Self Administered Drugs Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: self-administered-drugs
Self Administered Drugs Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Self Administered Drugs market, covering significant data points, trends, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
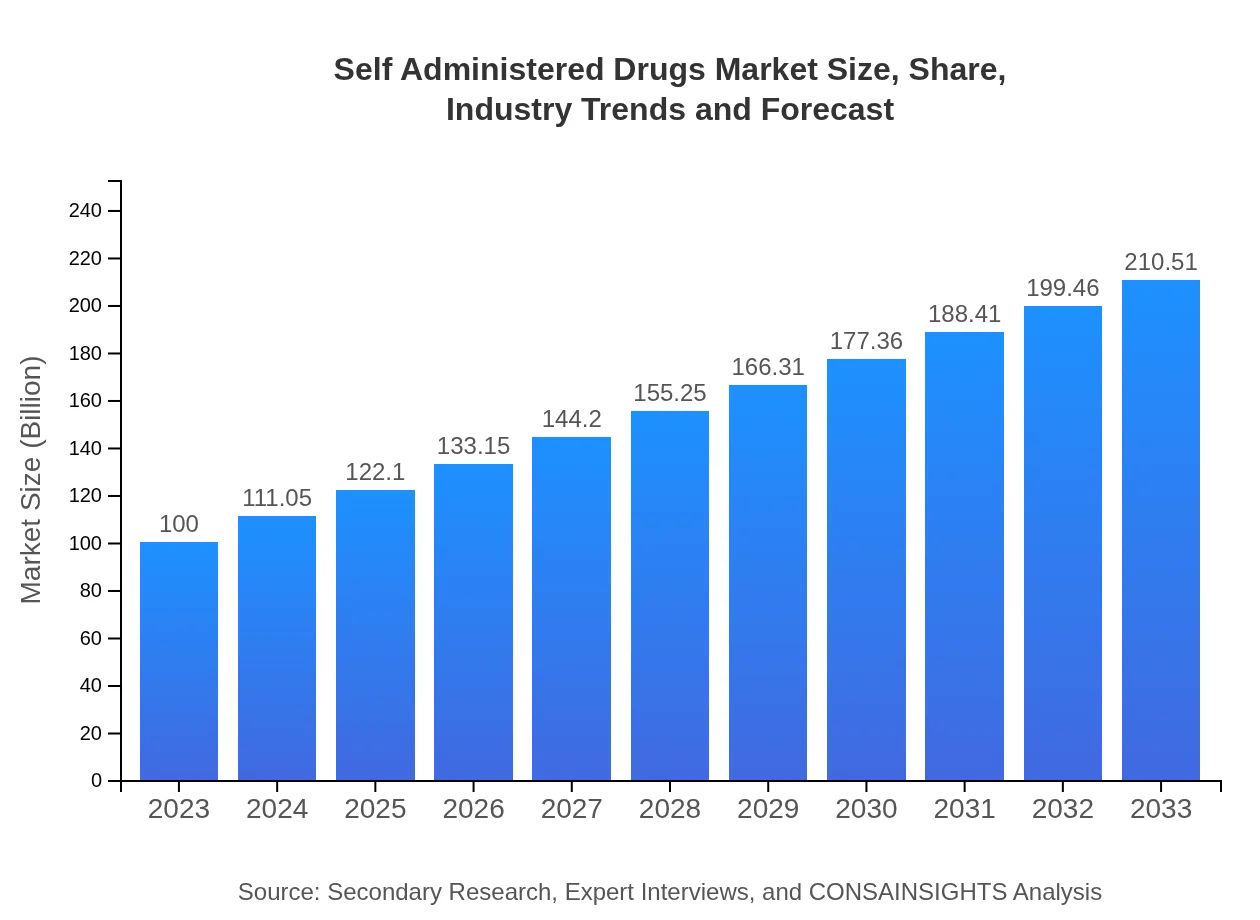
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $210.51 Billion |
| Top Companies | AbbVie, Roche, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer , Merck & Co. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Self Administered Drugs Market Overview
Customize Self Administered Drugs Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Self Administered Drugs market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Self Administered Drugs's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Self Administered Drugs
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Self Administered Drugs market in 2023 and 2033?
Self Administered Drugs Industry Analysis
Self Administered Drugs Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Self Administered Drugs Market Report:
The European market was valued at $33.05 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach $69.57 billion by 2033. Factors such as strong regulatory frameworks, high standards of healthcare delivery, and rising awareness of self-care options fuel growth. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, alongside supportive healthcare policies, creates a conducive environment for the self-administered drugs market.Asia Pacific Self Administered Drugs Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific market stood at $16.48 billion and is projected to reach $34.69 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, increasing healthcare expenditures, and a burgeoning population drive demand in this region. Emerging economies like India and China play pivotal roles in market expansion due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and growing awareness around self-medication.North America Self Administered Drugs Market Report:
In North America, the market valuation was approximately $35.51 billion in 2023, set to exceed $74.75 billion by 2033. The region's market is significantly influenced by high healthcare spending, advanced healthcare technologies, and strong consumer acceptance of self-administration. Moreover, the aging population is a critical contributor to market growth.South America Self Administered Drugs Market Report:
The South American Self Administered Drugs market was valued at $9.13 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow to $19.22 billion by 2033. The growth is attributed to improving healthcare infrastructure and increased access to medications. Rising disposable incomes and changing consumer preferences towards self-administered medications are also notable factors.Middle East & Africa Self Administered Drugs Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market stood at $5.83 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $12.27 billion by 2033. While the market is currently smaller than other regions, it displays significant potential for growth due to improving healthcare services, increasing awareness of self-treatment, and a shift towards modern healthcare solutions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis By Drug Type
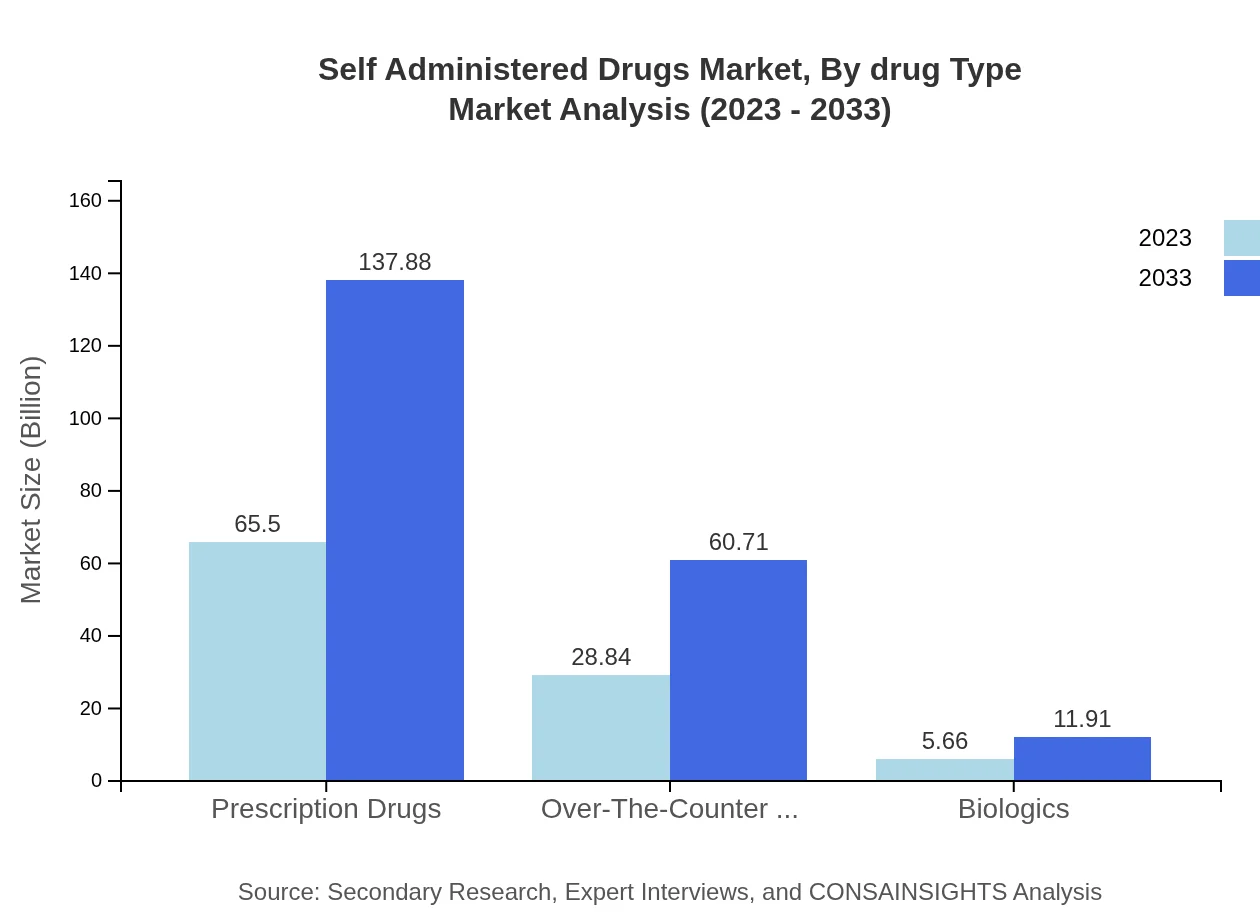
The Self-Administered Drugs market can be segmented into prescription drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, and biologics. Prescription drugs accounted for the largest share, valued at $65.50 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $137.88 billion by 2033. OTC drugs are also popular, showing healthy growth from $28.84 billion to $60.71 billion in the same period. Biologics, while a smaller segment, is projected to grow from $5.66 billion to $11.91 billion, driven by advancements in biotechnology and personalized medicine.
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis By Therapy Area
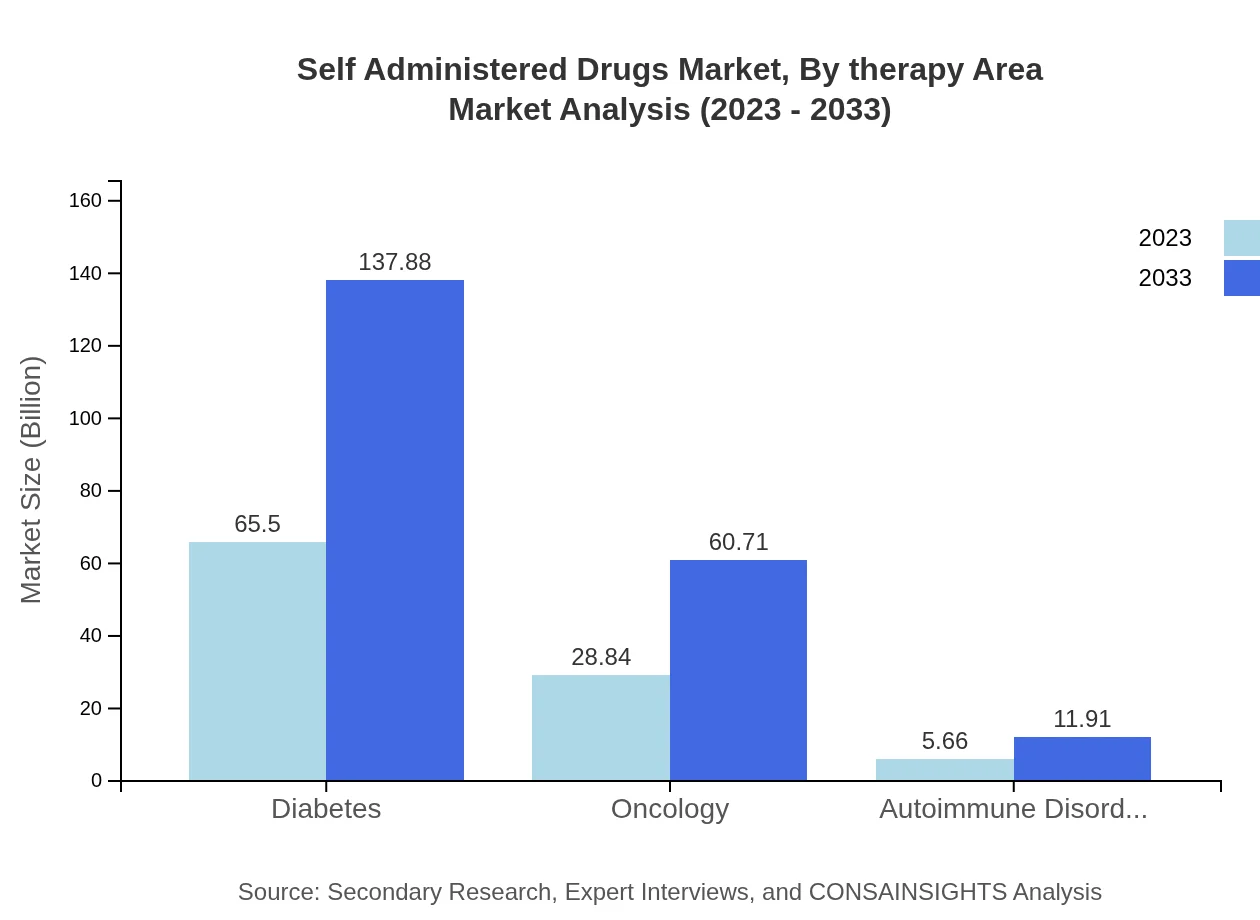
In therapy areas, self-administered drugs are prominently used in diabetes, oncology, and autoimmune disorders. The diabetes segment, valued at $65.50 billion in 2023, is expected to increase to $137.88 billion, mirroring the growing number of diabetes cases globally. Oncology, valued at $28.84 billion in 2023, is projected to rise to $60.71 billion, propelled by advancements in cancer treatments. Autoimmune disorders are also set to expand from $5.66 billion to $11.91 billion, fostering a greater need for self-administered therapies.
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis By Delivery Method
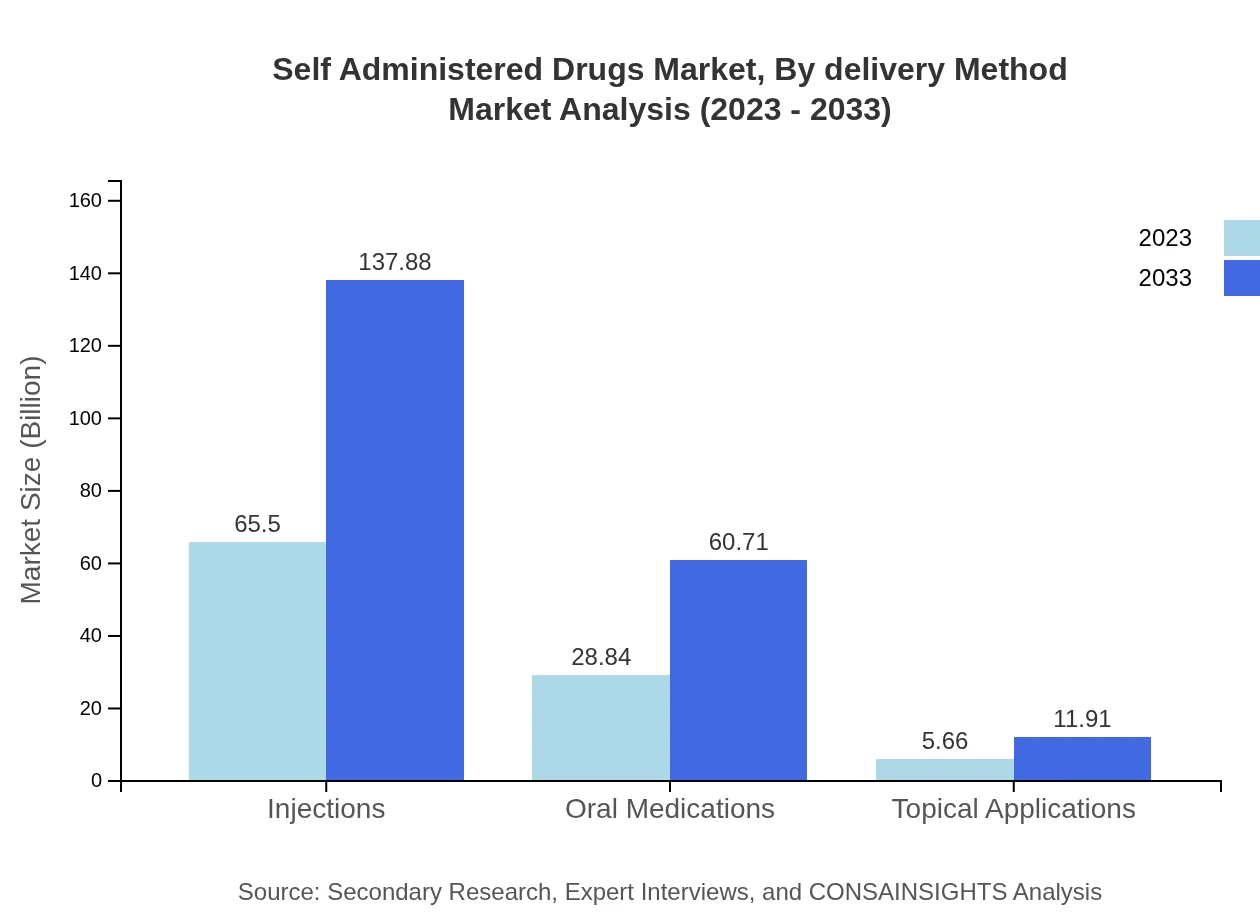
The Self-Administered Drugs market is categorized by delivery methods: injections, oral medications, and topical applications. Injections are dominant, estimated at $65.50 billion in 2023 and anticipated to reach $137.88 billion by 2033. Oral medications follow closely with a growth from $28.84 billion to $60.71 billion. Topical applications, while smaller at $5.66 billion, show potential for growth as consumer preferences shift towards localized treatments.
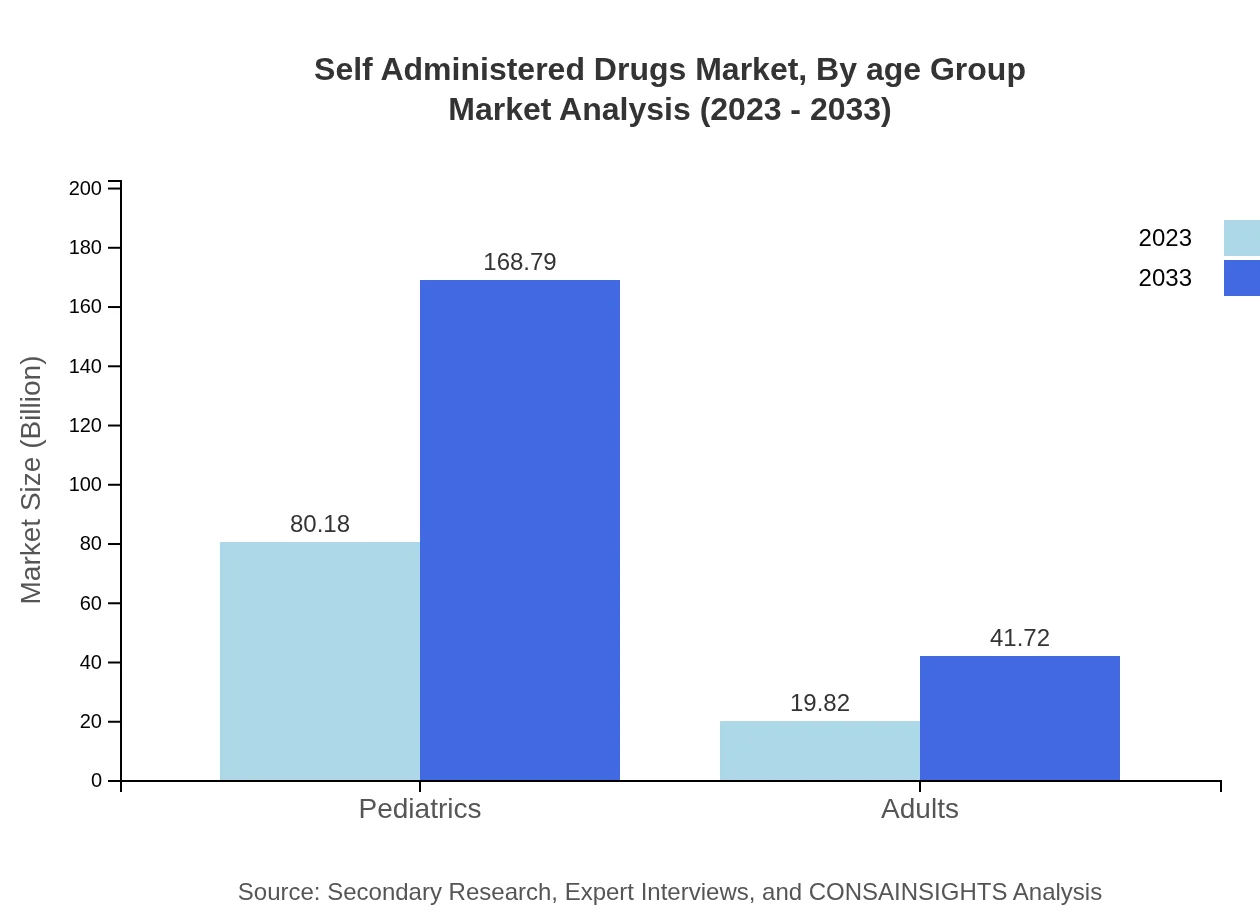
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis By Age Group
The market also differentiates between age groups, primarily focusing on pediatrics and adults. The pediatrics segment dominates with market values of $80.18 billion in 2023, growing to $168.79 billion by 2033. The adult segment is projected to expand from $19.82 billion to $41.72 billion, reflecting the increasing trend of self-treatment among older populations.
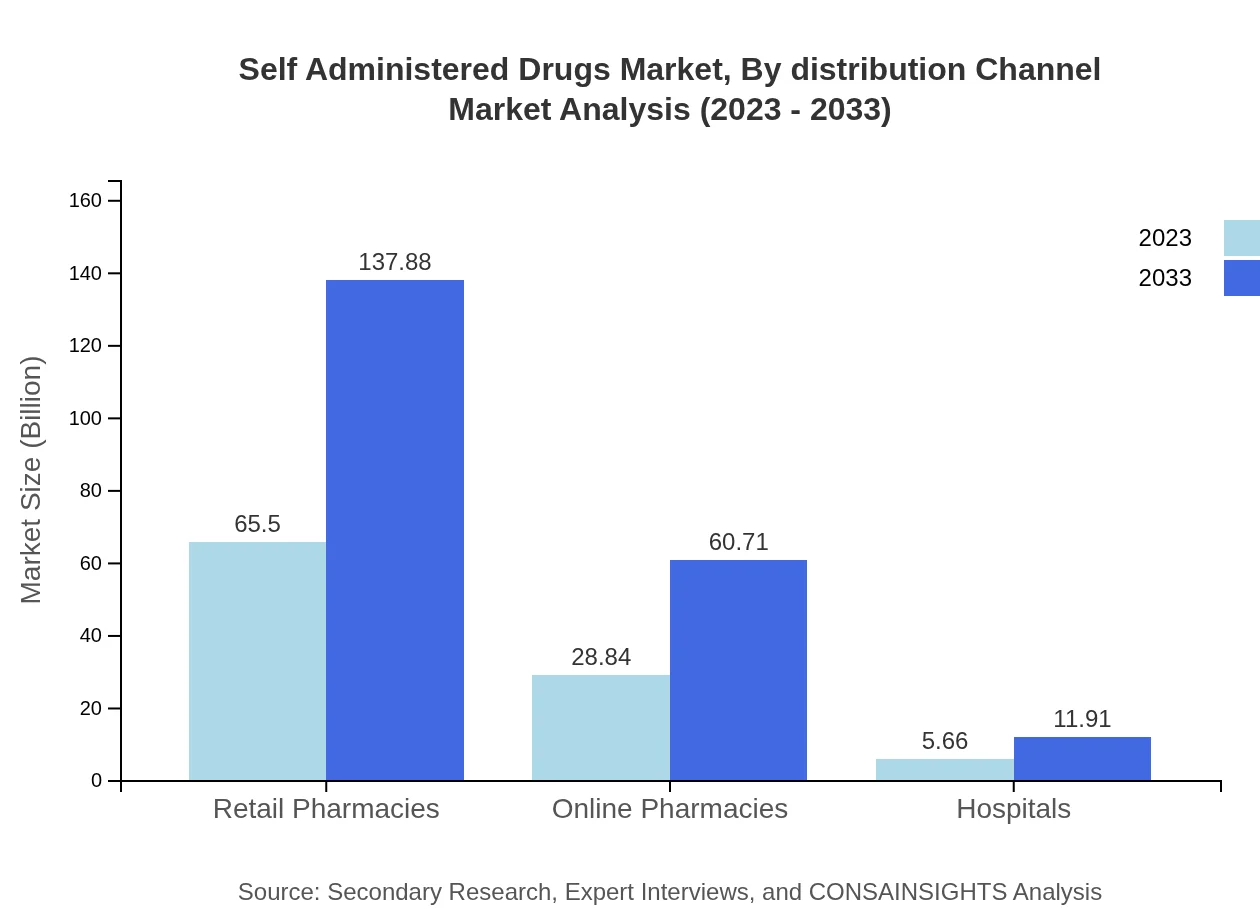
Self Administered Drugs Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels for Self-Administered Drugs include retail pharmacies, online pharmacies, and hospitals. Retail pharmacies lead the market with sales of $65.50 billion in 2023, expected to reach $137.88 billion by 2033. Online pharmacies are also gaining traction, with values growing from $28.84 billion to $60.71 billion. Hospitals, while less significant, are projected to grow from $5.66 billion to $11.91 billion as integration of self-administered drugs into healthcare systems increases.
Self Administered Drugs Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Self Administered Drugs Industry
AbbVie:
AbbVie is a biopharmaceutical company that develops innovative therapies for complex diseases, leading in self-administered drugs for oncology and autoimmune conditions.Roche:
Roche is a global leader in pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, offering self-administered biologics particularly in oncology and chronic disease management.Johnson & Johnson:
Johnson & Johnson provides a comprehensive range of self-administered drugs across various therapeutic areas, focusing on consumer health and medical devices.Pfizer :
Pfizer, a key player in the pharmaceutical industry, contributes significantly to self-administered therapies, particularly in pain management and infectious diseases.Merck & Co.:
Merck & Co. is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally, known for its innovative self-administered drugs in the diabetes and autoimmune disorder segments.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of self Administered drugs?
The self-administered drugs market is currently valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% anticipated through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this self Administered drugs industry?
Key players in the self-administered drugs market include major pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms specializing in therapeutics, particularly those focusing on biologics and over-the-counter solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the self Administered drugs industry?
Growth in the self-administered drugs market is primarily driven by increasing patient preference for at-home treatments, technological advancements in drug delivery systems, and rising healthcare costs compelling patients to opt for self-administration.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the self Administered drugs market?
The fastest-growing region in the self-administered drugs market is Asia Pacific. The market size is projected to grow from $16.48 billion in 2023 to $34.69 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the self Administered drugs industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific inquiries regarding the self-administered drugs industry, ensuring clients receive data that meets their unique research needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this self Administered drugs market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive reports detailing market trends, regional analyses, competitor landscapes, and segmented data on various product categories within the self-administered drugs market.
What are the market trends of self Administered drugs?
Current market trends in self-administered drugs include increasing adoption of digital health technologies, a rise in chronic diseases requiring ongoing management, and a shift towards biologics and personalized medicine.