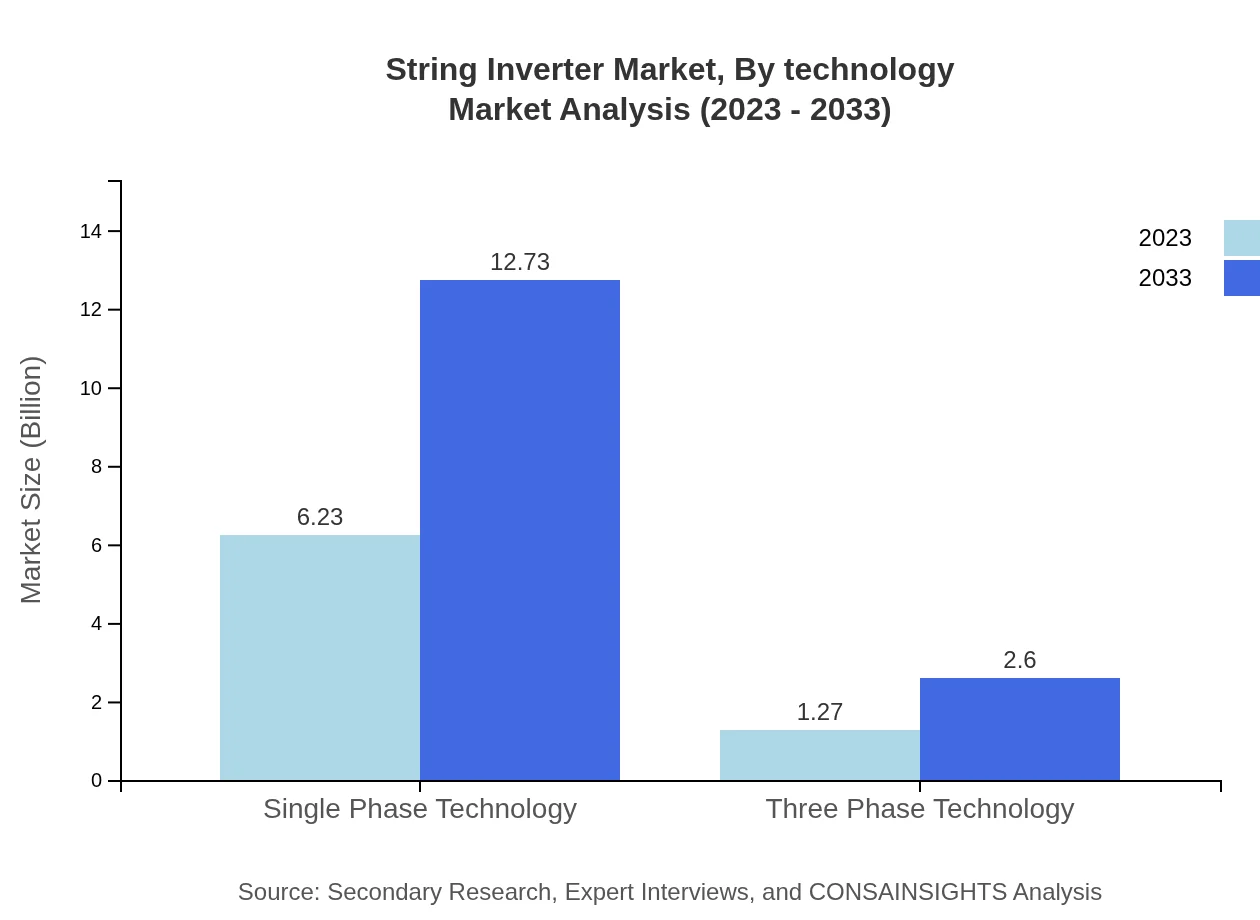
The String Inverter market sees a varied performance between single-phase and three-phase technologies. In 2023, single-phase technology is leading with a market size of $6.23 billion, which is projected to grow to $12.73 billion by 2033, signifying its popularity among residential users.
String Inverter Market Analysis By Connection Type
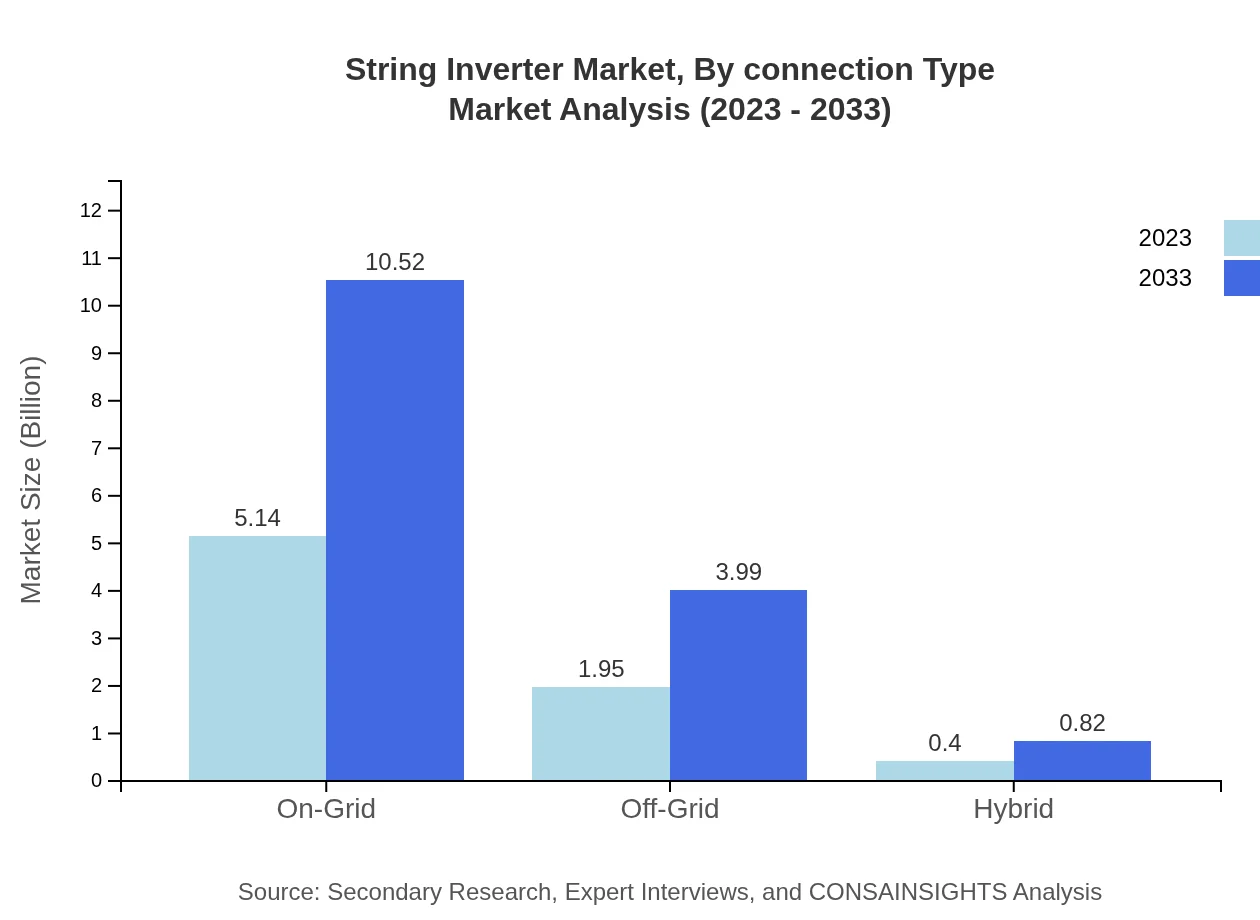
The String Inverter market includes both on-grid and off-grid systems. The on-grid segment holds around 68.6% market share in 2023, mainly due to the growing integration of solar systems into existing electricity grids, with expectations for continued growth through 2033.
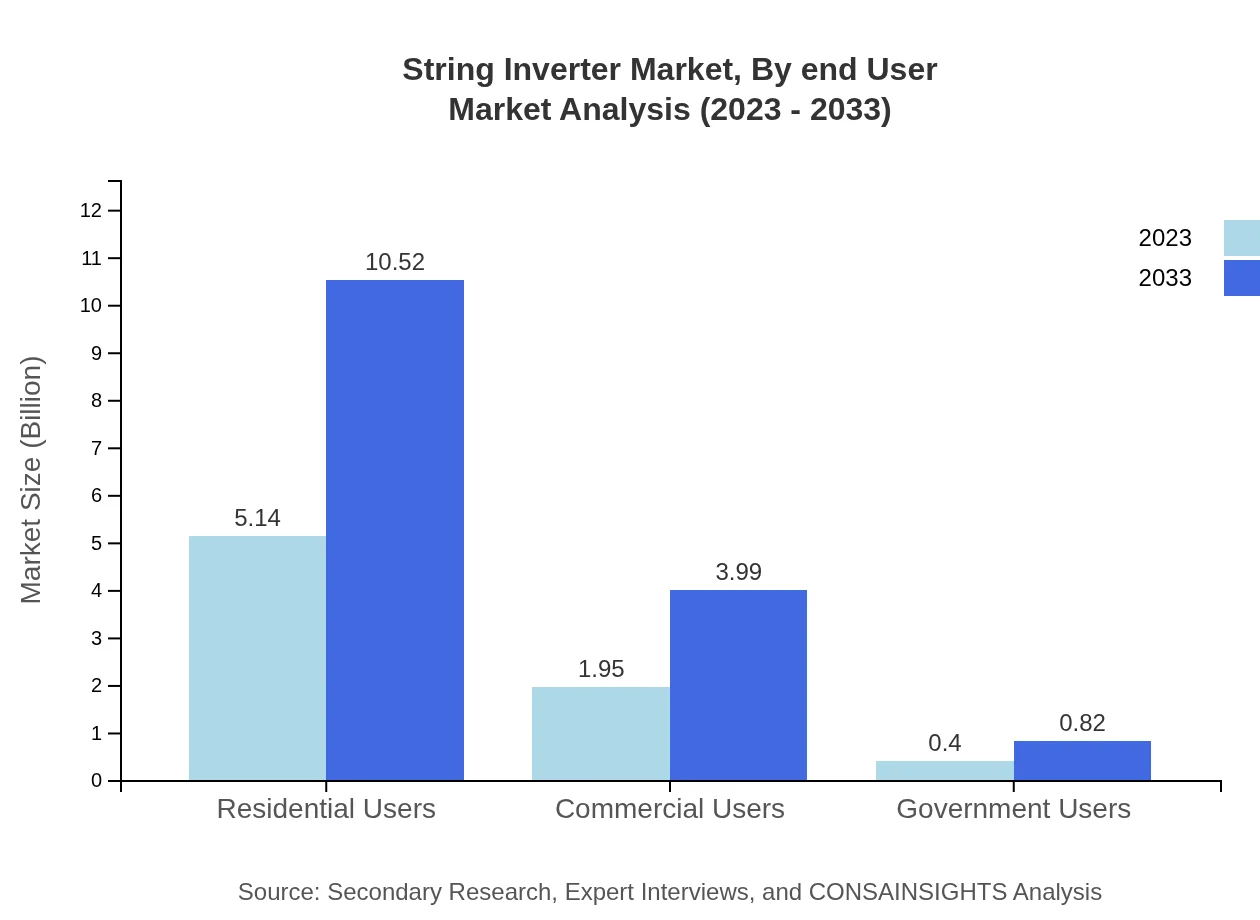
String Inverter Market Analysis By End User
The various end-users include residential, commercial, and government applications. The residential sector leads with expected growth from $5.14 billion in 2023 to $10.52 billion by 2033 owing to sustainable energy goals and incentives encouraging solar installations.
String Inverter Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in String Inverter Industry
SMA Solar Technology AG:
A leading manufacturer of inverter technology that focuses on innovation and sustainability in solar energy systems.Fronius International GmbH:
Known for its quality and efficiency in inverters, Fronius has a strong presence in both residential and commercial markets.SolarEdge Technologies, Inc.:
A pioneer in inverter technologies that maximize power output through optimized string inverters and design.Enphase Energy:
Specializes in microinverters but has expanded into string inverter markets to enhance its product offerings.ABB Ltd.:
A major player in energy technology solutions, ABB has a strong portfolio in solar inverters and energy management systems.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of string inverters?
The global string inverter market is currently valued at approximately $7.5 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% over the next decade, reaching significant milestones by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the string inverter industry?
Leading companies in the string inverter market include SMA Solar Technology AG, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd., Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., and Enphase Energy, which play pivotal roles in market dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the string inverter industry?
Key factors driving the growth of the string inverter industry include the rising adoption of renewable energy sources, advancements in solar technology, and increasing energy efficiency initiatives worldwide.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the string inverter market?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the string inverter market, projected to grow from $2.62 billion in 2023 to $5.35 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust demand for solar solutions.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the string inverter industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the string inverter industry, enabling clients to gain insights that are relevant and actionable.
What deliverables can I expect from this string inverter market research project?
From the string inverter market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, detailed segmentation analysis, and competitive landscape insights.
What are the market trends of string inverters?
Current market trends in the string inverter sector include increased efficiency in solar technologies, a shift towards smart energy systems, and rising preferences for decentralized energy solutions.