Smart Agriculture Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: smart-agriculture
Smart Agriculture Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the Smart Agriculture market, covering insights, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Key focus areas include market dynamics, size, regional evaluations, and technology impacts to equip stakeholders with crucial decision-making insights.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
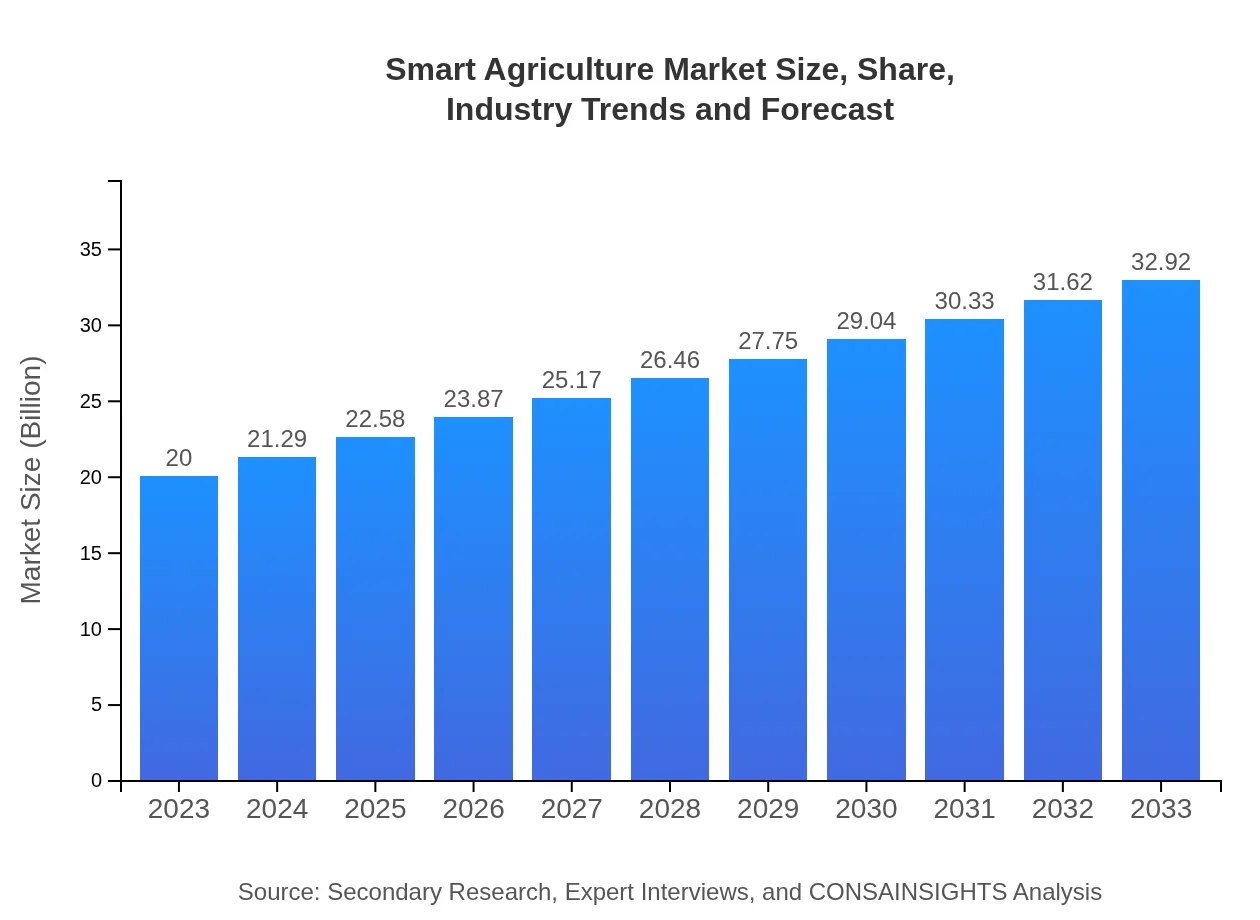
| 2023 Market Size | $20.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | Trimble Inc., John Deere, AG Leader Technology, PrecisionHawk, senseFly |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Smart Agriculture Market Overview
Customize Smart Agriculture Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Agriculture market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Agriculture's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Agriculture
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Agriculture market in 2023?
Smart Agriculture Industry Analysis
Smart Agriculture Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Agriculture Market Report:
In 2023, Europe's market is valued at USD 4.95 billion, projected to increase to USD 8.15 billion by 2033. The region's focus on sustainable practices and compliance with stringent environmental regulations encourages the adoption of smart agriculture technologies.Asia Pacific Smart Agriculture Market Report:
In 2023, the Smart Agriculture market in Asia Pacific is estimated at USD 3.81 billion, forecasted to grow to USD 6.27 billion by 2033. Rapid adoption of smart farming technologies, coupled with increasing agricultural investment, is accelerating market growth in countries like China and India, where population pressures necessitate enhanced productivity.North America Smart Agriculture Market Report:
North America leads the Smart Agriculture market with a valuation of USD 7.70 billion in 2023, expected to rise to USD 12.67 billion by 2033. The strong presence of technology providers, coupled with early adoption of smart farming techniques, has positioned this region at the forefront of agricultural innovation.South America Smart Agriculture Market Report:
The South American Smart Agriculture market is expected to grow from USD 1.29 billion in 2023 to USD 2.13 billion by 2033. Key countries like Brazil are increasingly investing in precision agriculture to improve crop quality and yield, driven by a growing demand for exports and sustainable practices.Middle East & Africa Smart Agriculture Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market size of Smart Agriculture is estimated at USD 2.24 billion in 2023, growing to USD 3.69 billion by 2033. Increased investment in agricultural technology and initiatives focused on enhancing food security are key growth drivers in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
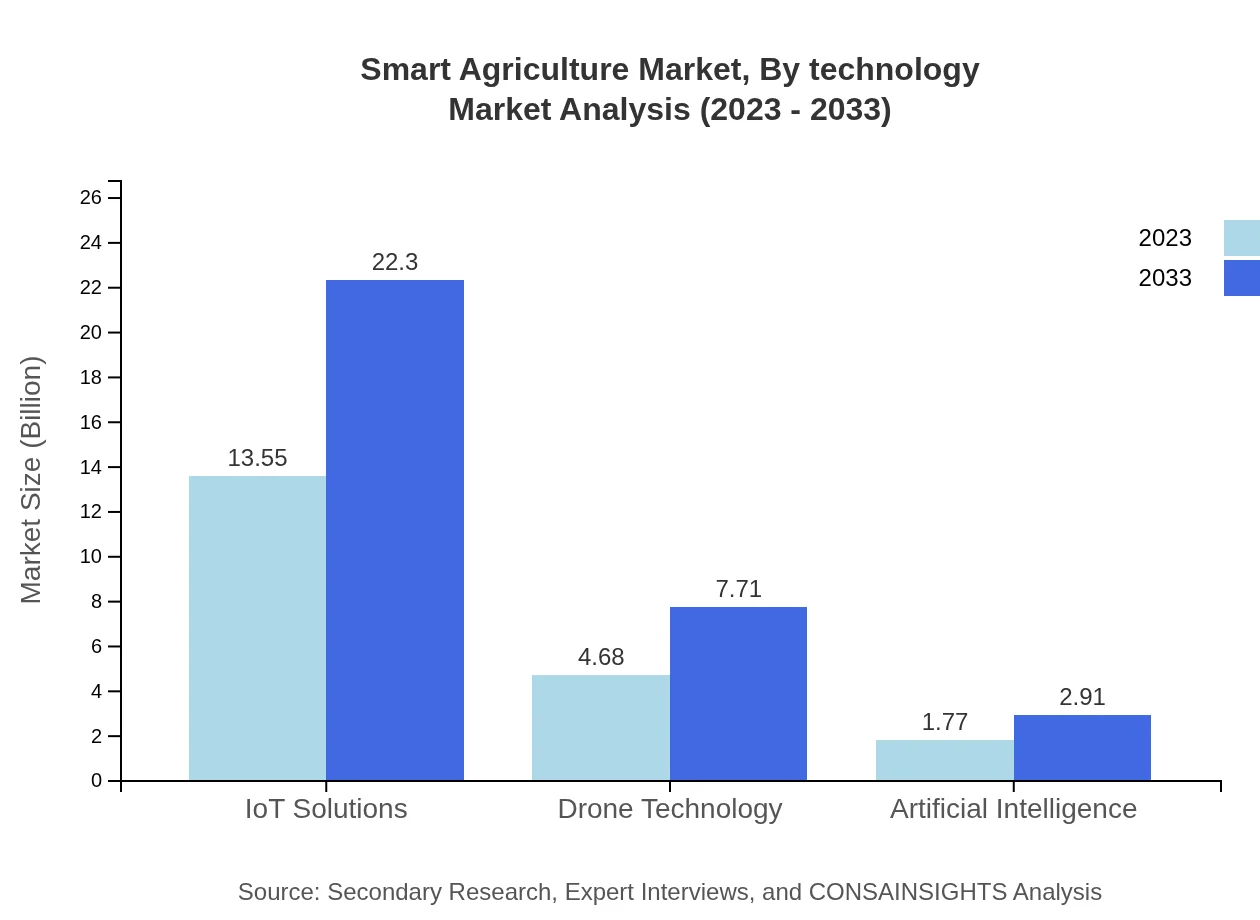
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis By Technology
The technological segment of Smart Agriculture is dominated by IoT solutions, representing a significant market size of USD 13.55 billion in 2023, projected to rise to USD 22.30 billion by 2033, showcasing a share of 67.74%. Drone technology and AI are also noteworthy, contributing significantly to enhancing operational efficiency through data collection and processing.
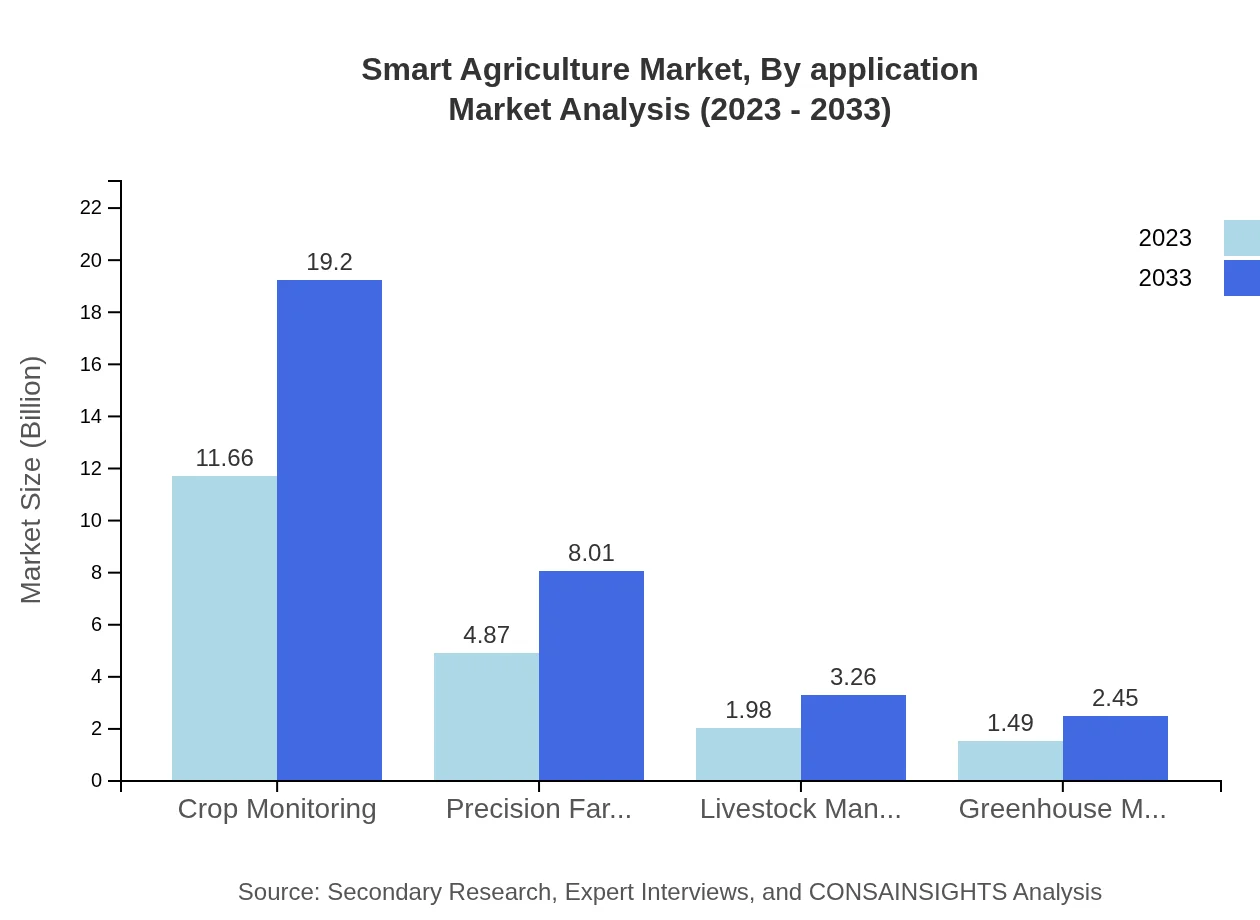
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis By Application
Crop Monitoring leads the application segment, with a market size of USD 11.66 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 19.20 billion by 2033. Precision farming follows, estimated at USD 4.87 billion in 2023, expanding to USD 8.01 billion by 2033. Livestock management and greenhouse management also play pivotal roles in optimizing various farming practices.
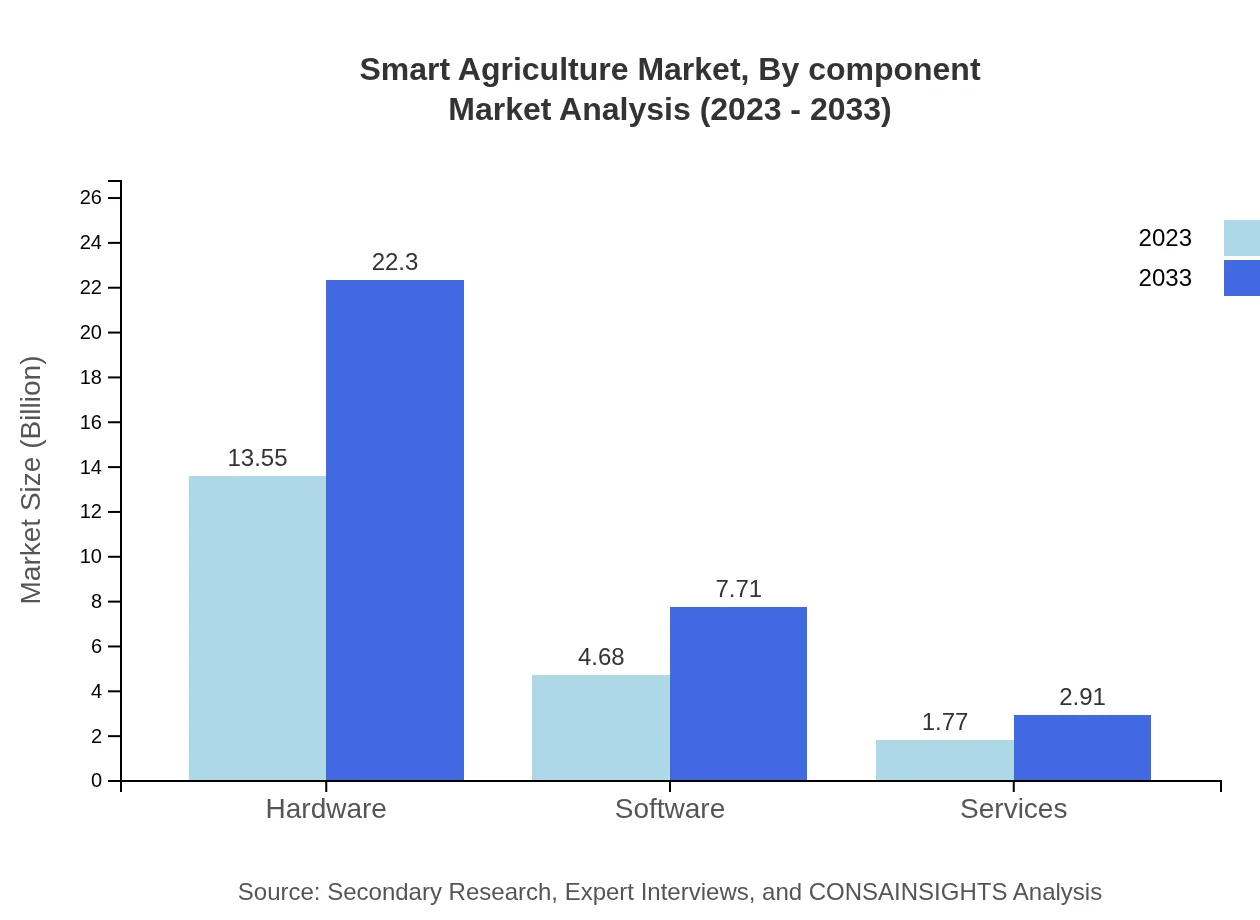
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis By Component
The component analysis reveals hardware as the dominant segment, valued at USD 13.55 billion in 2023, expected to grow to USD 22.30 billion by 2033. Software solutions are projected to enhance services, expected to move from USD 4.68 billion in 2023 to USD 7.71 billion by 2033.
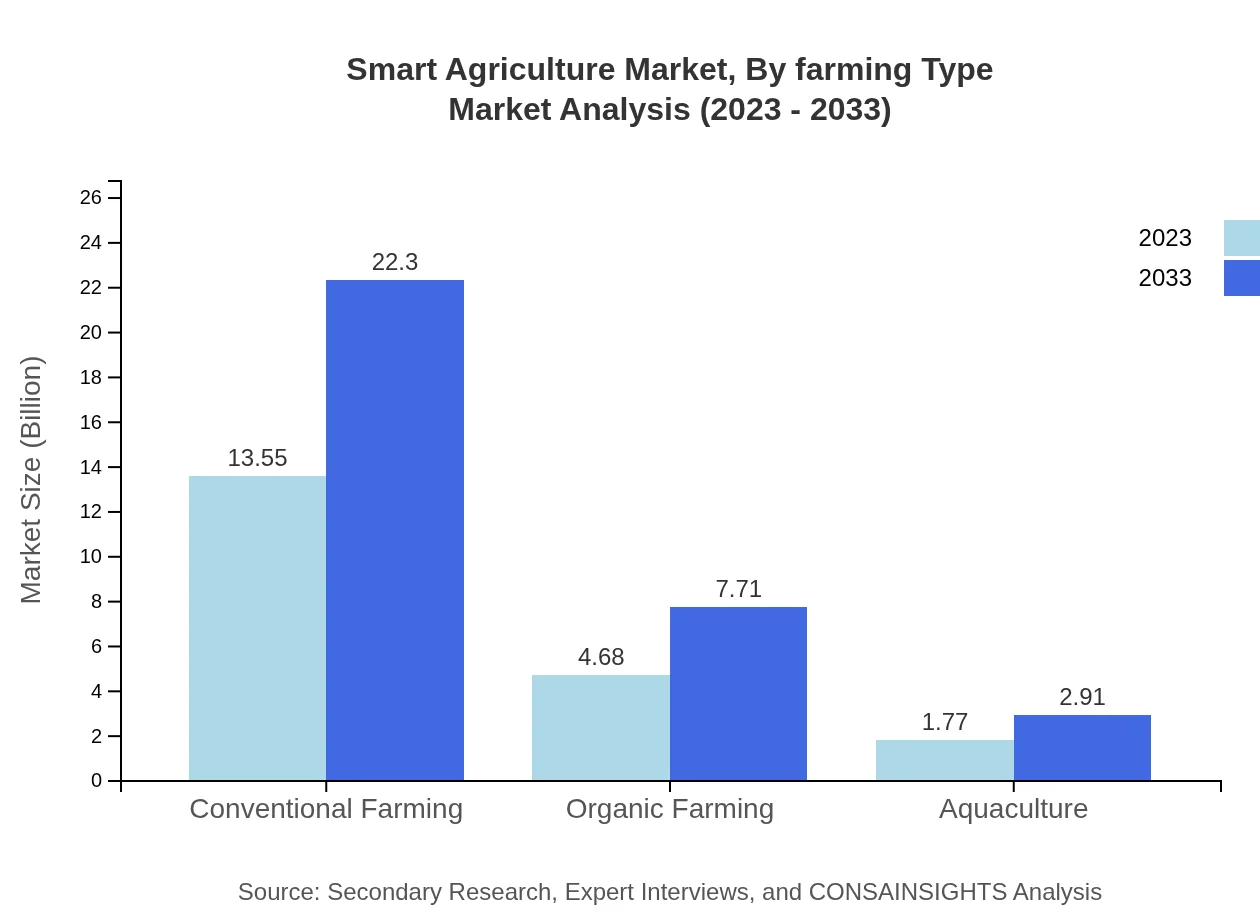
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis By Farming Type
Conventional farming methods represent the largest market share with USD 13.55 billion in 2023, increasing to USD 22.30 billion by 2033. Organic farming is also on the rise, moving from USD 4.68 billion in 2023 to USD 7.71 billion by 2033, driven by consumer demand for organic produce.
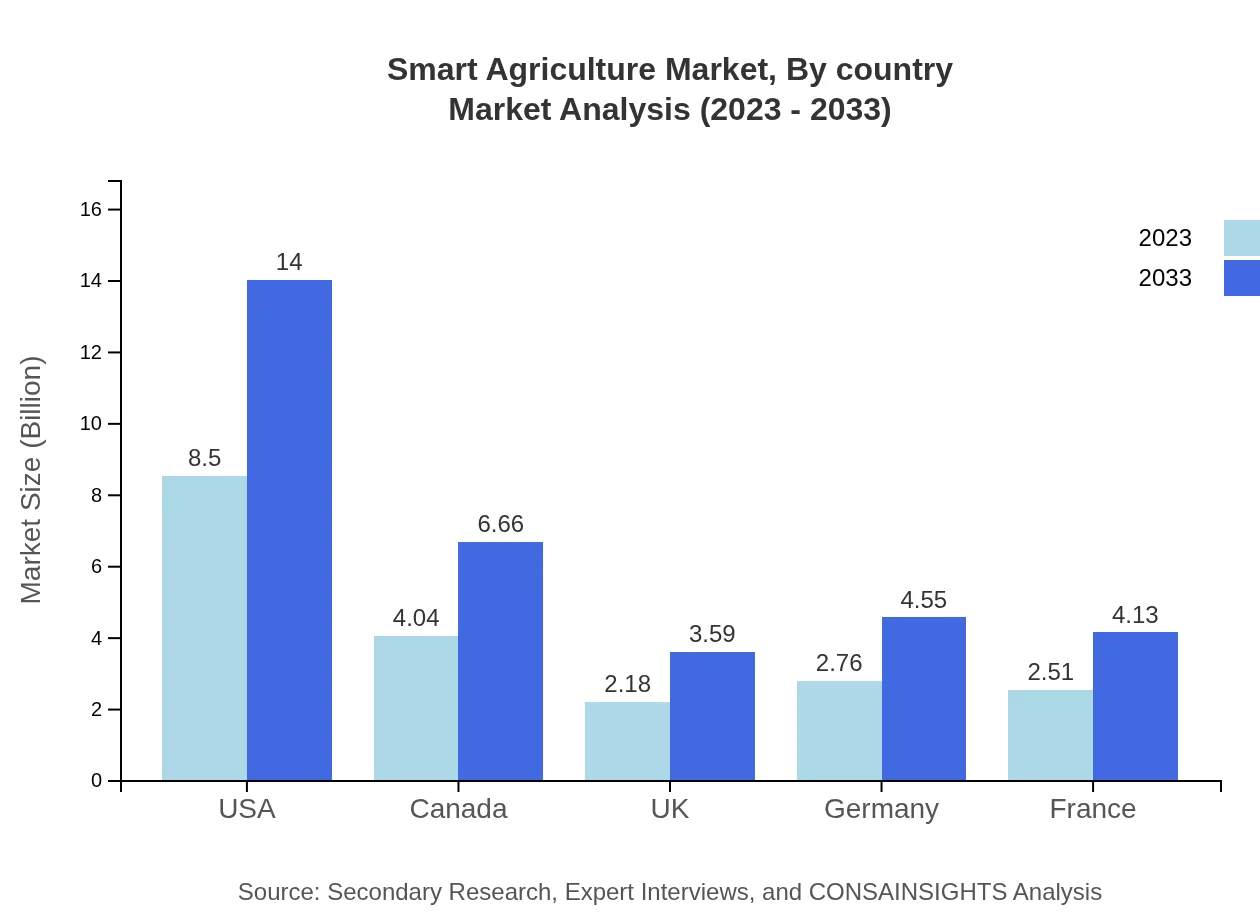
Smart Agriculture Market Analysis By Country
The USA leads the smart agriculture market with a size of USD 8.50 billion in 2023 forecasted to increase to USD 14.00 billion by 2033. Canada and the UK follow, both showing robust growth driven by technological adoption and government support for agritech initiatives.
Smart Agriculture Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Agriculture Industry
Trimble Inc.:
Trimble Inc. integrates technologies ranging from GPS to proprietary software to create advanced precision agriculture solutions, enhancing productivity and sustainability.John Deere:
As a leader in agricultural machinery, John Deere focuses on leveraging smart farming technologies to equip farmers with intelligent machinery for optimized operations.AG Leader Technology:
AG Leader Technology develops innovative precision farming solutions encompassing hardware and software that improve agricultural efficiency and effectiveness.PrecisionHawk:
PrecisionHawk specializes in drone technology and advanced data analytics to provide actionable insights that drive precision agriculture.senseFly:
senseFly, a Parrot company, offers fixed-wing drones designed for mapping and monitoring agricultural fields, facilitating data-driven decisions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Agriculture?
The global smart agriculture market is projected to reach approximately $20 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5% from current figures. This growth reflects the increasing demand for innovative and sustainable farming practices worldwide.
What are the key market players or companies in this smart Agriculture industry?
The smart agriculture market features several leading players, including John Deere, Trimble Inc., AG Leader Technology, and BASF. These companies are pivotal in driving technological innovations and expanding market offerings in precision farming and IoT solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart Agriculture industry?
Key growth drivers in the smart agriculture market include the increasing adoption of IoT devices, demand for precision farming solutions, and technological advancements. Additionally, rising food demand and a focus on sustainable practices significantly propel market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart Agriculture market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing area in the smart agriculture market, projected to expand from $3.81 billion in 2023 to $6.27 billion by 2033. This growth reflects enhanced agricultural practices and government support for innovation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart Agriculture industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the smart agriculture industry. Clients can access tailored insights that address specific business questions, competitive analysis, and market entry strategies within their target segments.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart Agriculture market research project?
From this smart agriculture market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape profiling, regional insights, and actionable recommendations for effective strategic planning.
What are the market trends of smart Agriculture?
Trends in smart agriculture include the rise of precision farming, increasing use of drones for crop monitoring, enhanced IoT applications, and AI integration for data analytics. These trends are essential for improving crop yields and sustainability.