Railway System Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: railway-system
Railway System Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Railway System market, focusing on market size, trends, segmentation, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights into regional markets, industry leaders, technological advancements, and challenges facing the sector are also included.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
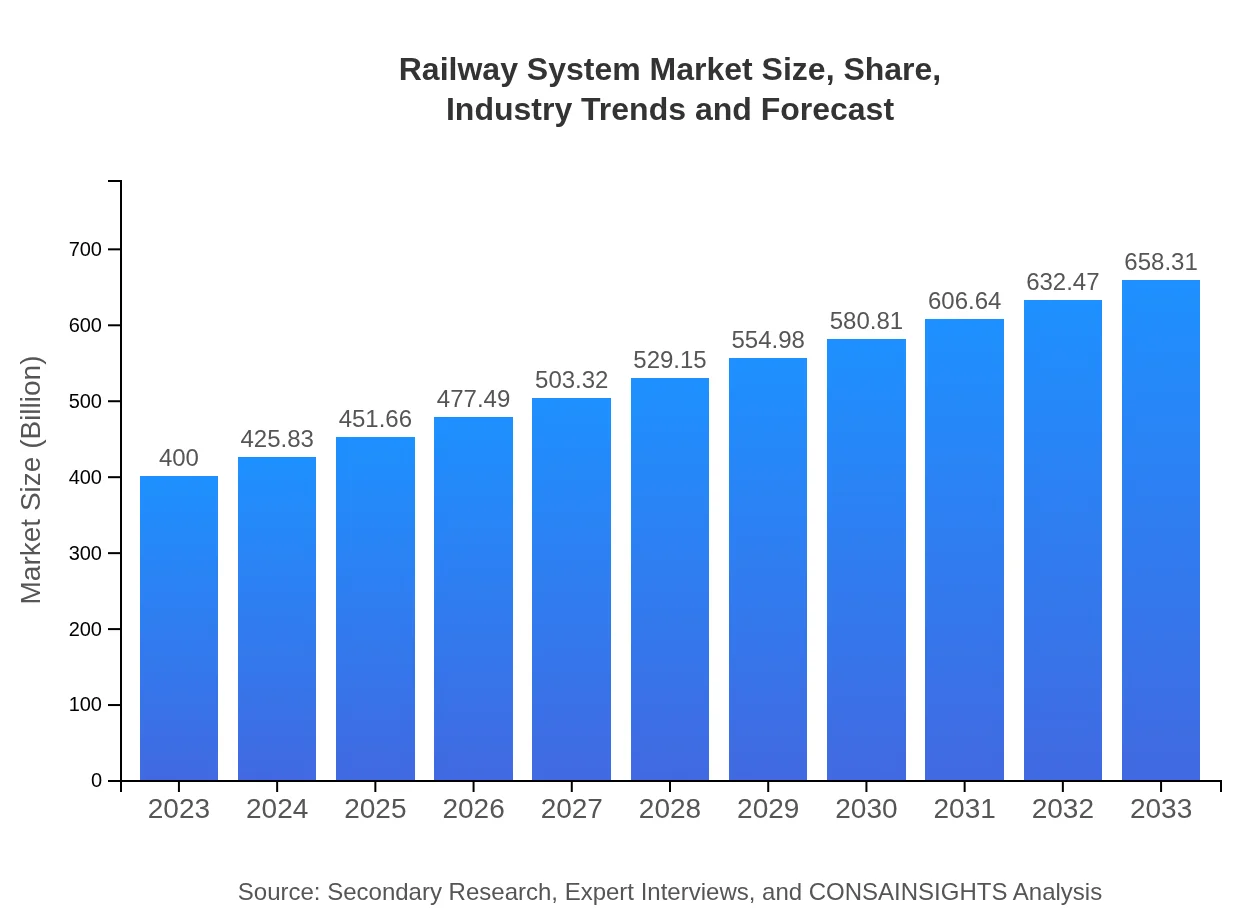
| 2023 Market Size | $400.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $658.31 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Bombardier Inc., General Electric (GE) |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Railway System Market Overview
Customize Railway System Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Railway System market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Railway System's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Railway System
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Railway System market in 2023?
Railway System Industry Analysis
Railway System Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Railway System Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Railway System Market Report:
In Europe, the Railway System market is anticipated to grow from $97.52 billion in 2023 to $160.49 billion by 2033. The shift towards sustainable transport modes, coupled with significant investment in high-speed rail networks and electrification projects, is contributing to this growth.Asia Pacific Railway System Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Railway System market is expected to grow from approximately $82.60 billion in 2023 to $135.94 billion by 2033. This growth is mainly attributed to rapid urbanization, government investments in infrastructure, and the increasing demand for public transport modes to mitigate congestion and pollution.North America Railway System Market Report:
North America's Railway System market is poised for growth, increasing from $152.40 billion in 2023 to approximately $250.81 billion by 2033. Factors such as increasing freight demand, governmental green initiatives, and technological innovations in rail systems are driving this growth.South America Railway System Market Report:
The South American Railway System market is projected to expand from $13.00 billion in 2023 to $21.39 billion by 2033. Investment in modernizing existing rail networks and expanding services to underserved areas is driving growth. However, challenges in funding and infrastructure maintenance remain significant.Middle East & Africa Railway System Market Report:
The Railway System market in the Middle East and Africa is expected to witness significant growth, increasing from $54.48 billion in 2023 to $89.66 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, rising standards of living, and the need for efficient public transport systems are key drivers in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
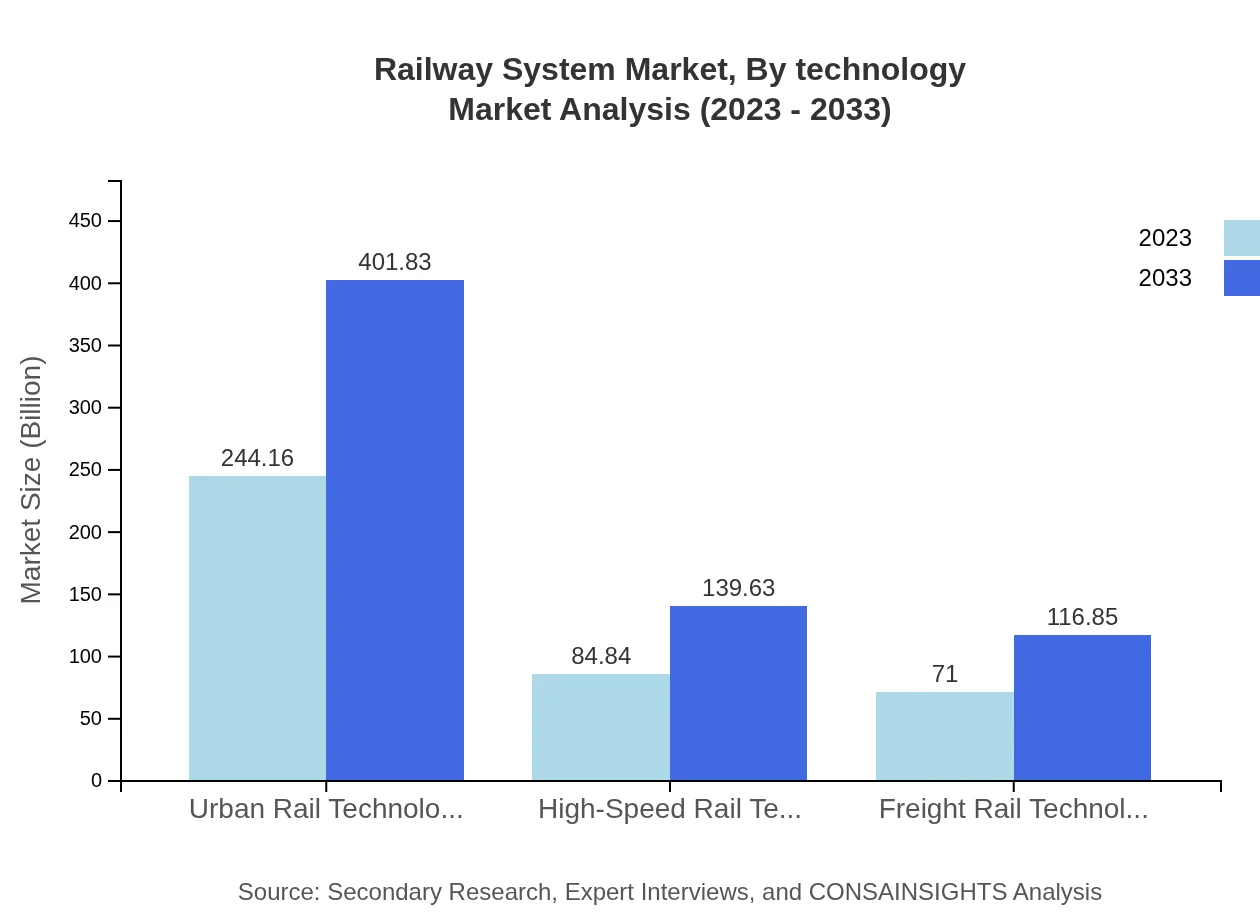
Railway System Market Analysis By Technology
The technological segment is evolving rapidly, with the digital solutions for railways market expected to grow from $338.04 billion in 2023 to $556.33 billion by 2033. Urban rail technology is pivotal for urban transport solutions, expected to grow from $244.16 billion in 2023 to $401.83 billion in 2033. High-speed rail and freight rail technologies will also show significant growth, reflecting the shifting transportation preferences and increasing freight needs.
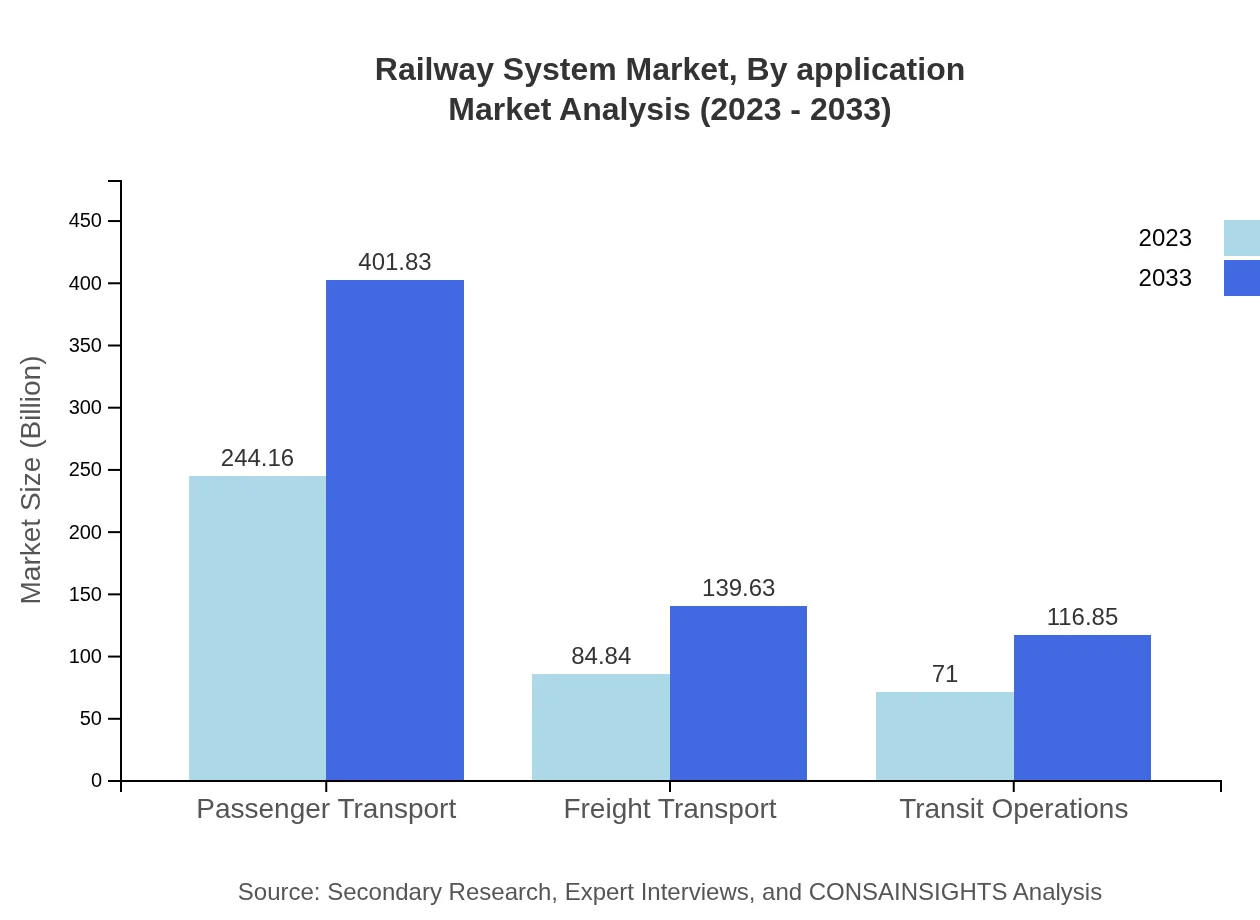
Railway System Market Analysis By Application
Passenger transport remains a primary application of railway systems, accounting for a significant market size of $244.16 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $401.83 billion by 2033. Freight transport, while smaller, also holds a significant share with an expected increase from $84.84 billion to $139.63 billion during the same period.
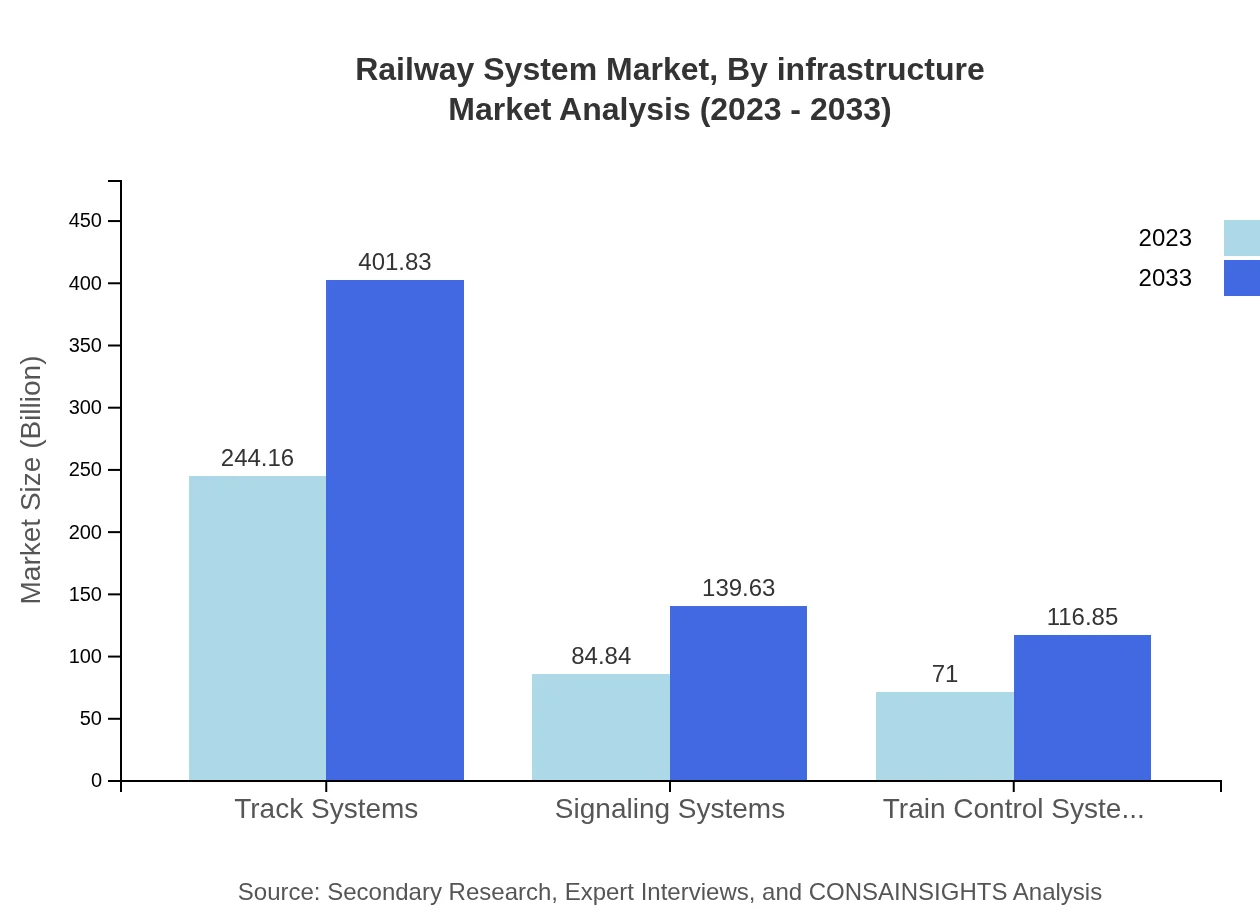
Railway System Market Analysis By Infrastructure
The infrastructure segment includes critical areas such as track systems and signaling systems. Track systems are projected to grow from $244.16 billion in 2023 to $401.83 billion by 2033. Signaling systems are also set for growth, expanding from $84.84 billion to $139.63 billion, driven by the need for enhanced safety and efficiency in railway operations.
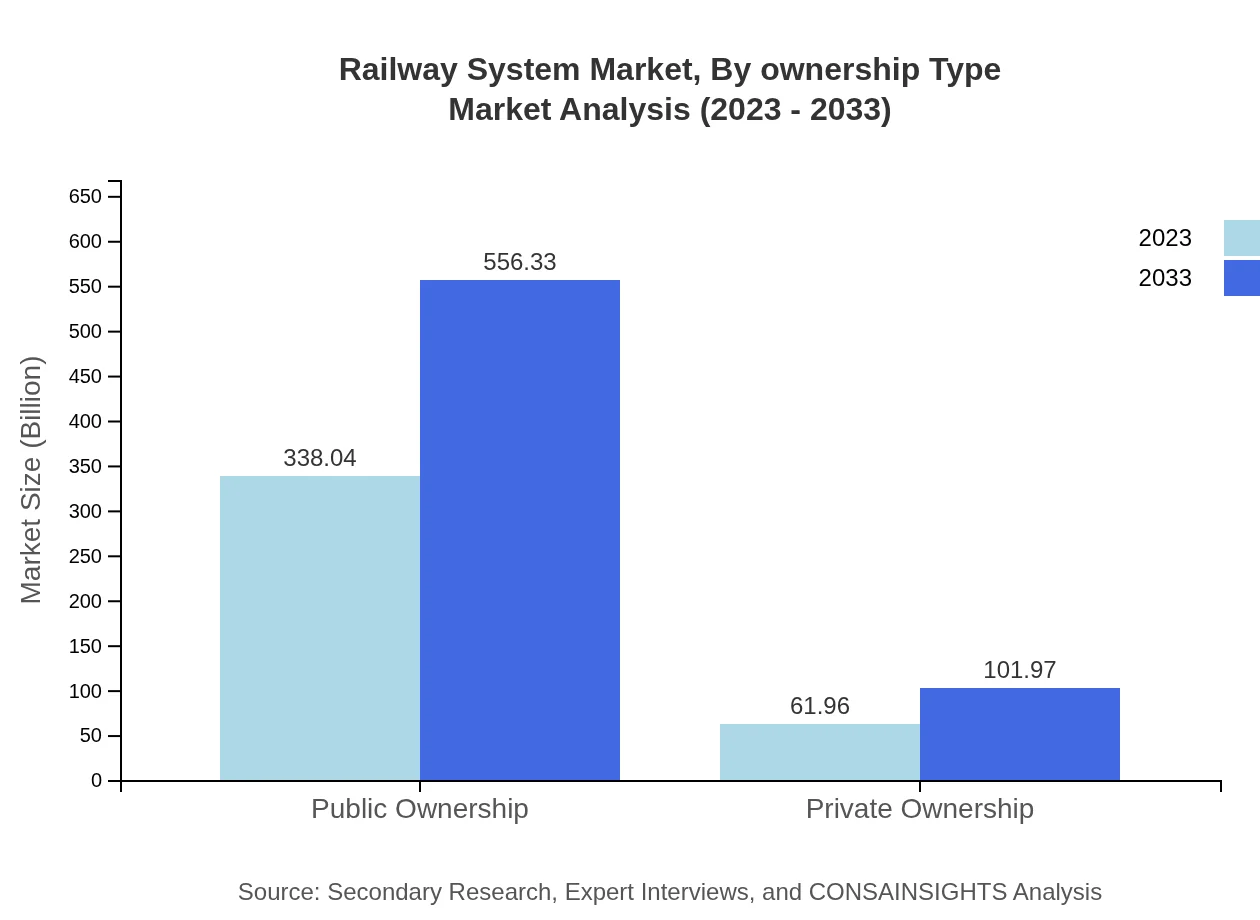
Railway System Market Analysis By Ownership Type
Public ownership of railway systems dominates the market, with a significant size of $338.04 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $556.33 billion by 2033. Private ownership, while smaller, is also significant, growing from $61.96 billion in 2023 to $101.97 billion by 2033, reflecting a growing trend toward privatization in certain regions.
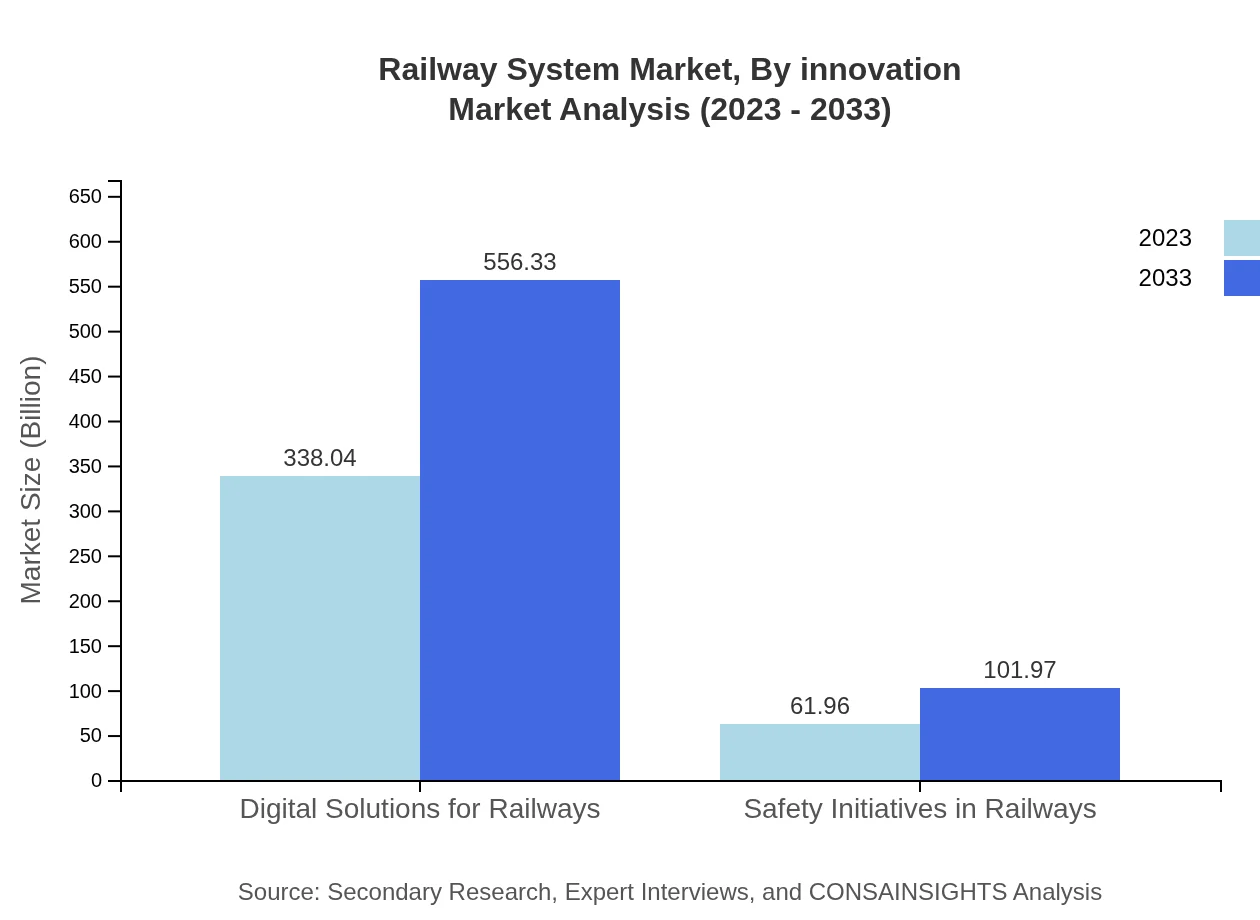
Railway System Market Analysis By Innovation
Innovations in safety initiatives are crucial for the railway industry, expected to grow from $61.96 billion in 2023 to $101.97 billion by 2033. The focus on safety technologies and protocols is a significant trend as the industry prioritizes reducing accidents and improving service reliability.
Railway System Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Railway System Industry
Siemens AG:
A global powerhouse in electrification, automation, and digitalization in railways, Siemens AG leads in providing innovative solutions that drive efficiency and safety in transport solutions.Bombardier Inc.:
Specializing in rail transport solutions, Bombardier offers a wide range of products, including trains, signaling equipment, and maintenance services, focusing on customer-centric solutions.General Electric (GE):
GE is a leader in locomotive technology and has extensive experience in railway solutions, working on enhancing operational efficiency and performance across rail networks.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of the railway system?
The global railway system market is valued at approximately $400 billion in 2023, with a projected growth rate of 5% CAGR. By 2033, it is expected to significantly expand, capturing a larger share of the transportation market.
What are the key market players or companies in the railway system industry?
Key players in the railway system industry include global leaders such as Siemens, Bombardier, Alstom, and Hitachi. These companies play vital roles in driving innovation, safety, and efficiency in rail transport.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the railway system industry?
Growth in the railway system industry is driven by increased urbanization, rising demand for efficient public transport, advancements in technology, and the need for sustainable transportation solutions as environmental concerns rise.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the railway system?
The Asia Pacific region is projected to be the fastest-growing market for railway systems, with growth from $82.60 billion in 2023 to $135.94 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rapid urbanization and infrastructure investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the railway system industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports for the railway system industry. Tailored studies help clients understand specific market dynamics, competitive landscapes, and regional trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this railway system market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, detailed segmentation data, strategic insights, regional market forecasts, and competitive assessments tailored to your specific needs within the railway system industry.
What are the market trends of the railway system?
Market trends indicate a shift towards digital solutions, with digital technology in railways expected to grow from $338.04 billion in 2023 to $556.33 billion by 2033, showcasing a strong focus on integrating technology into rail transport.