Passive Optical Lan Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: passive-optical-lan
Passive Optical Lan Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Passive Optical Lan market between 2023 and 2033, focusing on market trends, growth factors, segmentation, regional insights, and key players shaping the industry landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
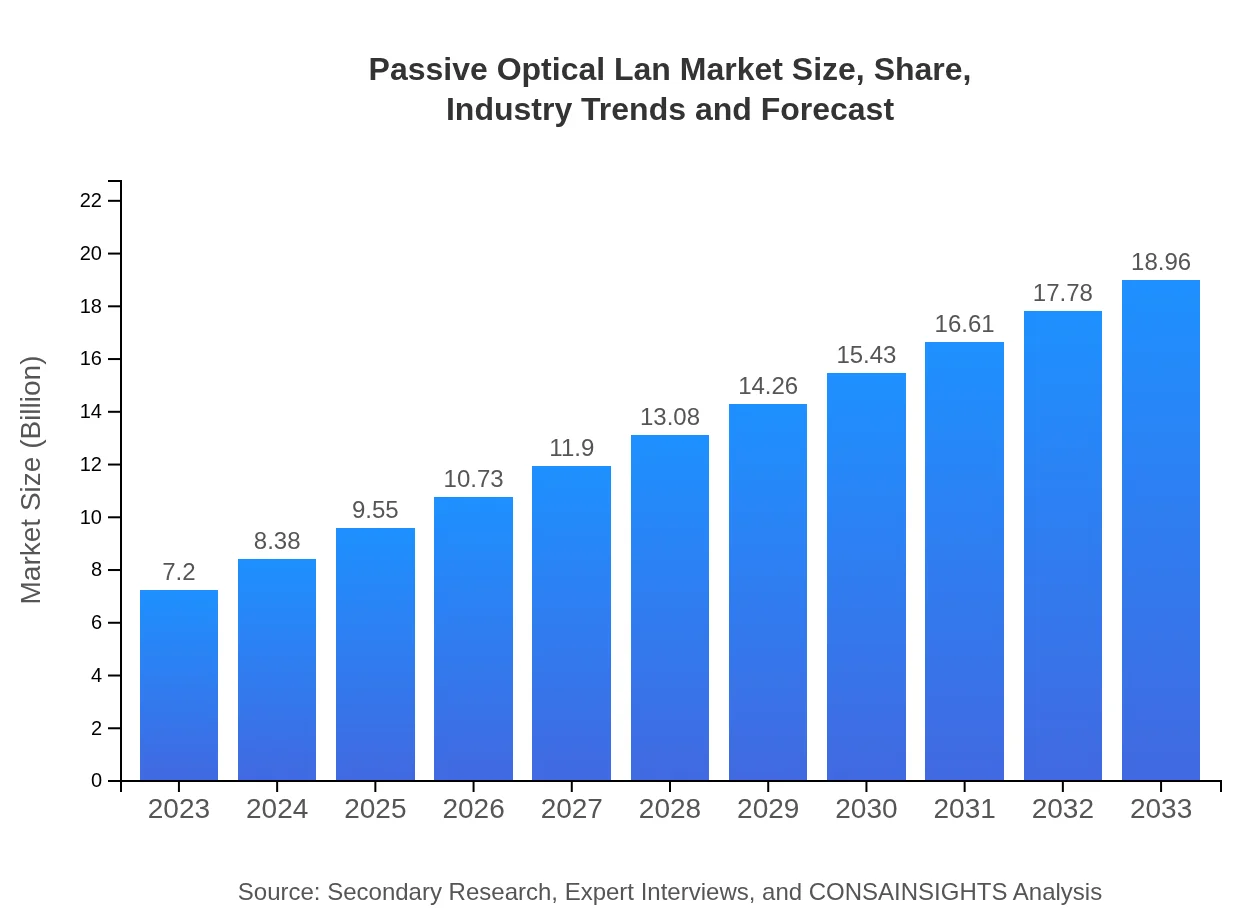
| 2023 Market Size | $7.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.96 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Nokia Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Passive Optical Lan Market Overview
Customize Passive Optical Lan Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Passive Optical Lan market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Passive Optical Lan's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Passive Optical Lan
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Passive Optical Lan market in 2023?
Passive Optical Lan Industry Analysis
Passive Optical Lan Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Passive Optical Lan Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Passive Optical Lan Market Report:
The European POL market is set to increase from $2.19 billion in 2023 to $5.75 billion by 2033. High demand for efficient data services and a strong push towards sustainable networking solutions will foster such growth in established markets like Germany, France, and the UK.Asia Pacific Passive Optical Lan Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Passive Optical Lan market is expected to grow from $1.48 billion in 2023 to an impressive $3.90 billion by 2033. The growth is supported by rising urbanization, increasing internet penetration, and government initiatives encouraging digital infrastructure investments, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and India.North America Passive Optical Lan Market Report:
North America is projected to be a significant contributor, with the market expanding from $2.40 billion in 2023 to $6.33 billion by 2033. The proliferation of smart home technologies and heightened demand for high-speed internet services, especially in enterprise environments, strongly influences this growth.South America Passive Optical Lan Market Report:
The South American POL market is anticipated to rise from $0.62 billion in 2023 to $1.62 billion by 2033. Demand in this region is driven by the need for improved connectivity in both urban and rural areas. Increased investment in telecommunications infrastructure by governments and private sector entities is essential for accelerating market growth.Middle East & Africa Passive Optical Lan Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Passive Optical Lan market is set for considerable growth, moving from $0.51 billion in 2023 to $1.35 billion by 2033. Initiatives toward smart city projects and infrastructural improvements are pivotal in enhancing connectivity and technological infrastructure.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
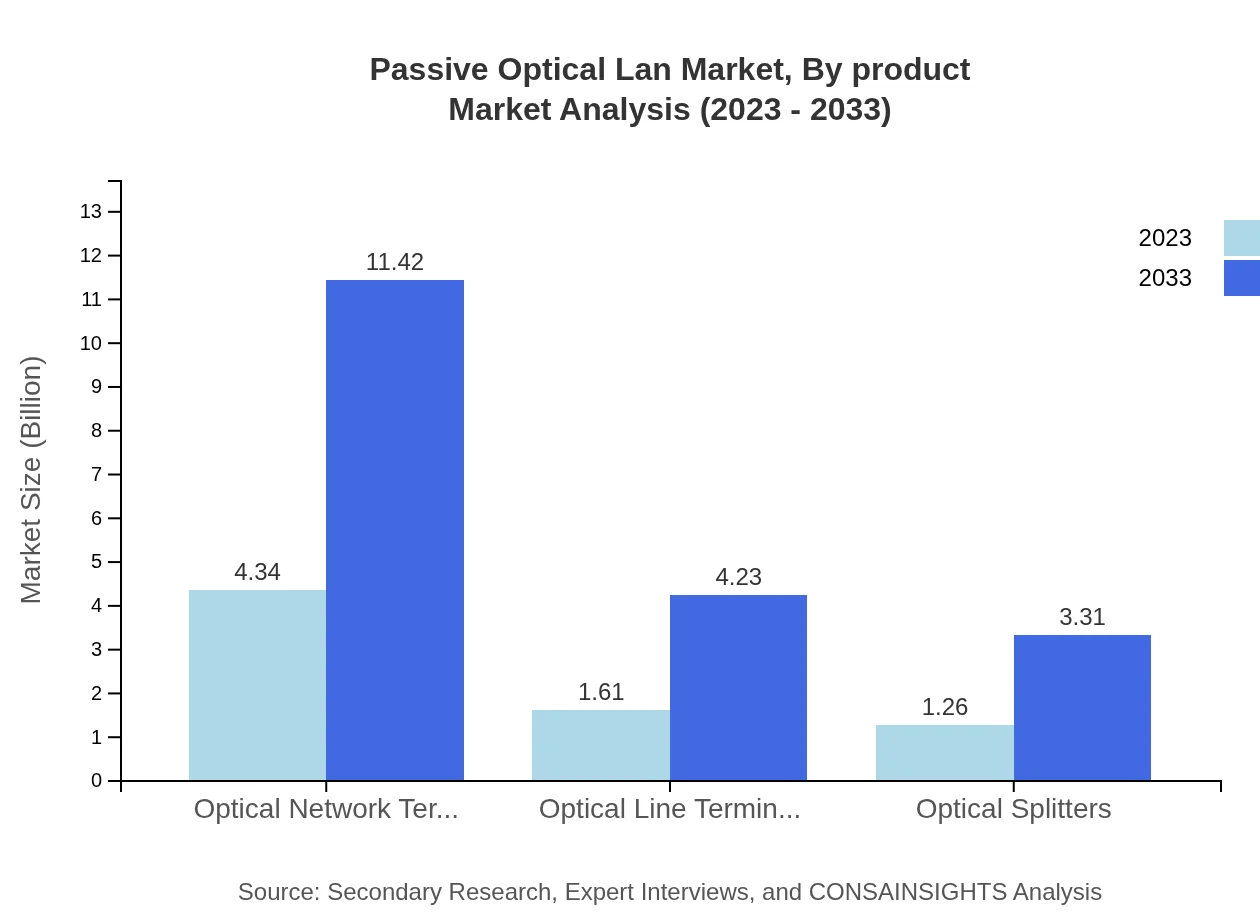
Passive Optical Lan Market Analysis By Product
The market is dominated by Optical Network Terminals (ONT), projected to grow from $4.34 billion in 2023 to $11.42 billion by 2033, reflecting a share of 60.24%. Optical Line Terminals (OLT) is anticipated to expand to $4.23 billion, maintaining a 22.3% share. Optical Splitters are also gaining traction, with estimates reaching $3.31 billion by 2033 and holding 17.46% of the market.
Passive Optical Lan Market Analysis By Application
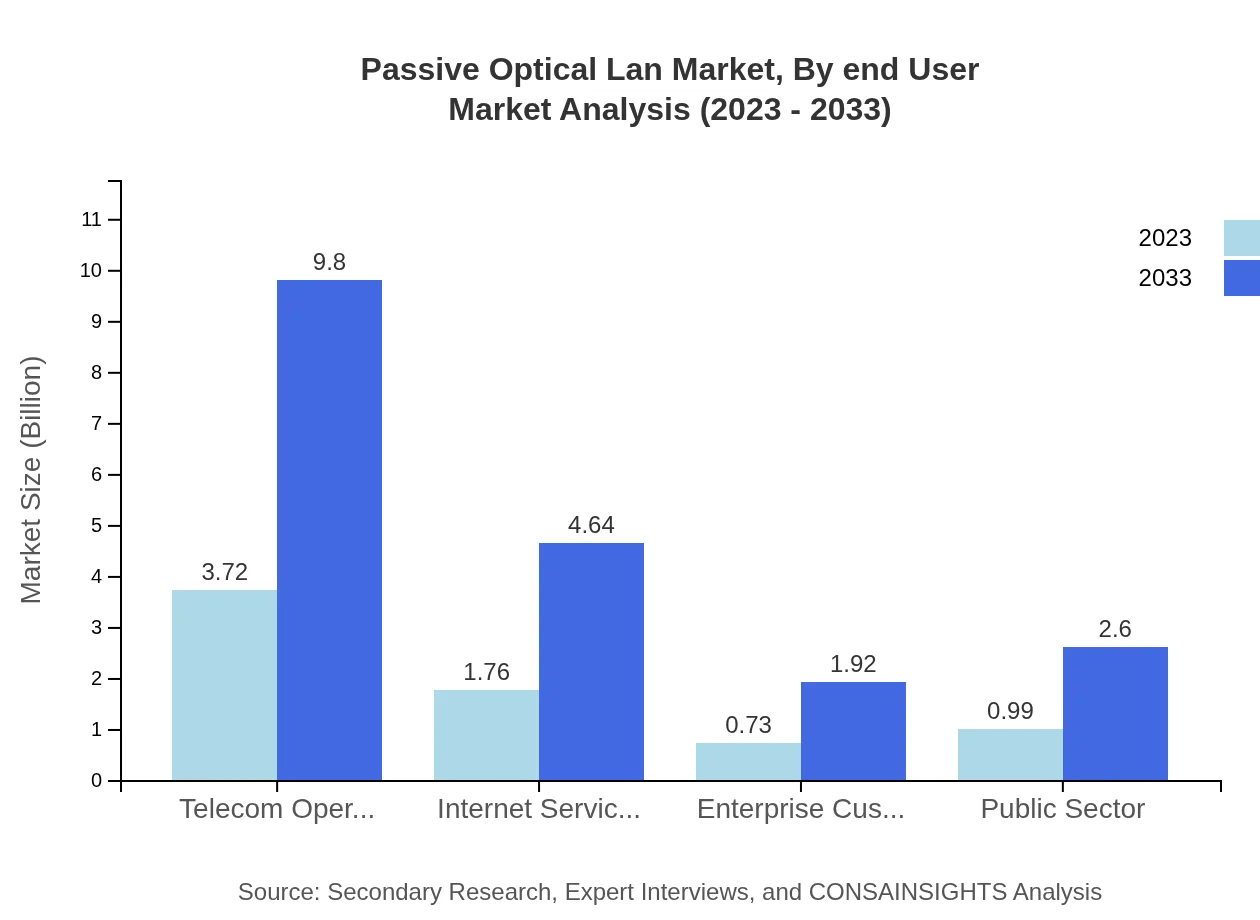
Telecom operators remain the largest segment, with size increasing from $3.72 billion in 2023 to $9.80 billion by 2033. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) follow closely, expanding from $1.76 billion to $4.64 billion. Enterprise customers, public sectors, and governmental applications continue to represent significant areas of growth.
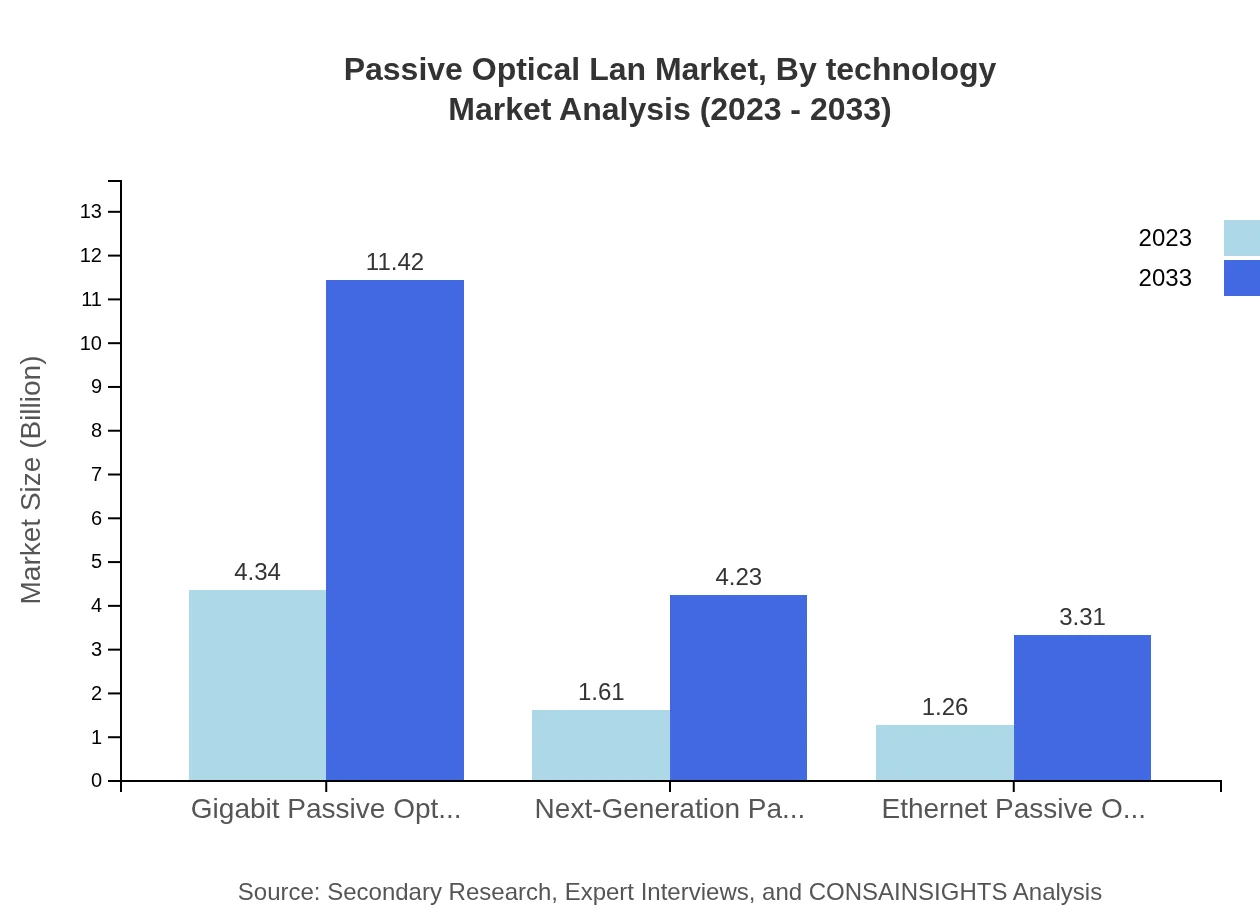
Passive Optical Lan Market Analysis By Technology
The market for Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) leads with sizes rising from $4.34 billion to $11.42 billion while maintaining 60.24% market share. Next-Generation Passive Optical Network 2 (NG-PON2) and Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) are identified as emerging technologies contributing to the market growth, with sizes projected at $4.23 billion and $3.31 billion respectively by 2033.
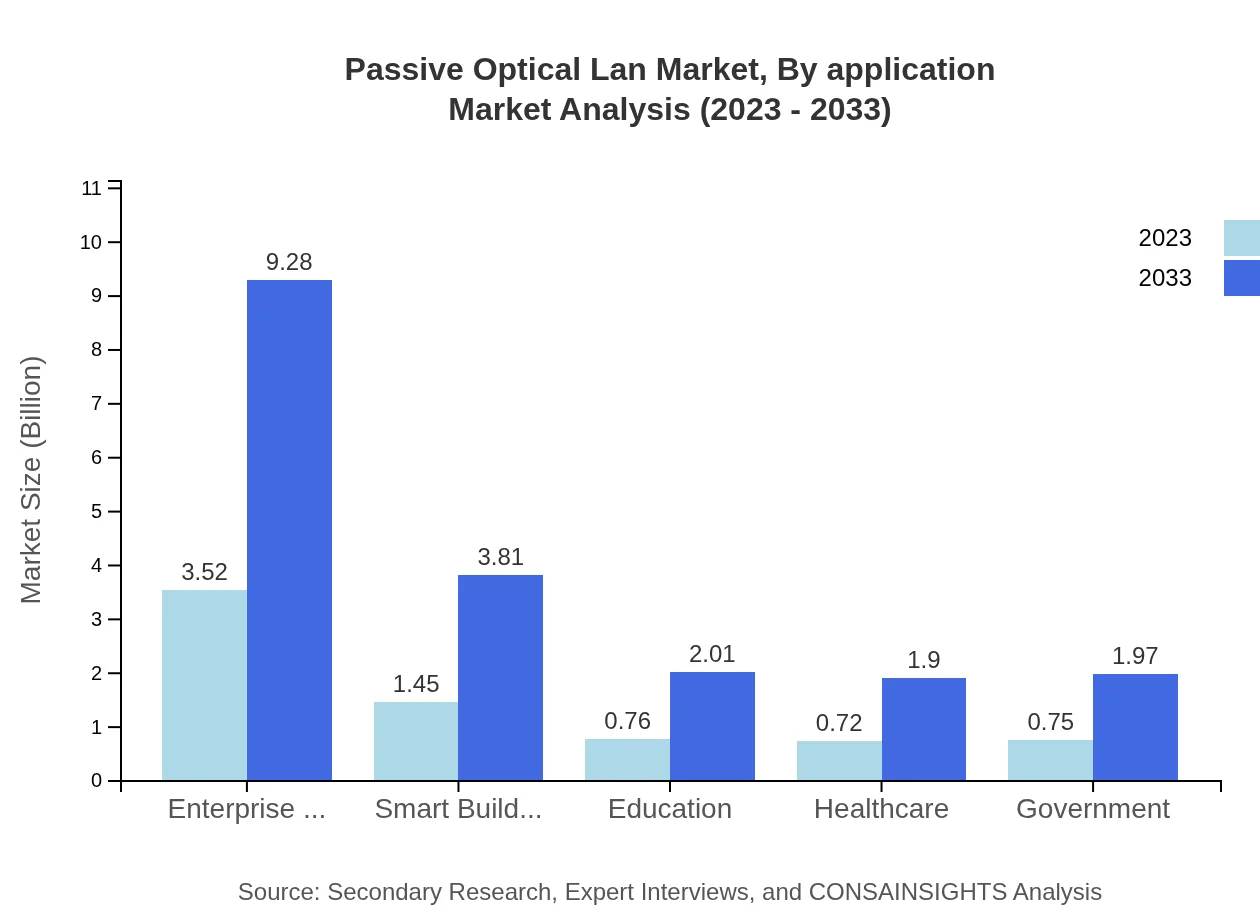
Passive Optical Lan Market Analysis By End User
Significant end-users include enterprise networking, with a size growth from $3.52 billion to $9.28 billion; smart buildings and education sectors show promising trends towards increased investment in smarter, more efficient networking solutions, expected to grow to $3.81 billion and $2.01 billion, respectively.
Passive Optical Lan Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Passive Optical Lan Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
A leading provider of networking technology, Cisco offers comprehensive passive optical solutions that focus on efficiency, scalability, and next-gen network capabilities.Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.:
Huawei is a frontrunner in optical networking technology, providing innovative products and solutions that enhance connectivity and operational productivity.ZTE Corporation:
ZTE specializes in telecommunications and broadband network solutions, driving advancements in passive optical technology to support data transmission.Nokia Corporation:
Nokia delivers a range of passive optical systems designed to meet the demands of modern-day networking in enterprise and urban environments.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of the Passive Optical LAN?
The Passive Optical LAN market is projected to grow from $7.2 billion in 2023 to significant heights by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8%. This growth reflects the increasing adoption of high-speed internet solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the Passive Optical LAN industry?
Key players in the Passive Optical LAN market include major network providers and technology companies that specialize in optical networking equipment. These companies are focused on innovations to improve data transmission and expand their service offerings.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Passive Optical LAN industry?
The growth of the Passive Optical LAN industry is driven by the increasing demand for high-speed broadband and internet services, the rise of smart buildings, and advancements in networking technologies that enhance connectivity and efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Passive Optical LAN?
North America is recognized as the fastest-growing region in the Passive Optical LAN market, with its market expanding from $2.40 billion in 2023 to $6.33 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by a robust demand for advanced networking solutions.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the Passive Optical LAN industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to the requirements of clients in the Passive Optical LAN industry. This includes insights into market trends, competitive analysis, and regional market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this Passive Optical LAN market research project?
Upon completion of the Passive Optical LAN market research project, you can expect detailed reports including market size analysis, trend identification, segmentation data, competitive landscape, and future growth forecasts.
What are the market trends of Passive Optical LAN?
Current trends in the Passive Optical LAN market include a shift towards hybrid networking solutions, increased integration of IoT devices, and the continual advancement of optical networking technologies to enhance bandwidth and connectivity.