Tin Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: tin
Tin Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the tin market, covering trends, regional performances, and future growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It offers insights on market size, segmentation, leading players, and emerging technologies that impact the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
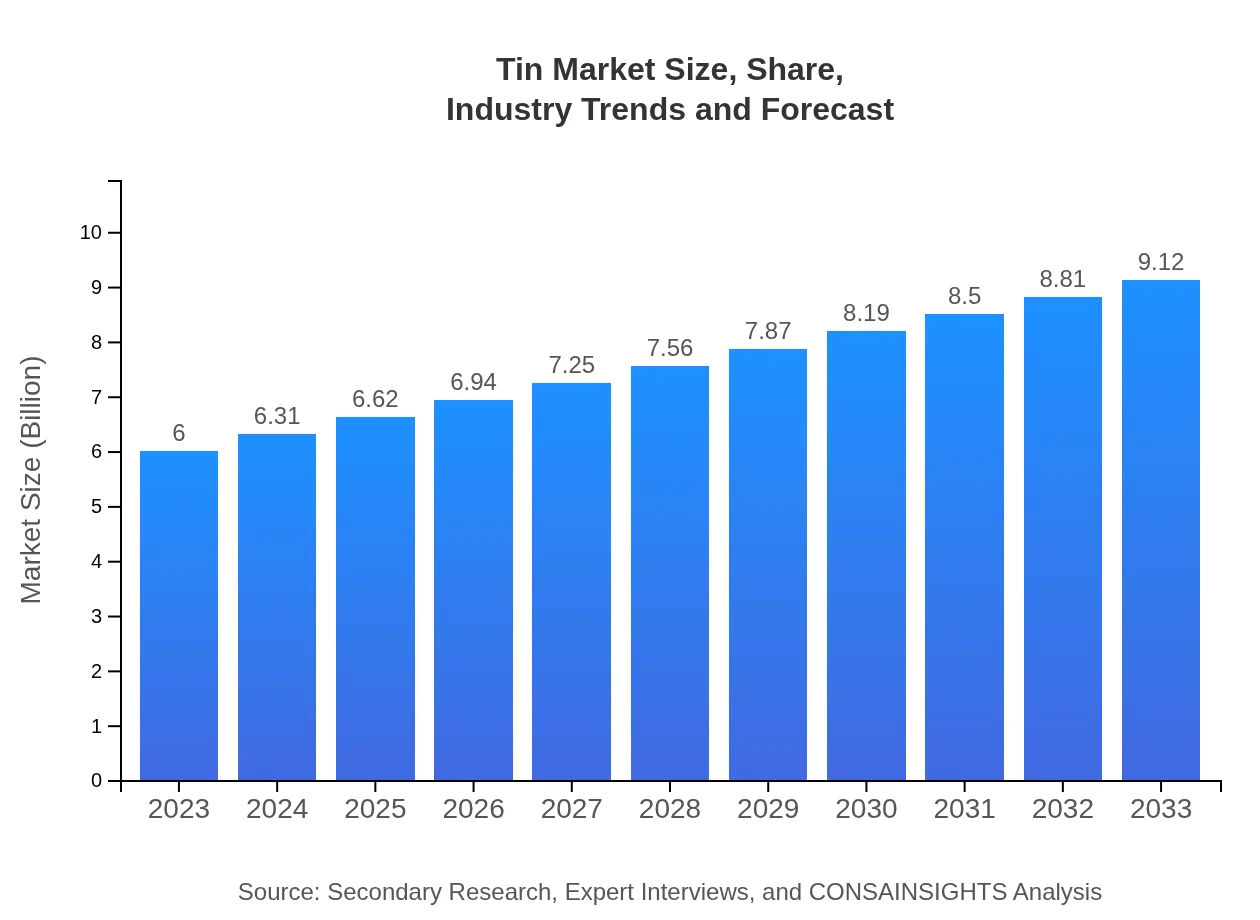
| 2023 Market Size | $6.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $9.12 Billion |
| Top Companies | Yunnan Tin Company Limited, Metallurgical Corporation of China, Minsur, Thai Metal Trade Public Company Limited |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Tin Market Overview
Customize Tin Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Tin market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Tin's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Tin
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Tin market in 2023 & 2033?
Tin Industry Analysis
Tin Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Tin Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Tin Market Report:
Europe's tin market is valued at $1.86 billion in 2023, expected to climb to $2.83 billion by 2033. The region's focus on sustainable manufacturing and the circular economy enhances the role of tin, particularly in the automotive and construction industries.Asia Pacific Tin Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is the largest market for tin, with a valuation of $1.06 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $1.60 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by booming electronics manufacturing in countries like China and India, along with increasing automotive production.North America Tin Market Report:
North America holds a significant market size of $2.27 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $3.45 billion by 2033. The U.S. electronics sector remains a principal driver alongside robust automotive demand.South America Tin Market Report:
In South America, the tin market accounted for $0.17 billion in 2023, expected to reach $0.26 billion by 2033. Countries like Brazil and Bolivia are focusing on mining activities, which are crucial for regional growth.Middle East & Africa Tin Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market was valued at $0.64 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to reach approximately $0.98 billion by 2033. Growth is supported by ongoing investment in mining and processing capabilities, and increased demand for tin in construction applications.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
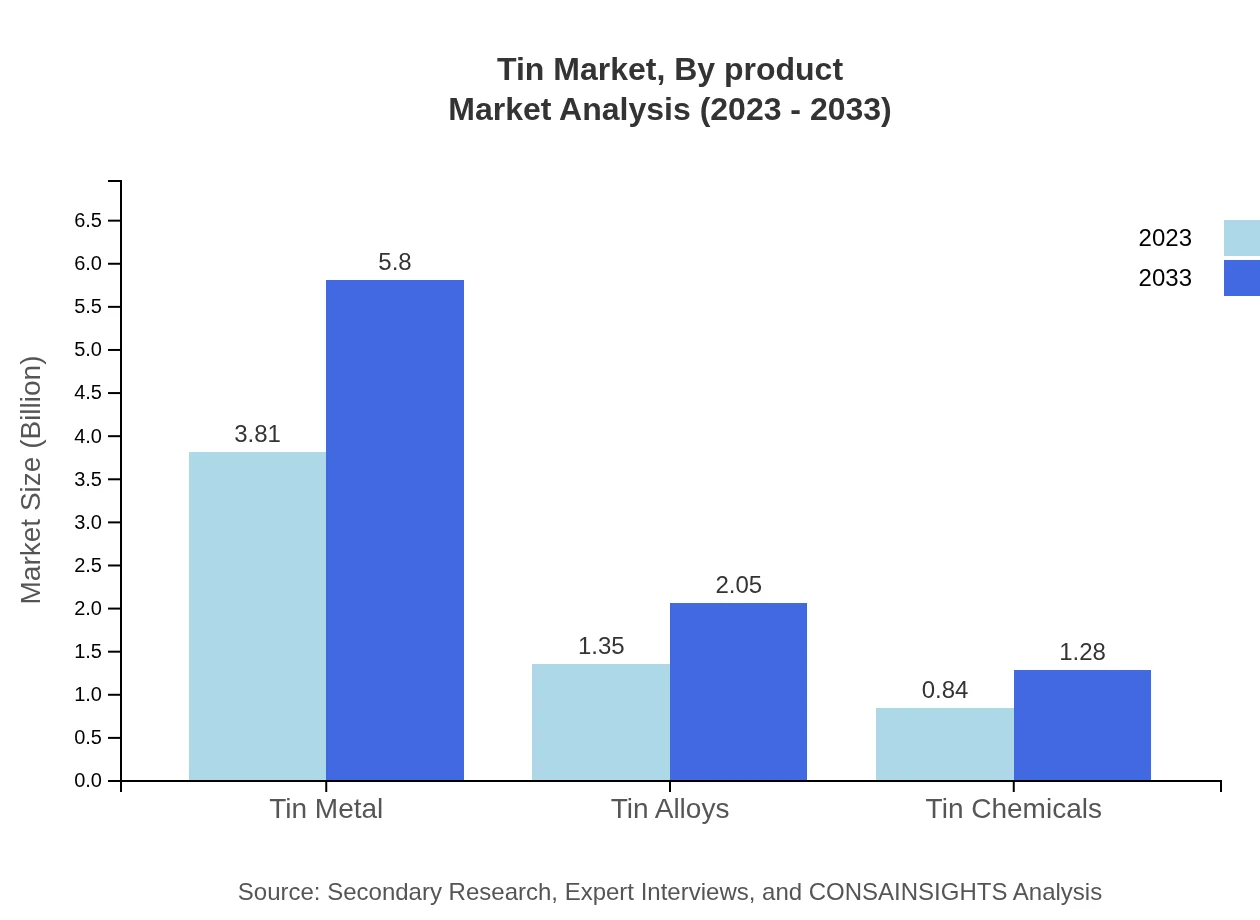
Tin Market Analysis By Product
Tin metal comprises the largest share of the market with a size of $3.81 billion in 2023, projected to reach $5.80 billion by 2033, representing a stable growth trend driven primarily by electronics. Tin alloys, crucial for various applications, account for $1.35 billion in 2023, growing to $2.05 billion by 2033. Tin chemicals, though smaller, show significant growth potential from $0.84 billion to $1.28 billion over the same period.
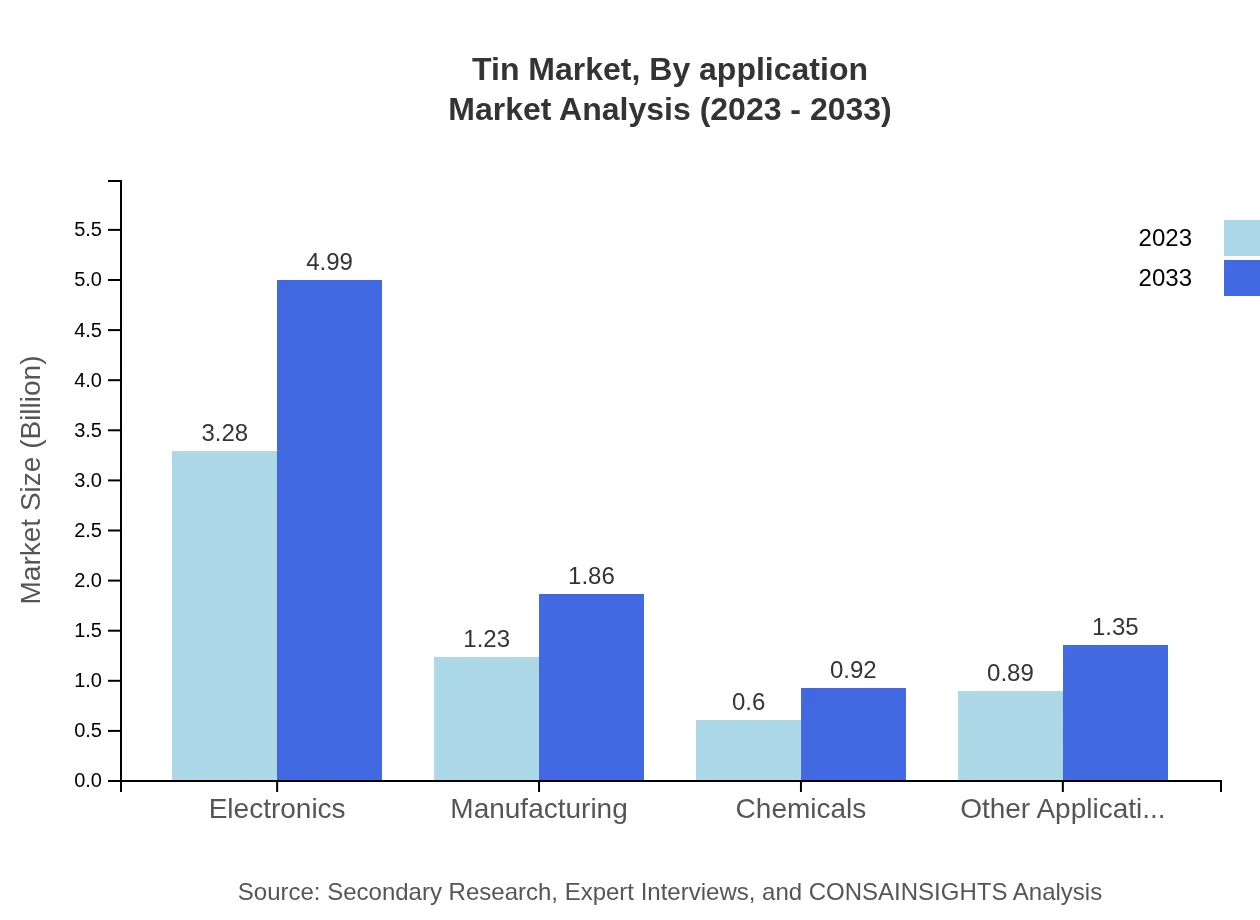
Tin Market Analysis By Application
Consumer electronics dominate the tin application market, valued at $3.28 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $4.99 billion by 2033. The automotive sector accounts for $1.23 billion, with predictions to climb to $1.86 billion. Other sectors like construction and packaging are also gaining a significant share in the market.
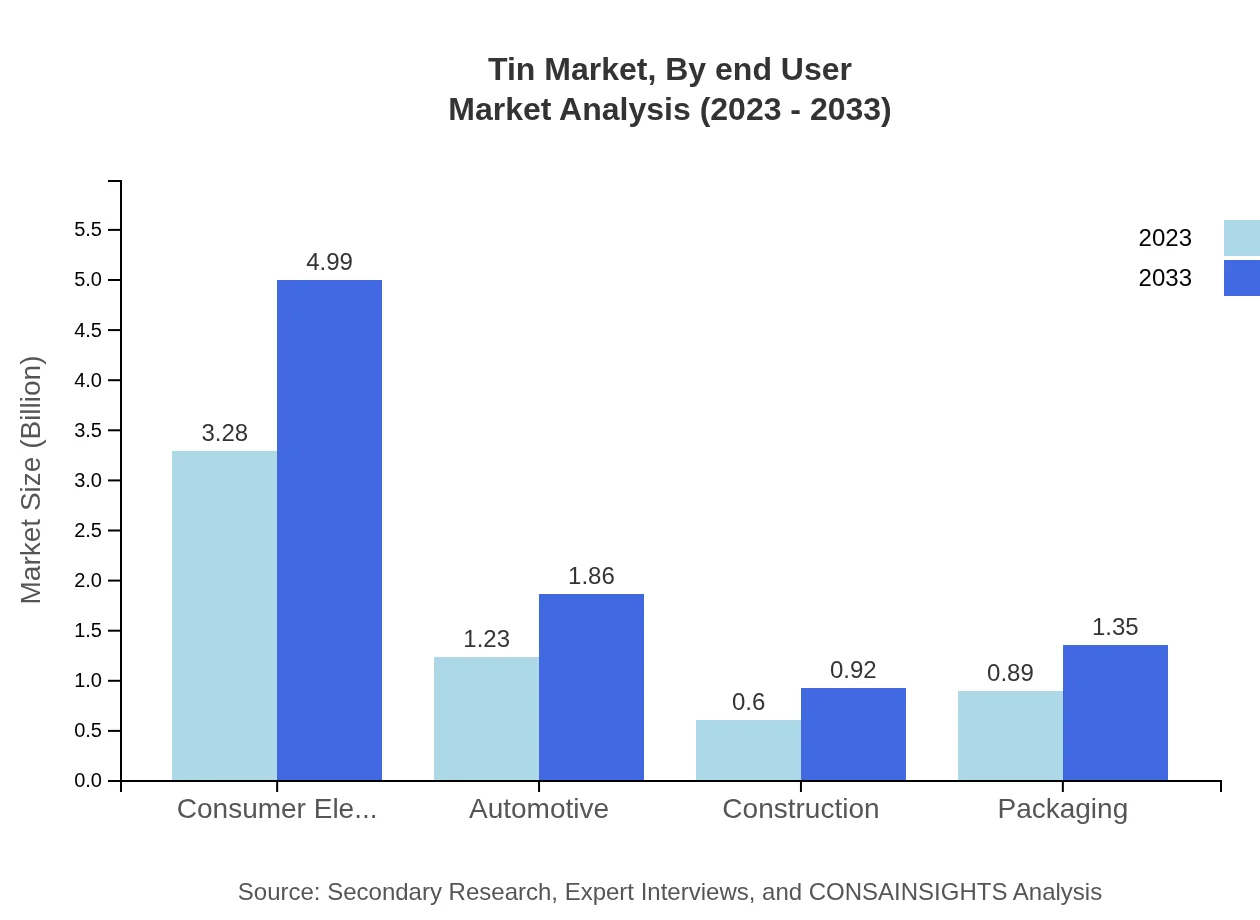
Tin Market Analysis By End User
The electronics and consumer goods industries are the largest end-users of tin, followed by automotive and construction sectors. With the increasing innovation in consumer technologies, demand for tin continues to rise beyond traditional usages.
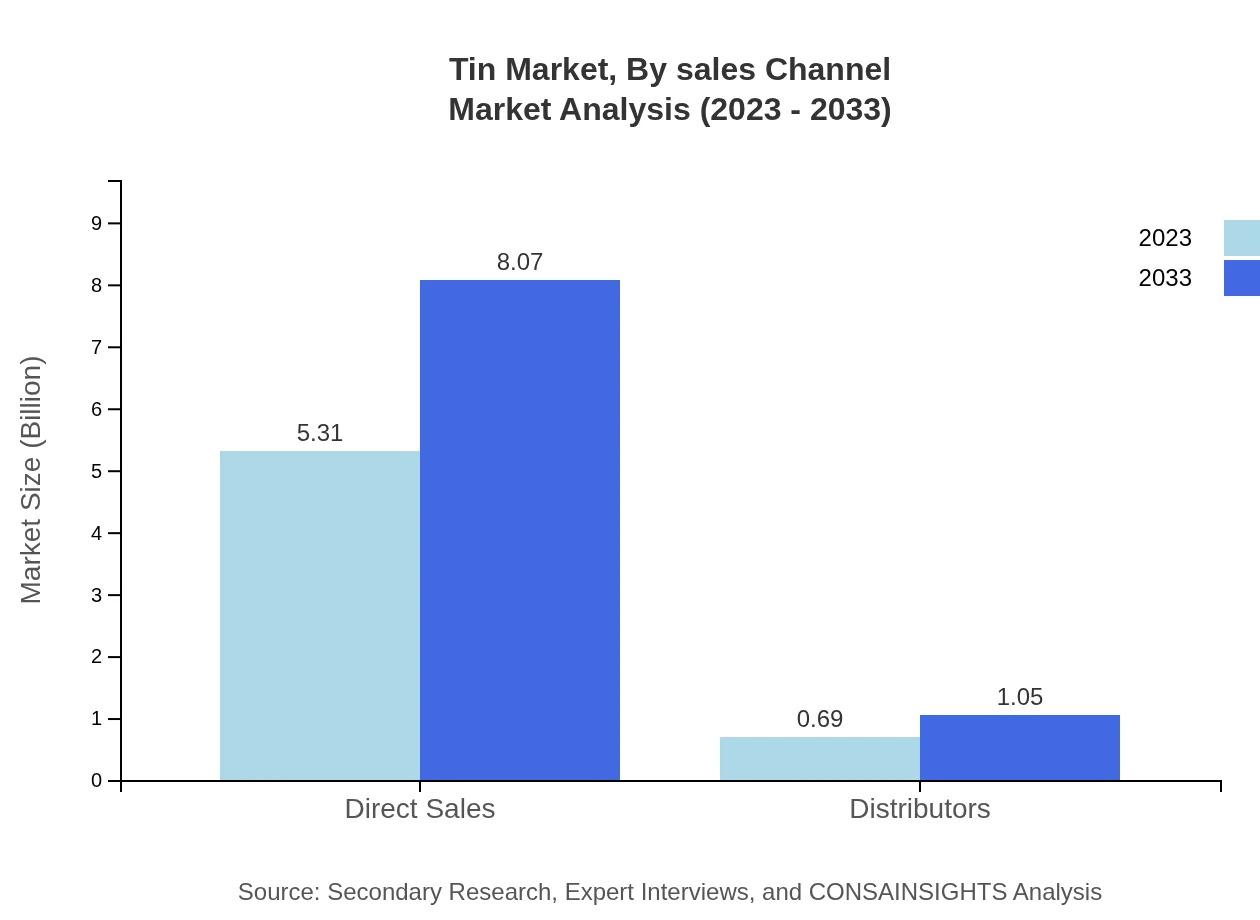
Tin Market Analysis By Sales Channel
Direct sales lead the market, accounting for 88% of the total sales in 2023, projecting clear dominance throughout the forecasted period. Distributors also play a vital role, with a notable market share as they support numerous end-user sectors.
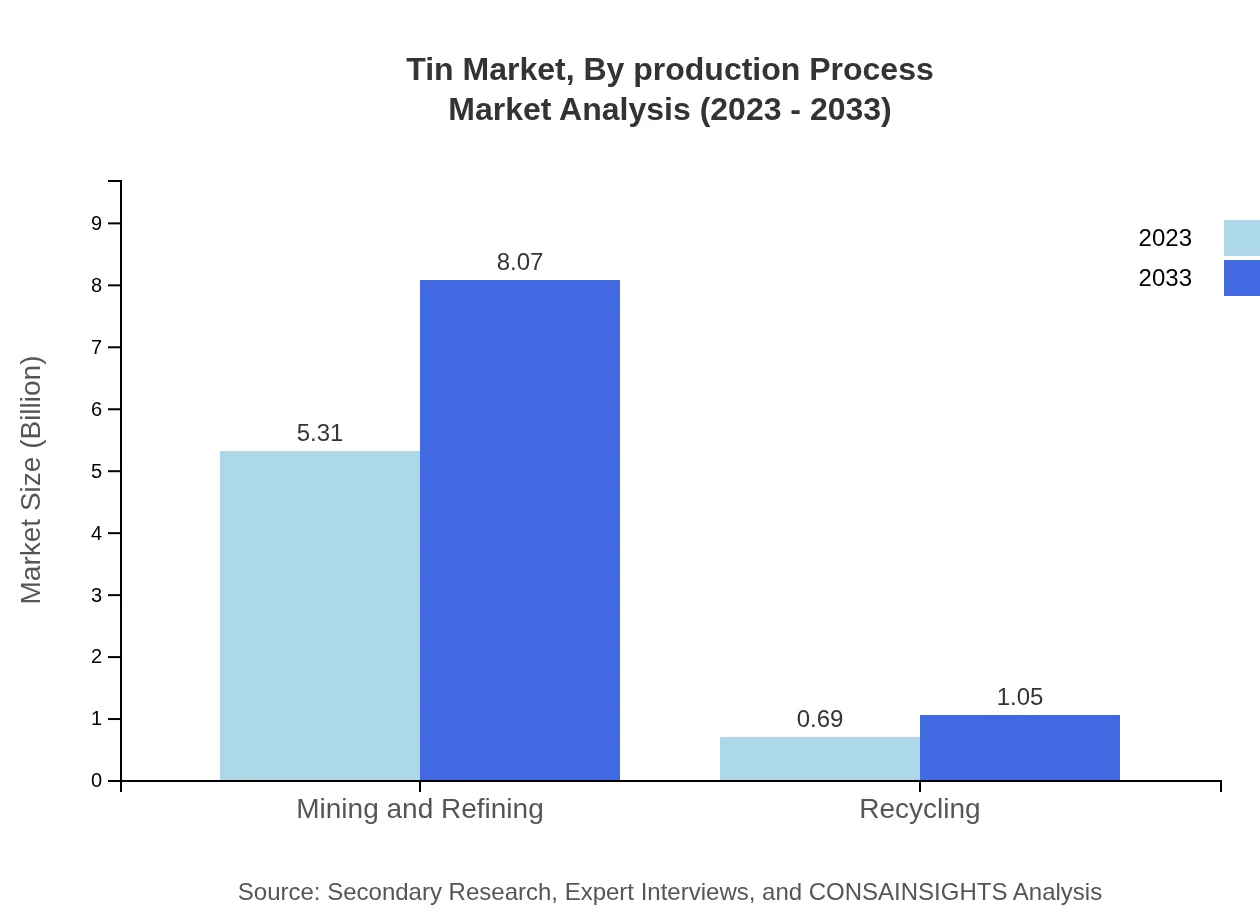
Tin Market Analysis By Production Process
Mining and refining remain the primary processes yielding tin, accounting for the majority of the market. Furthermore, recycling processes are gaining traction, emphasizing sustainability and resource efficiency.
Tin Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Tin Industry
Yunnan Tin Company Limited:
One of the largest producers of tin worldwide, Yunnan Tin plays a significant role in the supply of refined tin and tin alloys.Metallurgical Corporation of China:
A key player in tin production and processing, this corporation has a wide-ranging impact on the global tin supply chain.Minsur:
Based in Peru, Minsur is focused on sustainable tin mining, significantly contributing to the global market through its vast operations.Thai Metal Trade Public Company Limited:
A leading tin trader in Thailand, responsible for a substantial portion of the Southeast Asian tin supply.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of tin?
The global tin market is valued at approximately $6 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.2% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this tin industry?
Key players in the tin market include leading mining and refining companies, tin producers, and manufacturers of tin products, who drive competition and innovation in the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the tin industry?
The growth in the tin industry is primarily driven by increasing demand from the electronics and automotive sectors, coupled with infrastructure development and innovations in tin alloy production.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the tin market?
The fastest-growing region in the tin market is North America, projected to rise from approximately $2.27 billion in 2023 to $3.45 billion by 2033, driven by technological advancements.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the tin industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights provides customized market report data tailored to specific client needs and industry segments within the tin market.
What deliverables can I expect from this tin market research project?
Deliverables from the tin market research project include detailed market analysis reports, growth forecasts, competitor insights, and regional breakdowns.
What are the market trends of tin?
Current trends in the tin market include a shift towards sustainable sourcing, increasing applications in new technologies, and the growing importance of recycling in the supply chain.